India
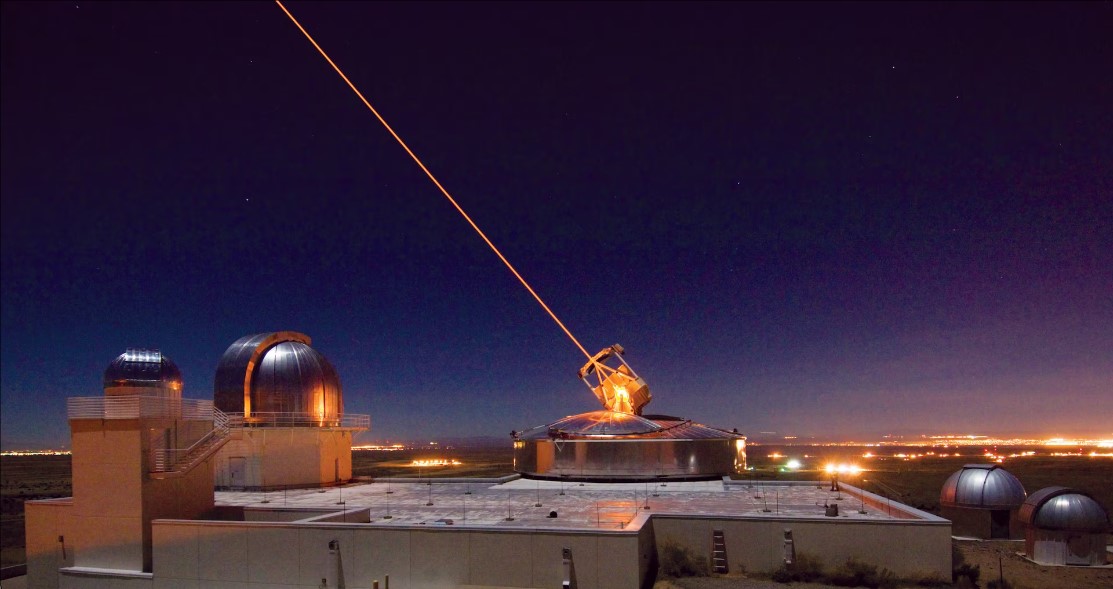
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has officially set its sights on building one of the most powerful homegrown laser weapons to date — a 300-kilowatt (kW) directed-energy weapon named ‘Surya’, expected to be tested and ready by the year 2027. This step puts India among an elite group of nations like the United States, China, and Russia that are advancing high-energy laser weapons for the future of warfare. What is Surya? Surya is designed as a Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) — a system that uses highly focused energy, in this case, a powerful laser beam, to disable or destroy enemy aerial targets like drones, UAVs, and potentially even missiles. Unlike conventional weapons, laser weapons travel at the speed of light, hit with pinpoint accuracy, and can engage multiple targets without running out of ammunition. With a planned 20-kilometre range, the Surya system will be capable of detecting, tracking, and destroying fast-moving threats in the sky, making it ideal for modern battlefield and border security scenarios. Key Specifications of the Surya Laser Weapon: Type: Ground-based Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) Laser Power Output: 300 kilowatts (kW), continuous wave Range: Up to 20 kilometres (effective against drones and aerial threats) Beam Director Aperture: 60 cm (helps focus laser over long distances) Beam Quality: Rated < 2 MQ (ensures high-precision targeting) Mobility: Mounted on two 8x8 military trucks, with a third for command and control operations Modular Design: Future-ready; can scale up to higher power levels (possibly megawatt-class) by combining multiple laser modules Technology Behind Surya To achieve such a powerful and accurate system, DRDO is combining several next-gen technologies developed indigenously: High-Energy Laser Generation: Uses Centrifugal Bubble Singlet Oxygen Generator (SOG) technology to create a stable and high-quality laser beam. Power Efficiency Systems: Incorporates sealed exhausts and supersonic nozzles to optimize performance and reduce energy waste. Precision Tracking and Lock-On: Advanced electro-optical sensors and radar systems enable fast target detection and precise engagement over long distances. Atmospheric Distortion Compensation: Adaptive optics and beam shaping technologies help adjust the laser beam in real-time to maintain accuracy, even in turbulent air. Centralized Beam Control: A highly integrated system controls targeting, power delivery, and beam steering — all in sync to neutralize moving targets in seconds. Why It Matters The Surya laser system will offer India significant strategic advantages. Unlike missiles or guns, it does not rely on explosive ammunition, has near-zero per-shot cost once powered, and can respond instantly to threats. In the future, it could also be adapted for naval or airborne platforms, greatly expanding its role. This initiative not only strengthens India’s defensive capabilities but also aligns with the goal of Aatmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) in high-tech military innovations. With the successful development of Surya by 2027, India is expected to leap ahead in the field of advanced energy weapons — building a futuristic defence shield that can protect against next-generation aerial threats, quickly and effectively.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-13 14:40:23World
More than 100 people, including at least 20 children, are feared dead after a series of brutal attacks by Sudan's paramilitary group, the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), in the war-torn region of Darfur. The United Nations confirmed that the violence erupted in El-Fasher city and the nearby Zamzam and Abu Shouk camps, where thousands of displaced people are already battling hunger and a collapsing health system. The coordinated assaults, which began Friday, involved both ground troops and aerial bombings. El-Fasher, the last major Darfur city still held by the Sudanese army, has become a key target for the RSF after the military recently regained control of Khartoum, Sudan’s capital. Initial reports from volunteer groups placed the death toll at 57, but the army later reported at least 74 civilian deaths in El-Fasher alone, with dozens more injured. In Zamzam camp, where the situation remains unclear due to internet and communication blackouts, activists suspect many more may have died. Among the dead are nine humanitarian workers who were running one of the last operational medical centers in the camp. UN Humanitarian Coordinator Clementine Nkweta-Salami condemned the killings, calling them part of a disturbing pattern of attacks on displaced civilians and aid workers. “These attacks are not just acts of violence; they are acts of cruelty targeting the most vulnerable,” she stated. The RSF has denied targeting civilians, claiming a video shared by activists showing the aftermath of the Zamzam attack was fabricated. But local advocacy groups and eyewitnesses reported renewed clashes on Saturday morning, with sustained gunfire and chaos spreading through the camps. Zamzam camp, one of Sudan's largest displacement sites, was the first area where a UN-backed study declared famine last year. Since then, famine conditions have expanded to other camps and are now threatening El-Fasher itself, with May predicted to bring widespread starvation. Sudan’s civil war, which began in April 2023 between the RSF and the national army, has already taken tens of thousands of lives and displaced over 12 million people. With both sides facing accusations of war crimes, the international community has repeatedly called for restraint, yet the violence continues to intensify, particularly in Darfur — a region already scarred by past genocide and conflict. What is happening now in Darfur is more than just another battle in Sudan's civil war — it’s a humanitarian catastrophe unfolding in real time. The RSF’s increasing aggression in El-Fasher signals their intent to completely control Darfur, which could push the war into an even more dangerous phase. El-Fasher is not only a military stronghold but also a lifeline for millions relying on humanitarian aid. Its fall would have devastating consequences. Furthermore, the killing of humanitarian workers highlights the growing threat to aid operations. When the people responsible for delivering food, medicine, and care are being targeted, the entire support system begins to collapse. That’s already visible in places like Zamzam, where famine is not a risk but a grim reality. This situation is worsened by a lack of international visibility. With communication lines down and aid agencies increasingly under attack, the true scale of the suffering is likely much larger than reported. Unless global pressure is applied urgently to end the violence and ensure the protection of civilians and aid workers, the tragedy in Darfur could mirror — or even surpass — the horrors of the early 2000s. Sudan is on the brink of another dark chapter, and the world cannot afford to look away.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-13 14:37:24World
In a major boost to the UK Royal Navy’s future surface fleet, Babcock has secured a £65 million (approximately $84 million) contract to implement a series of vital capability upgrades for the new Type 31 frigates. This important step, known as the Capability Insertion Period (CIP), aims to enhance the operational performance and flexibility of these next-generation warships. The CIP focuses on integrating and testing new technologies and systems that will strengthen the frigates’ combat and mission capabilities. Paul Watson, Managing Director of Arrowhead at Babcock, emphasized that the contract significantly builds upon the original design and construction agreement signed back in 2019. He also highlighted Babcock’s deep knowledge of the vessel design, which will ensure seamless system integration and efficient long-term support. "As the design and build partner, Babcock is expertly placed to provide the know-how and technical information to deliver these important activities in the development of the ships through the CIP,” Watson said. The Type 31 Frigate Program The Type 31 frigates, also known as the Inspiration-class, are a class of five general-purpose warships currently under construction for the Royal Navy. These ships are intended to replace the aging Type 23 general-purpose frigates and are being built at Babcock’s advanced shipbuilding facility in Rosyth, Scotland. Construction on the third vessel began in October last year, marking steady progress in the timeline that aims for all five ships to enter service by 2028. Key Specifications of the Type 31 Frigates Displacement: Around 5,700 tonnes Length: Approximately 138 meters Speed: In excess of 28 knots Range: Over 7,500 nautical miles Crew Capacity: Core crew of 105 with additional accommodation for mission-specific personnel Main Armament: 57mm main gun, 40mm secondary guns, and space for containerized mission modules Aviation Capability: Flight deck and hangar to support a Merlin helicopter and unmanned aerial systems Mission Flexibility: Equipped with flexible mission bays and modular design for rapid role adaptation The Type 31 will serve a wide range of tasks, from maritime security and anti-piracy to humanitarian assistance and joint operations with allies. Designed for adaptability, affordability, and rapid deployment, these frigates reflect a modern naval approach suited to global challenges. Once operational, the Type 31s will operate alongside the more specialized Type 26 frigates, which are tailored for anti-submarine warfare. Together, they form the backbone of the Royal Navy’s future surface combatant fleet. Babcock’s new contract ensures that the Type 31s will not only meet current defense standards but also remain upgradeable and relevant for decades to come.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:46:19World
In a groundbreaking leap for naval innovation, Blue Water Autonomy Inc. has officially emerged from stealth mode with a mission to revolutionize the future of ocean warfare and maritime operations. Backed by $14 million in seed funding from top venture capital firms including Eclipse, Riot, and Impatient Ventures, the company is setting out to build a new generation of fully autonomous, unmanned ships for the U.S. Navy. Founded in 2024 by experienced minds from Amazon Robotics, iRobot, and the U.S. Navy, Blue Water Autonomy is creating a full-stack solution for naval autonomy—combining advanced robotics, AI navigation, remote sensing, and modular payload integration into one seamless maritime platform. Within a year of its founding, the company has already launched saltwater testing and developed early concept designs for its autonomous vessels. Why Autonomous Ships Matter In today’s world of escalating global tensions, especially in the Pacific and Middle Eastern waters, navies are increasingly stretched thin. With Chinese shipyards launching vessels at breakneck speed and U.S. warships engaged in prolonged operations in hotspots like the Red Sea, there’s an urgent need for scalable and affordable naval support. Autonomous ships present a promising solution—capable of performing critical tasks without risking lives or overburdening human crews. These unmanned vessels could be deployed for a wide range of operations, from reconnaissance and surveillance to electronic warfare, logistics, and even direct combat support. By working in tandem with manned warships such as destroyers and aircraft carriers, these robotic ships could extend fleet capabilities and reduce operational costs dramatically. Inside the Technology Blue Water Autonomy’s vessel design is centered around full autonomy from the hull up. It includes: Full-stack Autonomy Suite: AI-driven navigation, threat detection, obstacle avoidance, and mission planning. Payload Flexibility: Can be configured for multiple missions including ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance), logistics resupply, mine detection, and more. Maritime-Grade Robotics: Developed by experts with experience delivering millions of commercial robots, ensuring robustness and scalability. Saltwater-Tested Systems: Already undergoing real-world environmental testing, showing rapid progression from lab to sea. Strategic Impact Blue Water Autonomy’s emergence is timely. As the U.S. and its allies aim to maintain control over vital sea lanes and counter threats from rising naval powers, autonomous ships offer a game-changing capability. They reduce dependence on large, expensive platforms, and enable quicker responses to maritime threats. These ships can be mass-produced at lower costs, offering a tactical edge where numbers and speed matter most. The leadership team’s unique combination of Silicon Valley innovation and military insight means Blue Water Autonomy is not just building ships—they’re building a new way of thinking about naval warfare. According to co-founder and CEO Rylan Hamilton, “Sea power has been the bedrock of America’s security and prosperity for centuries. We’re here to bring the Navy the technology it urgently needs.” Future Horizons While the initial focus is on serving the U.S. Navy, the ripple effects of this technology could soon spread to the commercial maritime sector. From automated cargo shipping and offshore energy platforms to fishing vessels and even luxury yachts, the core technologies developed by Blue Water Autonomy could redefine how the world moves across the seas. With $14 million in hand and a world-class team at the helm, Blue Water Autonomy is charting a bold course for the future—where human crews may one day watch from the shore as their robotic counterparts take to the oceans.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:33:02World
Spain has officially brought into service its first Airbus A330 MRTT (Multi-Role Tanker Transport), marking a major milestone for the Spanish Air and Space Force. The aircraft, now based at Torrejón de Ardoz Air Base near Madrid, has joined the 45th Wing and represents a significant leap in the nation’s aerial capabilities. This induction follows a 2021 acquisition plan by the Spanish Ministry of Defence for three A330 MRTT units. The aircraft, converted at Airbus’s Getafe facility near Madrid, is not just a traditional air tanker—it’s a multi-role strategic platform. It combines aerial refuelling, cargo and troop transport, and medical evacuation into one highly efficient package. With this, Spain steps into a select group of nations operating one of the most advanced and capable aerial tankers in the world. What sets the A330 MRTT apart is its versatility. Equipped with a hose-and-drogue refuelling system, it has an operational endurance of over 18 hours and a maximum range of 16,000 kilometres. It can carry up to 111 tonnes of fuel, allowing it to support long-distance refuelling missions without needing additional tanks. This ability dramatically enhances Spain’s power projection and joint operational reach across continents. Beyond refuelling, the A330 MRTT doubles as a heavy-lift transporter. It can carry up to 300 troops or 45 tonnes of cargo—ideal for strategic deployment missions, military logistics, or humanitarian relief efforts. Its cabin can also be reconfigured to carry medical evacuation kits (MEDEVAC), enabling it to evacuate wounded personnel or civilians during crises. This multi-role design makes it an all-in-one asset that is adaptable for a wide range of missions, from combat support to disaster response. The arrival of the MRTT aligns with Spain’s broader efforts to strengthen interoperability with NATO allies and improve its self-reliant operational readiness. As European and global military missions demand more flexible and far-reaching capabilities, Spain’s investment in the MRTT ensures it can support coalition operations while also maintaining national sovereignty in key scenarios. Two more A330 MRTTs are currently undergoing conversion at the Getafe site and are expected to join the fleet soon. Interestingly, before conversion, these aircraft had already proven useful in missions such as the evacuation of Spanish nationals from conflict-hit areas in Niger and Sudan, and during joint exercises like Pacific Skies 2024. Their performance in those missions reinforced the value of upgrading them into full MRTT configuration. In essence, the induction of the A330 MRTT is more than just adding a new aircraft to the fleet—it marks a shift in how Spain will approach global military logistics, joint operations, and emergency response. The A330 MRTT brings not only new technology but also strategic depth and operational flexibility, giving the Spanish Air and Space Force a powerful tool for the challenges of the modern world.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:30:07India
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is embarking on a transformative journey, aiming to untangle decades of logistical complexity created by its diverse fighter aircraft inventory. For years, India has operated an eclectic mix of jets from various countries—MiG-21s and Su-30MKIs from Russia, Mirage 2000s and Rafales from France, Jaguars from the UK, and the homegrown Tejas fighters. While each aircraft brought its own strengths to the table, the patchwork nature of the fleet has become increasingly unsustainable. Today, the IAF operates seven distinct types of fighter jets, a result of legacy procurement choices made under differing geopolitical and operational needs. However, this diversity is now weighing heavily on the force. With only 31 active squadrons against an authorized strength of 42, the IAF is under pressure to not only modernize but also optimize how it maintains, supports, and deploys its combat assets. Each aircraft type requires a unique set of tools, training, spare parts, and maintenance crews. With every additional vendor, the complexity multiplies. The older platforms, such as the MiG-21s (in service for over five decades) and Jaguars (around 45 years old), have become increasingly difficult to sustain. Spare parts are harder to procure, and safety concerns have grown, prompting scrutiny with each new incident involving these aging aircraft. At the same time, India’s frontline capability currently relies heavily on the Su-30MKI, a powerful but maintenance-intensive platform. The Rafales, though highly capable, are fewer in number and expensive to operate. Meanwhile, the Tejas Mk1A, India’s indigenous light combat aircraft, is slowly becoming more prominent, with the more advanced Tejas Mk2 and the fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) in the pipeline. This operational mosaic is not only resource-draining but also hinders the IAF’s ability to maintain consistent readiness across its squadrons. Experts note that a nation like China, with more uniform aircraft fleets, benefits from simpler logistics and higher mission availability—a comparison that adds urgency to India’s restructuring plan. To fix this, the IAF is now seriously considering a radical fleet rationalization. The goal is to bring down the fighter jet inventory to three or four core aircraft types. This would not only streamline training, spares, and maintenance but also bring much-needed clarity and efficiency to air operations. The focus is clearly shifting toward indigenous solutions, bolstered by growing capabilities within India’s aerospace industry. The proposed future structure would see: Tejas Mk1A replacing legacy light fighters like the MiG-21, Tejas Mk2 taking over from the Mirage 2000 and MiG-29 as a medium-weight multirole fighter, AMCA, the future stealth fighter, stepping into the role of a high-end air dominance platform, and Rafale, retained in limited numbers for strategic and nuclear delivery missions. An essential part of this streamlining is engine commonality. The GE F404 engine already powers the Tejas Mk1A, and the more advanced F414 engine has been selected for the Tejas Mk2 and the initial AMCA variants. Having multiple aircraft run on the same engine family reduces logistical stress dramatically. It simplifies everything from spare part inventory to maintenance crew specialization. Further ahead, a powerful indigenous engine is under development for future AMCA variants, aiming to boost self-reliance. This strategic simplification of the IAF’s inventory is not just about reducing costs—it’s about increasing availability. Aircraft that are easier to maintain spend less time grounded. With fewer types, the force can invest deeper in training, infrastructure, and innovation. The savings in logistics, combined with higher operational readiness, could give the IAF a significant edge in future conflicts. If this vision materializes, the IAF could realistically aim to reach its 42-squadron goal by the early 2040s. And unlike today, that force would be largely indigenous, modern, and logistically lean. In the long run, this pivot from a cluttered, multi-vendor fleet to a streamlined, self-reliant structure could redefine India’s aerial warfare doctrine—boosting efficiency, resilience, and strategic independence for decades to come.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:28:01World
In a bold and escalating development, North Korea has reportedly shipped hundreds of ballistic missiles and a vast number of artillery shells to Russia, significantly boosting Moscow's firepower in its ongoing war in Ukraine. This alarming revelation was made by Admiral Samuel Paparo, commander of the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command, during a testimony before the U.S. Senate Armed Services Committee. According to Admiral Paparo, North Korea has already transferred “thousands, maybe hundreds of thousands” of artillery shells and “hundreds of short-range missiles” to the Russian military. In exchange, Russia is expected to supply North Korea with advanced air defense systems—likely including modern surface-to-air missile (SAM) technology that could help Pyongyang protect itself against future airstrikes or surveillance missions. Paparo described the arrangement as a “transactional symbiosis,” where each country fills the strategic weaknesses of the other. While Russia receives desperately needed munitions for its war against Ukraine, North Korea gains access to advanced defense technologies, thereby enhancing its military posture on the Korean Peninsula. What Weapons Is North Korea Supplying? Among the missiles reportedly sent by North Korea are: KN-23 Short-Range Ballistic Missiles (SRBMs): These missiles have a range of approximately 400 to 600 kilometers and are capable of maneuvering during flight, making them harder to intercept. They are similar in design to Russia’s Iskander missile system and are suitable for targeting both military and civilian infrastructure. KN-15 (Pukguksong-2) Medium-Range Ballistic Missiles (MRBMs): Spotted earlier via satellite images in a Russian military convoy, the KN-15 is a solid-fueled, road-mobile missile with an estimated range of around 1,200 kilometers. This type of missile is significant because it can be launched quickly and from remote locations, making it more survivable in conflict scenarios. 122mm and 152mm Artillery Shells: These are compatible with Soviet-era artillery still in use by the Russian military. North Korea, having stockpiles of such ammunition, has become a convenient supplier for Russia as Western sanctions restrict Moscow's own production capabilities. What Is North Korea Receiving in Return? In return for its military support, Pyongyang is reportedly receiving: Advanced Air Defense Systems: These could include radar-guided SAM platforms capable of protecting North Korea from aerial threats posed by the U.S., South Korea, and Japan. Such systems could drastically improve North Korea’s ability to intercept incoming aircraft or missiles. Technical Assistance: Russia may also be providing engineering or scientific support to help North Korea upgrade its defense and missile infrastructure. This could speed up development of newer, longer-range missile systems. Growing Military Cooperation Raises Alarms This expanding military relationship between Moscow and Pyongyang has raised serious concerns among U.S. and allied officials. The exchange not only helps Russia maintain its offensive in Ukraine but also empowers North Korea to upgrade its own strategic capabilities, particularly in missile defense and long-range strike potential. Military analysts suggest that this deal could destabilize both Europe and East Asia. If North Korea gains significant advancements in air defense, it could become bolder in its military posture toward South Korea and Japan. Simultaneously, Russia continues to find new ways to circumvent Western arms sanctions. The growing arms-for-defense partnership between North Korea and Russia represents a dangerous convergence of two isolated, heavily sanctioned states. Each is helping the other extend their reach and resilience in their respective conflicts. As North Korean missiles rain down on Ukraine, and Russian technology strengthens Pyongyang’s shield, the international community faces a new axis of military cooperation that could threaten peace in multiple regions. The consequences of this exchange could reshape the military balance in both Eastern Europe and the Asia-Pacific for years to come.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:24:33World
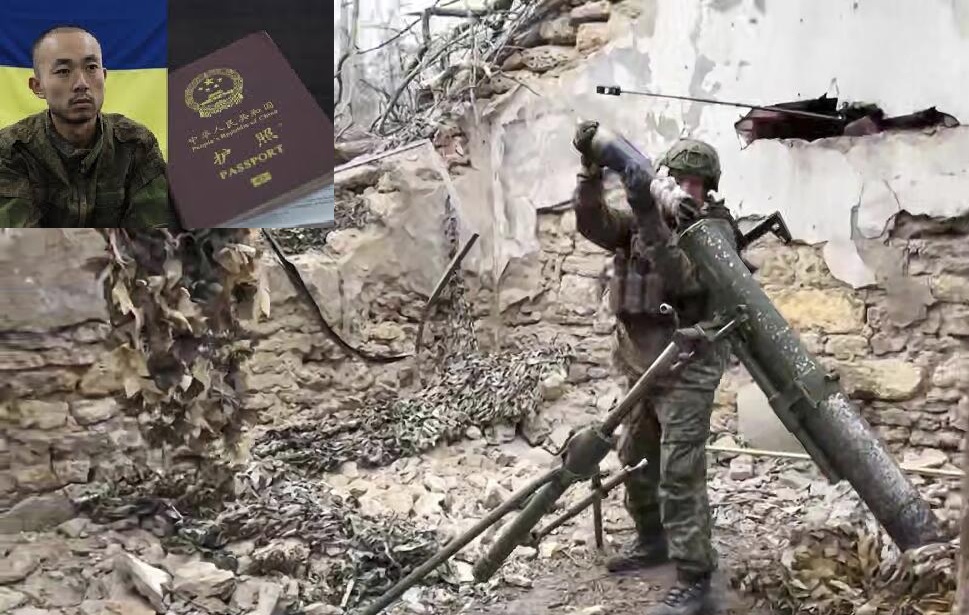
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has claimed that several hundred Chinese nationals are currently fighting alongside Russian forces on the frontlines in Ukraine. His statement, made during a meeting with allied military chiefs in Brussels, has added a new and concerning layer to the already complex dynamics of the ongoing war. Speaking via video from his hometown of Kryvyi Rih — which recently suffered a devastating missile strike that killed 19 civilians, including nine children — Zelensky alleged that Russia is using foreign nationals to stretch and prolong the war. “We have information that at least several hundred Chinese nationals are fighting as part of Russia’s occupation forces,” he said. “This means Russia is clearly trying to prolong the war — even by using Chinese lives.” The Ukrainian president’s comments followed Kyiv’s recent capture of two Chinese fighters in the eastern Donetsk region. These individuals were reportedly engaged in combat operations on behalf of Russia, intensifying fears that Beijing could be drawn more directly into the war. While Zelensky accused Moscow of dragging China into the conflict, the Kremlin firmly denied the claims. China, in turn, cautioned both parties against making what it called “irresponsible remarks.” Although there is no official confirmation from Beijing regarding Chinese nationals fighting in Ukraine, Zelensky’s allegations come at a sensitive time when global powers are already on edge about the war’s potential to spill beyond Eastern Europe. If proven true, the involvement of Chinese citizens on the battlefield — even as volunteers or mercenaries — could strain Beijing's carefully balanced diplomatic posture and give the West a new argument for tougher positions against China. Zelensky's remarks seem aimed not only at exposing what he sees as Russia’s manipulative tactics but also at pressuring international partners to act more decisively. He renewed his plea for enhanced air defense support, especially the American-made Patriot missile systems, which are among the few capable of intercepting Russian ballistic missiles. "Ukraine has a shortage of air defense systems. Patriot systems can effectively protect against ballistic threats. I ask you to focus first of all on air defense for Ukraine," he said. In a further push for international support, Zelensky disclosed that a full ceasefire proposed by the United States — and approved by Ukraine — was recently rejected by Russia. This rejection, according to Zelensky, shows that Moscow is not interested in ending the war but rather escalating it. Looking ahead, Zelensky called for the development of a multinational security contingent that could act as a stabilizing force in post-war Ukraine. He stressed the need for clear planning regarding the size, structure, deployment, logistics, and the armament of such a force to deter any future aggression from Moscow. A Strategic Move with Global Ripples Zelensky’s statement about Chinese nationals fighting for Russia serves several purposes. Firstly, it attempts to isolate Russia further by portraying it as a global manipulator willing to risk lives from other nations for its own military objectives. Secondly, it puts China in a difficult position: either distance itself from Russia or face accusations of complicity. Finally, it renews his call for military aid, especially advanced air defenses, which he believes are vital to protect Ukrainian cities and civilians. From a broader perspective, even the suggestion of Chinese involvement — direct or indirect — raises alarms about the war's potential to evolve into a more globalized conflict. With Western and NATO powers already backing Ukraine, and China maintaining ambiguous ties with Russia, the entrance of foreign fighters into the mix may only deepen geopolitical fault lines. As the war grinds on, the question is no longer just about territory in Eastern Europe. It’s about who’s willing to get involved, how far they’ll go, and what the global consequences might be.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:17:56World
In a significant move to enhance its self-reliance in defence technology, Ukraine has initiated the development of a domestic air defence missile system designed to counter the increasing threat of Russian ballistic missile attacks. This new system aims to serve as an alternative to the US-made Patriot system, which is currently the only platform in Ukraine capable of intercepting such high-speed threats. Minister for Strategic Industries, Herman Smetanin, recently confirmed that Ukraine’s defence industry is actively engaged in creating its own version of the Patriot. “So far, there are no analogues to the Patriot air defence missile systems on the territory of Ukraine, but our defence industry has a corresponding project, and we are working on it,” he stated during a 2024 defence industry conference. Focus on Self-Reliance and Domestic Capability Ukraine’s move to develop an indigenous system stems from a growing need to secure its skies without being solely dependent on external partners. The new system is expected to be capable of detecting, tracking, and neutralising a wide range of aerial threats, particularly ballistic and cruise missiles. According to defence insiders, the Ukrainian system is projected to include the following core specifications: Radar Range: Up to 150 km for target detection Intercept Range: 70–90 km against tactical ballistic missiles Target Engagement Altitude: Up to 25 km Missile Speed: Up to Mach 4 Multi-target Tracking: Capable of tracking and engaging multiple targets simultaneously The system will likely incorporate active radar guidance, high mobility platforms, and modular launch systems to make it adaptive for mobile warfare, similar to the Patriot system's capabilities. Strategic Partnerships and Co-Production Ukraine is not working alone in this endeavour. The government has entered into preliminary discussions with international partners regarding co-production of missile defence technologies. Smetanin highlighted that negotiations have been held with manufacturers of systems like the Patriot to explore possibilities of localising part of the production in Ukraine. This not only boosts Ukraine's defence manufacturing but also creates jobs and enhances technical expertise within the country. “The United States has partners with whom it co-produces these systems. We’ve held a number of negotiations with manufacturers of similar systems, including the Patriot, regarding partial localization of their production in Ukraine,” Smetanin said. Real-Time Battlefield Collaboration While Ukraine works on developing its own solution, its forces continue to rely on the US-supplied Patriot systems for frontline defence. Following a recent wave of Russian missile strikes on April 6, Ukrainian Air Force spokesman Yurii Ihnat underscored the vital role of the Patriot system in Ukraine’s current operations. “As of now, only American Patriot systems are capable of performing this function,” he noted. Ukrainian forces are also cooperating with the US to share battlefield data, helping to refine and improve the Patriot’s effectiveness in real-time combat scenarios. This cooperation is essential for better threat analysis, faster response times, and improved missile interception rates. Looking Ahead Ukraine’s drive to develop a domestic air defence system reflects its broader vision for military independence and technological advancement. While the indigenous system is still under development, the steps taken so far indicate a clear and determined strategy to ensure national security through homegrown solutions. As the conflict with Russia continues to evolve, Ukraine’s ability to produce and deploy its own advanced defence systems will play a crucial role in shaping the future of its military resilience and strategic autonomy.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:15:31India
In a landmark move that could shape the future of nuclear energy in India, the state of Maharashtra has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Russia’s state-owned ROSATOM to jointly explore the development of a thorium-based Small Modular Reactor (SMR). This agreement marks the first time a state government in India is formally entering the nuclear energy space, which until now has been solely under the jurisdiction of the central government's Department of Atomic Energy (DAE). The MoU was signed in the presence of Maharashtra Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis, between Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Ltd (MAHAGENCO) and ROSATOM. This collaboration is seen as a major step towards harnessing India’s vast thorium reserves and developing a safer, more sustainable form of nuclear energy. The project, which will be strategically supported by the Maharashtra Institution for Transformation (MITRA), aims to develop a thorium-fueled SMR, ensure its safety as per Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) standards, and ultimately commercialize its production under the “Make in Maharashtra” initiative. A joint working group consisting of members from MAHAGENCO, Rosatom Energy Projects, MITRA, and Global Technology Alliance will steer the project forward. While the agreement does not yet authorize the construction of the reactor, a senior official clarified that all future steps will only proceed with the approval of the central government and in compliance with all nuclear safety laws. The state’s role, for now, focuses on research, feasibility studies, and technological exploration. Former Atomic Energy Commission chairman Anil Kakodkar welcomed the initiative, noting there’s no harm in conducting preliminary studies at the state level, even if the actual deployment will remain a central subject. India has long envisioned a three-stage nuclear program where thorium plays a central role in the final phase. India is rich in thorium deposits, but thorium itself isn’t fissile, meaning it can't directly produce energy. It must first be converted into fissile uranium-233 through a process called nuclear transmutation. Currently, India is in the second stage of its nuclear roadmap, using Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs). These reactors breed more fuel than they consume and can potentially be modified to use thorium. The Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR), being developed by Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Ltd (BHAVINI), uses uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel. It has a surrounding blanket of uranium-238 that transforms into more fissile material, and eventually thorium blankets are also expected to be introduced, further pushing the country towards the third stage of the thorium-based cycle. SMRs, especially those based on thorium, are increasingly being recognized for their potential to offer decentralized power generation with enhanced safety. Unlike traditional large reactors, SMRs have a smaller footprint, are easier to construct and maintain, and have passive safety systems that allow for automatic shutdowns in case of emergencies. These features make them particularly suitable for a country like India, where distributed energy solutions are essential for reaching remote areas. If Maharashtra’s collaboration with ROSATOM bears fruit, it could significantly accelerate India’s long-term nuclear ambitions and create a new model for state-level innovation in nuclear energy, all while aligning with the national goal of sustainable, low-carbon growth. The project may also position India as a global leader in thorium reactor technology, an area where few countries have ventured due to the technical complexities involved. While the road ahead remains long and technically challenging, the MoU represents a bold first step toward realizing the immense, yet untapped, potential of thorium energy in India’s future.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:13:18World
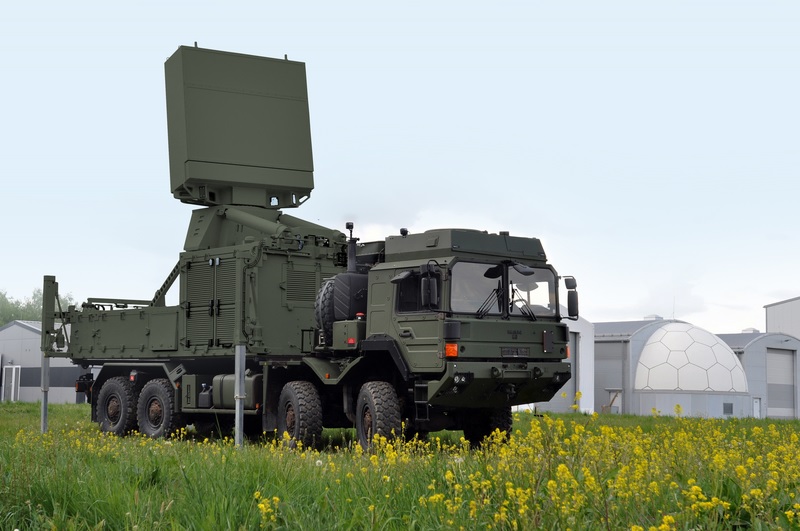
Switzerland has taken a major step towards enhancing its air defence capabilities by successfully completing crucial trials of the TRML-4D radar. These tests are part of the country’s development of a new medium-range ground-based air defence (GBAD MR) system, which is expected to play a key role in protecting Swiss airspace from modern aerial threats. The radar trials, conducted by the Swiss Federal Office for Defence Procurement, armasuisse, in collaboration with the Swiss Armed Forces, took place between 31 March and 11 April 2025. Two key locations were selected for testing — the federally-owned Homberg site and the Emmen aerodrome — due to their diverse terrains and relevance to Switzerland’s unique geographical conditions. Realistic Testing in Swiss Terrain The TRML-4D radar was tested under realistic and operationally relevant conditions. The main focus of the trials was to assess the radar’s ability to detect, classify, and track various airborne targets, while also ensuring that it operates without interfering with civilian systems like weather radar. Several aircraft, including the PC-12, PC-7, F/A-18 jets, and helicopters, were used to simulate various flight profiles, speeds, and altitudes. In addition to live aircraft, a radar target simulator was deployed to create simulated targets with different radar cross-sections and velocities, mimicking modern aerial threats such as cruise missiles. Importantly, the radar emits non-ionising radiation (NIR), and armasuisse confirmed that the levels of electromagnetic radiation remained within safe limits, posing no health risk outside the radar’s security zone. TRML-4D Radar – Core of Swiss Medium-Range Air Defence The TRML-4D is a cutting-edge, multi-functional radar system developed by HENSOLDT, known for its high detection accuracy, fast target acquisition, and simultaneous tracking of multiple airborne threats. It operates in the C-band frequency range and uses advanced AESA (Active Electronically Scanned Array) technology. Key Specifications of TRML-4D Radar: Detection Range: Over 250 km for aircraft and missiles Target Tracking: Capable of tracking up to 1,500 targets simultaneously Radar Technology: AESA-based with rapid beam steering Mobility: Mounted on mobile platforms for quick deployment Weather Resilience: Effective performance even under adverse weather conditions 360-Degree Coverage: Provides full spherical situational awareness This radar will be a central sensor in Switzerland’s new GBAD MR system and is a vital part of the country’s Integrated Air Defence strategy, aiming to defend against medium-range threats, including stand-off weapons and cruise missiles. Replacing Outdated Air Defence Systems Switzerland’s current air defence systems, such as the shoulder-launched Stinger missiles and legacy medium-range anti-aircraft artillery, are no longer sufficient against today’s high-speed, high-altitude threats. The GBAD MR project, valued at CHF 660 million, is therefore critical to closing this operational gap. As part of the program, Switzerland plans to acquire four or five IRIS-T SLM surface-to-air missile systems from Diehl Defence of Germany. These advanced systems are designed for highly accurate interception of aerial threats and will work in tandem with the TRML-4D radar. Contract finalization is expected by the third quarter of 2025. The procurement is also aligned with the European Sky Shield Initiative, a multinational effort to strengthen collective European air defences. Strengthening Swiss Air Sovereignty Once fully operational, the GBAD MR system will significantly strengthen Switzerland’s ability to maintain air sovereignty, providing a modern and mobile solution to counter evolving aerial threats. It also demonstrates Switzerland’s commitment to investing in reliable and future-proof defence technologies to protect its citizens and territory. By completing the TRML-4D radar trials successfully, Switzerland has moved one step closer to deploying a comprehensive and state-of-the-art medium-range air defence system that can stand up to the challenges of modern warfare.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:09:37World
In a groundbreaking shift in Russian tank design, Uralvagonzavod (UVZ), the primary tank manufacturer under the state-run Rostec corporation, has introduced a radically reimagined variant of the T-90 main battle tank—this time without its signature rotating turret. This innovation stems from valuable battlefield insights, especially from the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. Combat experience has underscored several critical vulnerabilities in traditional tank designs—most notably, the rotating turret, which has long been a staple in Soviet and Russian tank architecture since the T-64 era. A Bold Departure from Tradition At the heart of this redesign is the removal of the turret, a structural change that significantly improves the tank’s ability to survive direct hits from modern anti-tank systems. UVZ engineers have re-evaluated the importance of mobility and rapid target acquisition—advantages typically attributed to the rotating turret—and concluded that these are no longer essential in today’s evolving combat scenarios. Instead, the focus has shifted towards maximizing protection, firepower delivery from static or semi-static positions, and eliminating design weaknesses that have led to catastrophic battlefield losses. Addressing the "Turret Toss" Problem One of the most critical reasons for abandoning the turret lies in the infamous “turret toss” phenomenon, where a direct hit to the tank’s turret ammunition storage results in a violent explosion that can eject the turret from the chassis. UVZ expert Alexey Ustyantsev emphasized that the turret’s structure not only posed a safety risk but also limited the integration of next-generation defense technologies. By eliminating the turret, the new T-90 variant removes a major weak point, creating space for a more compact, better-armoured, and potentially lower-profile design that is harder to detect and destroy. New Approach to Tank Warfare Despite the drastic redesign, UVZ has retained the core principles of tank warfare: delivering high-caliber firepower, surviving enemy attacks, and maneuvering across challenging terrain. But instead of relying on the traditional turreted configuration, the new model may incorporate alternative weapon mounting systems—possibly fixed or limited-angle gun mounts with advanced stabilization technologies. This layout also simplifies the installation of Active Protection Systems (APS) like Russia's Arena-M, designed to intercept and destroy incoming projectiles before they hit the tank. Without the rotating turret, such systems can be more seamlessly integrated into the vehicle's structure, enhancing all-around defense coverage. Key Specifications (Expected/Conceptual) While exact details are still under wraps, based on UVZ’s statements and trends in armored vehicle development, the following features are anticipated: Armament: High-velocity main gun (likely 125mm), fixed or in a limited traverse mount Protection: Enhanced frontal and top armor, integrated Active Protection System (Arena-M) Crew Safety: Enclosed armored capsule or heavily fortified hull compartment Mobility: Advanced torsion bar suspension, upgraded engine (possibly 1130+ HP), improved terrain navigation Electronics: Upgraded fire control system, AI-assisted targeting, drone integration support Dimensions: Potentially lower profile due to turret removal, improving stealth and survivability Ammunition Storage: Compartmentalized and blast-proof sections to reduce risk of internal explosions Shaping the Future of Armored Combat UVZ’s new turretless T-90 reflects a broader shift in global tank design philosophies. Other nations are also experimenting with unmanned turrets, remote weapon stations, and protected crew capsules. This signals a potential global transition from traditional designs toward survivability-centric platforms in response to the proliferation of drone strikes, guided missiles, and smart munitions. The introduction of this modified T-90 showcases Russia’s attempt to adapt to modern threats and rethink armored warfare. If successful, this could become a model for next-generation main battle tanks, balancing raw firepower with advanced protection and crew survivability. This evolution is not just about building a better tank—it’s about reshaping the very nature of ground combat for the 21st century.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-12 15:07:41World
In a significant move reflecting rising global tensions, the United States has fast-tracked the development of its next-generation nuclear bomb, the B61-13. The advanced weapon, originally slated for production next year, will now be ready seven months ahead of schedule — a more than 25% acceleration in the original timeline. This step marks a serious shift in Washington’s nuclear strategy as it responds to what it sees as a more dangerous and unpredictable world. The bomb is being developed by Sandia National Laboratories under the guidance of the US Department of Energy and Department of Defense. Engineers and scientists were able to compress the timeline by reprioritizing qualification activities and focusing intensely on what it would take to deliver the weapon in under five years — a notably short period for such a complex and highly sensitive system. The B61-13 is designed to deliver a massive punch. With a maximum yield of 360 kilotons, it is nearly 24 times more powerful than the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima. This kind of destructive capability is aimed at hardened military targets and large-area installations that would be resistant to conventional strikes. In practical terms, it means the B61-13 could penetrate deeply buried bunkers or command centers — targets that are central in modern warfare calculations. This nuclear bomb is built for flexibility as well. It will be compatible with advanced strategic aircraft like the B-2 Spirit, and more notably, the forthcoming B-21 Raider stealth bomber, which is expected to be the backbone of the US Air Force’s long-range strike fleet in the coming decades. This ensures that the weapon can be deployed quickly and with reduced risk of detection, giving the US and its NATO allies a significant tactical edge in any potential conflict. The timing of this accelerated production is not coincidental. Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, global tensions have soared. Concerns are growing about the potential for a broader regional war, and the risk that nuclear weapons could become part of the conversation is no longer dismissed as far-fetched. As a leading NATO member, the United States is bound by Article 5 of the NATO treaty, pledging mutual defense if any member is attacked. In this context, enhancing nuclear deterrence serves not just as a warning to adversaries but also as reassurance to allies. The B61-13 program was launched in 2023, shortly after the National Nuclear Security Administration successfully completed a $9 billion life extension program for the B61-12, its predecessor. That program modernized the aging stockpile of US nuclear gravity bombs, giving them updated safety features, guidance systems, and reduced yields for more flexible use. With that effort complete, attention and resources shifted to building a weapon with even more advanced capabilities. Analysts note that this rapid acceleration of nuclear bomb production is part of a broader pattern. As major powers like China, Russia, and North Korea expand or modernize their own nuclear arsenals, the United States appears increasingly determined to maintain a strategic edge. This doesn’t necessarily mean that nuclear war is imminent, but it does signal a renewed era of nuclear competition — one not seen since the Cold War. The B61-13 isn’t just about having a bigger bomb; it’s about deterring aggression by signaling readiness, precision, and overwhelming retaliatory capability. In the delicate balance of international power, perception matters — and the US is making it clear that it is not willing to be caught off guard. In short, the US is not just modernizing its nuclear arsenal — it’s doing so faster, more strategically, and with a clear eye on emerging threats. The B61-13 represents both a technological leap and a geopolitical statement: in an increasingly unstable world, nuclear deterrence remains a cornerstone of US national security.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:45:28India
In a major boost to India’s defence capabilities, the indigenously developed long-range glide bomb ‘Gaurav’ has successfully completed release trials from a Sukhoi-30 MKI fighter jet. Conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with the Indian Air Force (IAF), these trials took place over three days—from April 8 to April 10, 2025—demonstrating the bomb’s powerful performance and precision strike capability. What Makes 'Gaurav' Special? The Gaurav glide bomb belongs to the 1,000-kg class and is designed for precision targeting of strategic ground-based assets. During the trials, it was launched from various stations on the Su-30MKI in different warhead configurations, targeting a land-based island with exceptional accuracy. The bomb successfully struck targets from a range of nearly 100 kilometers, showcasing its advanced guidance system and aerodynamic efficiency. This weapon is equipped with a hybrid navigation system, which blends GPS satellite data with onboard sensors for high-precision mid-course correction and terminal guidance. This allows the bomb to glide over long distances after release and home in on the target with remarkable accuracy. Fully Made in India What truly sets Gaurav apart is that it is completely developed in India. The bomb has been designed by DRDO’s Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad, and Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE). Manufacturing support has come from Indian private defence players like Adani Defence Systems and Technologies, Bharat Forge, and several MSMEs, ensuring a strong public-private collaboration. Additionally, the bomb’s airworthiness and quality have been certified by the Centre for Military Airworthiness and Certification (CEMILAC) and the Directorate General of Aeronautical Quality Assurance (DGAQA). Ready for Induction into the IAF Senior DRDO and IAF officials monitored the successful test, which marks a significant step toward the formal induction of Gaurav into the Indian Air Force’s operational fleet. This will equip the IAF with a powerful, indigenous standoff weapon capable of striking targets from a safe distance without putting the aircraft in harm’s way. The Defence Ministry highlighted that the trials “are paving the way towards induction of the weapon into the IAF,” signaling that frontline fighter jets like the Su-30MKI may soon be armed with this precision-guided bomb. Defence Minister’s Appreciation Defence Minister Rajnath Singh praised the collaborative efforts of all agencies and stakeholders involved. In a public message, he said that Gaurav would “greatly enhance the operational capabilities of our armed forces,” reinforcing India’s commitment to achieving self-reliance in defence technologies. Specifications of Gaurav Glide Bomb Weight Class: 1,000 kg Range: Close to 100 km Launch Platform: Sukhoi-30 MKI (multi-station integration) Guidance System: Hybrid navigation (GPS + onboard sensors) Strike Accuracy: Pinpoint (within a few meters of the target) Development Agencies: DRDO (RCI Hyderabad & ARDE Pune) Industry Partners: Adani Defence, Bharat Forge, MSMEs Certifying Agencies: CEMILAC and DGAQA First Tested: August 2023 Latest Trials: April 8–10, 2025 A Leap Towards Strategic Autonomy The success of Gaurav underscores India’s growing expertise in developing next-generation precision weapons. With long-range capability and indigenous design, it adds a vital layer to the country’s aerial strike arsenal. Once inducted, this advanced bomb will give the Indian Air Force the ability to destroy critical enemy infrastructure—such as bunkers, bridges, or command centers—from a standoff distance, with no need for foreign-made munitions. In the age of modern warfare, where precision, range, and self-reliance are key, Gaurav is a shining symbol of India’s rising strength in the defence domain.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:43:44India
In a significant development that could pave the way for satellite-based emergency services on iPhones in India, Globalstar, the satellite communications partner for Apple Inc., has officially submitted an application to the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe). The move marks a critical step towards enabling Emergency SOS via Satellite functionality for Apple devices within the Indian subcontinent — a capability currently operational in select markets such as the US, Canada, UK, and parts of Europe. What is Apple’s Satellite Emergency Messaging? Apple’s Emergency SOS via Satellite feature allows iPhone users to send distress messages and share their location even when there is no cellular or Wi-Fi coverage. This service, introduced with the iPhone 14 series and extended to newer models like the iPhone 15, is designed to assist users in life-threatening situations, such as being stranded in remote areas without traditional connectivity. The service utilizes Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites to transmit short-burst data (SBD) packets that include the user’s GPS coordinates, emergency information, and battery level, among other critical metadata. Globalstar’s Role and Technical Infrastructure Apple partners with Globalstar Inc., a US-based satellite communications company, to power its Emergency SOS feature. Globalstar owns and operates a constellation of 25 LEO satellites in operational orbit (as of 2024), supported by ground stations and gateways worldwide. Key technical details include: Satellite Type: LEO (Low Earth Orbit) Orbital Altitude: ~1,414 km (880 miles) Frequency Bands Used: S-band for user links (2483.5 – 2500 MHz) and L-band for gateway links Bandwidth: Narrowband channels, optimized for low data rates suitable for emergency text messaging Data Rate: Typically under 9.6 kbps, sufficient for emergency communication packets Coverage: Nearly global, excluding polar regions, subject to regulatory approval Globalstar's satellites communicate directly with compatible iPhones, allowing users to point their devices toward passing satellites and send pre-defined emergency messages. Regulatory Pathway: Application to IN-SPACe India’s space sector was opened to private participation in 2020, and IN-SPACe (under the Department of Space) was established to act as a single-window authority for all commercial space activities. For any foreign or domestic entity to operate satellite services in India, it must obtain clearance from IN-SPACe, in addition to spectrum authorization from the Department of Telecommunications (DoT). Globalstar has now officially applied to IN-SPACe for permission to operate satellite-based messaging services in India. The application is reported to request clearance for: Use of satellite spectrum in the S-band for consumer terminals (iPhones) Ground station installation or collaboration with Indian partners for routing messages to emergency services Service integration with India’s public safety and disaster response infrastructure India’s Growing Focus on Satellite Communication The move aligns with India's growing emphasis on satellite communications for both consumer and national resilience applications. Domestic players like Bharti-backed OneWeb, JioSpaceFiber, and Starlink have also been actively pursuing spectrum and regulatory approvals to offer broadband or specialized services via satellites. Unlike broadband services, Apple’s Emergency SOS does not require persistent high-throughput connectivity. It relies on short-burst, store-and-forward messaging, making it more feasible in spectrum-constrained or regulatory-heavy environments. Potential Challenges and Opportunities While the application by Globalstar signals progress, the service rollout in India may still face several hurdles: Spectrum Licensing: India's DoT has traditionally auctioned satellite spectrum, which could delay or complicate approvals for narrowband services. Security Clearances: As messages might be routed via foreign satellites and ground stations, security agencies may seek end-to-end control and oversight mechanisms. Localization Needs: Apple may need to integrate with India's 112 Emergency Response System and provide multilingual support. However, the potential upside is immense. India’s vast rural and remote geography — including Himalayan regions, deserts, and coastal belts — makes it an ideal market for satellite-based emergency communications. What This Means for Apple Users in India If the IN-SPACe application is approved and subsequent regulatory steps are completed, iPhone users in India could gain access to Emergency SOS via Satellite, enhancing personal safety during natural disasters, treks in remote locations, or vehicular accidents where conventional networks are unavailable. The feature is free for two years upon iPhone activation in supported regions, and future pricing models may be regionally adapted depending on Apple's and Globalstar’s agreements with Indian regulators.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:38:16World
At SOFINS 2025, the French-German Research Institute of Saint-Louis (ISL) has revealed remarkable progress on a revolutionary defense technology: a 12.7 mm calibre guided sniper bullet. This breakthrough, known as the I-SMART (ISL Sniper Munition Actuated to Reach Target), is set to redefine the future of long-range marksmanship with unmatched precision and smart tracking capabilities. A New Era for Sniper Precision The I-SMART round represents a leap in sniper warfare by integrating advanced guidance electronics into a conventional 12.7×99 mm (.50 BMG) calibre bullet. The technology takes advantage of ISL’s prior developments in guided munitions, such as course-correcting artillery fuses and medium-calibre smart ammunition. But this time, the challenge is greater—the entire guidance system must be compacted into a projectile just 54 mm in length and 12.7 mm in diameter. What makes this even more impressive is that the internal systems must survive the extreme forces of a gun firing—something that has historically limited the feasibility of guided small-calibre rounds. Inside the I-SMART Guided Bullet The I-SMART bullet is an intricate design composed of five main modules: Optical Sensor (in the tip) – Acts as the eye of the bullet, enabling terminal guidance in the final moments of flight. Navigation Electronics – Calculates the bullet's position and adjusts its course during flight. Power Supply – A compact energy source that keeps all electronics operational throughout the bullet’s travel. Actuation Mechanism – Aerodynamic fins or similar actuators that make real-time course corrections. Communications System – Allows the bullet to “talk” to a ground-based sniper system during flight. Currently, guidance decisions are handled externally through a ground unit, but ISL intends to shift toward on-board autonomous navigation, reducing reliance on external systems and speeding up reaction time. Performance That Redefines Accuracy ISL’s goal with I-SMART is to achieve 50 meters of lateral correction at a range of 2,000 meters, effectively allowing the bullet to adjust in-flight and hit moving targets—even if they are traveling at 60 km/h. With an average flight time of around three seconds, such responsiveness would drastically increase hit probability and reduce the need for multiple shots or highly seasoned snipers. This makes I-SMART not only a force multiplier for elite marksmen but also a tool that can help less experienced personnel deliver precise shots with minimal training, opening up possibilities for wider battlefield use. A Global Perspective Until now, only the United States and Russia have publicly worked on similar sniper-guided ammunition. The U.S. DARPA program, called EXACTO (Extreme Accuracy Tasked Ordnance), demonstrated promising tests in 2015, but it never transitioned to a fielded product. Russia also explored a guided 12.7×108 mm round, although little is known about its current status. Unlike these earlier efforts, France’s ISL is moving ahead with plans to reach Technology Readiness Level 5 (TRL5) soon. This stage will mark a key milestone before the institute hands over the project to an industrial partner for full-scale development and manufacturing. The Road Ahead While no exact timeline has been announced for the final live-fire tests, the I-SMART project is being seen as a potential game-changer in the world of special operations and precision shooting. Once fully developed, it could not only boost the effectiveness of sniper teams but also change doctrines around how precision fire is used in combat. In summary, the guided sniper bullet unveiled at SOFINS 2025 is more than just a technical feat—it is the future of precision warfare. With the I-SMART round, ISL is aiming to deliver not just bullets, but intelligent munitions that think and adapt mid-flight, hitting targets previously thought unreachable.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:35:35World
American defense technology giant Leidos has introduced a new game-changer in underwater defense systems — the Sea Dart, a highly versatile and low-cost uncrewed underwater vessel (UUV). With a price tag starting at just $150,000, the Sea Dart is touted as one of the most cost-effective underwater platforms available today, offering a price point up to 80 to 90 percent lower than other small UUVs in the market. The Sea Dart stands out due to its modular and reconfigurable design, allowing it to be rapidly adapted for a variety of missions — from reconnaissance and surveillance to underwater mapping, mine detection, and more. This adaptability makes it highly suitable for modern naval operations, especially for countries and organizations seeking advanced undersea capabilities without the heavy financial burden. One of the key factors contributing to the Sea Dart's affordability is its use of commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) technologies. Instead of developing expensive proprietary systems, Leidos has built the Sea Dart using components that are already available in the commercial market. This approach significantly reduces development and production time while also ensuring easier maintenance and part replacement. Key Specifications and Features of the Sea Dart: Cost: Starts at approximately $150,000 per unit Design: Modular and easily reconfigurable for multiple mission types Construction: Utilizes commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) components to reduce costs Size: Compact, designed for easy transport and deployment Deployment Options: Can be launched from shorelines, ships, or submarines Applications: Intelligence gathering, mine countermeasures, maritime security, seabed survey, and more Endurance: Designed for extended underwater missions with efficient power systems Control System: Can operate autonomously or be guided remotely The Sea Dart has been developed with cost-efficiency, mission flexibility, and rapid deployment in mind. By reducing reliance on expensive defense-grade parts and focusing on adaptability, Leidos is offering a solution that can serve both military and commercial operators with limited budgets but high demands. With threats evolving in the maritime domain, especially in contested and littoral waters, systems like the Sea Dart could become crucial tools for navies and maritime agencies around the world. As nations look to scale up their underwater surveillance and defense capabilities, the Sea Dart's affordability and flexibility may position it as a front-runner in the next generation of uncrewed underwater systems.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:32:42World
Japan has reached a significant milestone in strengthening its naval defense capabilities by equipping the first Mogami-class multirole frigate with the American-made Mk 41 Vertical Launching System (VLS). This new development represents a key evolution in the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force’s (JMSDF) vision of fielding advanced, compact, stealthy warships in the face of growing maritime threats. The first ship to receive the VLS is JS Niyodo (FFM-7), the seventh vessel in the 12-ship Mogami-class program. The 16-cell Mk 41 launcher has been installed at Mitsubishi Heavy Industries’ (MHI) Nagasaki Shipyard, positioned right in front of the ship’s bridge as originally intended in the design plans. Mk 41 VLS: A New Offensive Backbone The Mk 41 VLS is a modular, multi-purpose launching system capable of firing a range of missiles for anti-air, anti-ship, and anti-submarine operations. By integrating this system, the Niyodo can now deploy guided missiles that significantly boost its combat effectiveness and broaden its mission capabilities. These include intercepting enemy missiles, targeting warships, and launching anti-submarine weapons. The Japanese Ministry of Defense had allocated 8.4 billion yen (around $57 million) in its FY2021 supplementary budget for acquiring the first two VLS units for JS Niyodo and its sister ship, JS Yubetsu (FFM-8). With both systems now delivered, all Mogami-class ships from the seventh vessel onward will be inducted with VLS pre-installed, reflecting a more integrated and combat-ready approach. The Mogami-Class Frigates: Japan’s Future Workhorse Designed by MHI, the Mogami-class FFMs are compact, stealthy, and highly capable vessels suited for diverse missions, from patrolling contested waters to conducting anti-mine operations. These ships mark a shift from Japan’s earlier model of large, single-role warships to a new generation of multi-mission frigates optimized for high readiness and versatility. Key Specifications: Standard Displacement: 3,900 tons Full Load Displacement: 5,500 tons Length: Approximately 130 meters Speed: Over 30 knots Helicopter Capacity: 1 onboard helicopter Unmanned Systems: UUV (Unmanned Underwater Vehicle) and USV (Unmanned Surface Vehicle) capable Weapons: 16-cell Mk 41 VLS, 127mm naval gun, anti-ship missiles, and CIWS (Close-In Weapon System) What makes the Mogami-class unique is its hybrid approach to manned and unmanned operations. Each frigate is capable of deploying an unmanned surface or underwater vehicle, marking the first time such systems are being integrated directly into Japanese frigates. Changing Defense Priorities Originally, Japan planned to build 22 Mogami-class ships, but the plan was revised to just 12, with the remaining fleet slots being reserved for an upgraded class known as the "New FFM." Starting from FY2024, Tokyo will begin acquiring this new generation of frigates, which will be larger, more powerful, and still based on the Mogami design. The first of these is scheduled for commissioning in fiscal year 2028. This change aligns with Japan's evolving defense strategy, especially with growing maritime tensions in the East China Sea and Nansei island chain. As China expands its naval footprint and Russia strengthens its presence through joint exercises, Japan aims to field faster, smarter, and better-armed vessels to monitor and secure its maritime borders. A Global Player in Frigate Exports? In a notable international development, MHI has also been shortlisted by the Australian government to provide a future general-purpose frigate under the SEA 3000 program. MHI is pitching its "New FFM" design, showcasing Japan’s ambition not just to defend its own waters but also to become a competitive exporter in the global naval market.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:29:58World
In a bold move that could reshape future warfare, China has unveiled what it claims is the world’s first anti-drone barrage weapon system—an advanced air defence platform specifically engineered to counter drone swarms, low-flying missiles, rockets, helicopters, and other fast-moving aerial threats. This new weapon, introduced by China’s defense industry in April 2025, doesn't just rely on conventional targeting. Instead, it utilizes a revolutionary "barrage" approach to blanket the skies with intense firepower. A New Era in Air Defense Unlike traditional anti-aircraft systems that aim to hit targets with precise point-to-point interception, China’s new system embraces a radical change: "plane-to-point" interception. At the heart of this innovation lies a 16-barrel gun, capable of unleashing a wall of firepower rather than a single focused shot. This creates a wide net of destruction, dramatically increasing the chances of intercepting agile, unpredictable threats like drone swarms or incoming missiles. As Yu Bin, the system's chief designer, explains: “This barrage can cover incoming positions of all targets, achieving effective interception with the concept of ‘plane to point’.” Key Specifications and Features Barrel Configuration: 16 closely aligned barrels Fire Mode: Barrage firing (high-density projectile curtain) Reload Capability: Fast reloading for sustained defense Coverage: Wide-area suppression, suitable for multiple aerial targets simultaneously Platform Compatibility: Modular—can be mounted on trucks, armored vehicles, ships Ammunition: Uses specially developed munitions for broad aerial saturation Operational Use: Capable of neutralizing drone swarms, missiles, mortars, and even artillery shells in field trials This system’s adaptability is particularly important. Its modular design allows it to be deployed across multiple environments—from land-based operations to naval defense—making it a versatile tool for the modern battlefield. Designed for Real-World Combat Conditions In live trials, the barrage system demonstrated its potency. One single volley was enough to eliminate entire formations of small drones, while also effectively intercepting high-speed rockets and mortar shells. Such performance makes it particularly relevant in the face of modern saturation attacks, where dozens or even hundreds of drones can be launched simultaneously to overwhelm traditional defenses. Current air defense systems struggle to deal with such threats due to their reliance on costly interceptors and slower response times. China’s new barrage weapon offers a cost-effective, high-efficiency solution to this pressing problem. Responding to Strategic Challenges The system’s unveiling comes amid rising tensions in the Asia-Pacific region, especially around Taiwan. Taiwan, backed by the United States, has been actively expanding its drone capabilities, including long-range surveillance drones like the MQ-4C Triton and MQ-9B Reaper, as well as thousands of domestically produced UAVs for tactical use. These drones are central to Taiwan’s asymmetric warfare strategy—meant to slow or deter a larger invading force by using advanced technology and hit-and-run tactics. China’s new anti-drone barrage system seems to be a direct answer to this evolving strategy, designed to destroy such drones before they can gather intelligence or strike. Eye on Global Demand Chinese defense experts believe the system also has strong potential for international exports. As drone warfare becomes a global concern, especially in low-cost, high-threat battle scenarios like in the Middle East, Africa, and Eastern Europe, countries are seeking affordable yet powerful air defense alternatives. This new barrage weapon may well find interest among countries facing frequent drone incursions or attacks from small aerial platforms. The Future of Drone Warfare The unveiling of this weapon underscores a broader shift in modern combat thinking: it’s no longer just about precision strikes and stealth fighters. The real challenge now lies in countering low-cost, mass-produced drones that can overwhelm defenses by sheer numbers. China’s new system reflects this transformation—introducing a brute-force but highly sophisticated approach that floods the air with projectiles instead of relying on expensive missile interceptors. As nations around the world continue to invest in drone technology, the race to build effective countermeasures is heating up. With its latest innovation, China appears to be setting the pace—proving that in tomorrow’s wars, it might take a storm of firepower to stop a swarm of machines.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:25:51India
India is stepping up efforts to acquire a new generation of airborne surveillance platforms dedicated to signals intelligence (SIGINT) and communications jamming (COMJAM), marking a crucial step in modernising its electronic warfare capabilities. This initiative, jointly spearheaded by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Air Force (IAF), is part of a broader strategy to counter growing threats along its borders—particularly from an increasingly assertive China. As of March 2025, the competition to supply these critical platforms is heating up, with three major contenders: the US defence giant L3Harris Technologies, France’s Thales Group, and India’s own Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL). Each of these players offers a distinct approach—balancing proven foreign technology with local manufacturing ambitions. The Mission: Three Advanced Spy Planes for Electronic Dominance India plans to convert three Airbus A319 aircraft into cutting-edge SIGINT/COMJAM platforms capable of deep electronic reconnaissance. These aircraft will have the ability to detect and intercept enemy radar, communication signals, and electronic emissions, while also jamming and disrupting enemy communications and control systems during times of conflict. This requirement stems from the need to keep pace with China, whose People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) regularly operates advanced ISR platforms like the KJ-500 and Y-9. With PLA bases like Hotan and Ngari Gunsa located dangerously close to India’s northern frontiers, New Delhi is keen to enhance its own airborne electronic surveillance assets. L3Harris: Backed by Combat-Proven Tech L3Harris enters the competition with a strong portfolio of US-tested systems. Known for providing the US Army with ARTEMIS and ARES platforms—based on Bombardier business jets—the company brings proven expertise in SIGINT, electronic warfare (EW), and rapid data processing technologies. Their proposal for India would likely include high-end electronic intelligence sensors, onboard data analysis tools, and robust jamming suites capable of intercepting enemy transmissions and degrading hostile radar capabilities in real time. From a purely technical perspective, L3Harris offers a mature, combat-tested solution—attractive to those seeking immediate capability with minimal development risk. However, reliance on American systems could come with strategic constraints, such as export controls, limited customization, and less room for domestic industry involvement—areas where India's policymakers are increasingly cautious. Thales: Riding the ‘Make in India’ Wave In contrast, France’s Thales is highlighting its long-standing collaboration with India’s defence sector. The company already plays a role in India's Rafale fighter jet program and has partnered with BEL to form BEL-Thales Systems. Thales also has experience developing France’s CUGE (Capacité Universelle de Guerre Électronique) aircraft—an electronic warfare platform similar in scope to India’s current requirements. For New Delhi, Thales’s bid holds particular appeal because of its emphasis on local industrial participation, aligning with the government’s 'Make in India' push. This approach not only promises greater technology transfer and domestic job creation but also helps in reducing long-term dependency on foreign suppliers. Thales is expected to offer modular ISR systems tailored to India’s strategic environment, with the potential to co-develop or locally manufacture key components—a diplomatic and industrial win-win. BEL: Indigenous Ambitions Face Capability Test Meanwhile, Bharat Electronics Limited, the homegrown contender, brings with it nationalistic appeal and cost advantages. BEL has already contributed to India’s AEW&C programs, particularly the DRDO-developed Netra system that operates onboard Brazilian Embraer jets. However, SIGINT and COMJAM capabilities represent a more sophisticated technological frontier. While BEL is trusted for radars and basic EW systems, questions remain about whether it can independently deliver a comprehensive solution matching the precision, miniaturisation, and real-time responsiveness offered by its foreign rivals. Still, if selected, BEL's involvement would significantly boost indigenous defence manufacturing, encourage further R&D, and offer India full ownership of the technology—crucial from a strategic autonomy perspective. A Strategic Tug of War At its core, the contest represents a classic trade-off between performance and sovereignty. L3Harris’s proposal may offer unmatched capabilities, but Thales and BEL appeal to India’s strategic and industrial independence goals. The choice India makes will reflect how it balances urgent defence readiness with long-term self-reliance. Given the escalating regional tensions, especially with China’s electronic and cyber warfare assets increasingly encroaching on India’s neighbourhood, time is of the essence. The new SIGINT/COMJAM aircraft will play a pivotal role in decoding enemy intentions, disrupting wartime communications, and protecting India’s airspace with an invisible shield of electronic dominance. The decision will not just define the future of India’s airborne intelligence fleet—it may also shape the path of India’s broader defence procurement philosophy in the years to come.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-11 15:23:16Search
Top Trending
-
 Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
-
 India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
-
 Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
-
 Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
-
 What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
-
 China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
-
 China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
-
 India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
Top Trending in 4 Days
-
 Rostec's UVZ Unveils Revolutionary T-90 Tank Design Without Turret to Boost Survivability in Modern Warzones
Rostec's UVZ Unveils Revolutionary T-90 Tank Design Without Turret to Boost Survivability in Modern Warzones
-
 DRDO Successfully Test 30 KW First Laser Weapon Against Aircraft, Missiles, and Drones
DRDO Successfully Test 30 KW First Laser Weapon Against Aircraft, Missiles, and Drones
-
 India’s ‘Surya’ Laser Weapon: DRDO to Develop 300kW Directed-Energy System with 20km Range by 2027
India’s ‘Surya’ Laser Weapon: DRDO to Develop 300kW Directed-Energy System with 20km Range by 2027
-
 Zelensky Claims Chinese Nationals Fighting for Russia in Ukraine, Warns of War Expansion
Zelensky Claims Chinese Nationals Fighting for Russia in Ukraine, Warns of War Expansion
-
 North Korea Sends Ballistic Missiles to Russia in Alarming Arms-for-Defense Deal
North Korea Sends Ballistic Missiles to Russia in Alarming Arms-for-Defense Deal
-
 Indian Army Neutralises Chinese Drone Near LoC Using DRDO’s Indigenous Laser Weapon
Indian Army Neutralises Chinese Drone Near LoC Using DRDO’s Indigenous Laser Weapon
-
 Bangalore’s EtherealX Unveils Razor Crest MK-1 — The World’s First Fully Reusable Medium-Lift Rocket
Bangalore’s EtherealX Unveils Razor Crest MK-1 — The World’s First Fully Reusable Medium-Lift Rocket
-
 IAF Charts Path from Chaos to Clarity: Plans to Replace Mixed Fighter Fleet with Unified Indigenous Powerhouse
IAF Charts Path from Chaos to Clarity: Plans to Replace Mixed Fighter Fleet with Unified Indigenous Powerhouse