India
In a significant leap for India's self-reliance in strategic electronics, researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, have successfully developed a high-power microwave transistor based on Gallium Nitride (GaN) grown on a silicon platform. This achievement marks the first time such a device has been entirely designed, fabricated, and tested in India—paving the way for critical applications in defence and advanced communication technologies. GaN-based microwave transistors are known for their ability to handle high voltages and amplify radio signals at very high frequencies. These features make them indispensable for radars, electronic warfare systems, jammers, and next-generation telecom infrastructure. However, due to their strategic significance, most GaN transistors are import-restricted and manufactured abroad, especially on silicon carbide (SiC) substrates, which are costly and less scalable. What makes this development exceptional is that the IISc researchers have built the transistor using GaN-on-silicon technology—an alternative approach that significantly reduces cost and supports large-scale production. This method, however, is technically complex due to the challenges in growing high-quality GaN layers on silicon substrates, which have different physical properties and can cause stress, cracks, or defects in the material. The team at IISc’s Centre for Nano Science and Engineering (CeNSE) tackled these challenges by carefully engineering the atomic structure of the material stack. They used precise layer-by-layer deposition techniques to build the transistor and achieved a power output of 8 watts at a frequency of 10 GHz—a performance level considered strategically valuable for many defence and communication applications. A unique aspect of their approach was the manipulation of a fundamental property of GaN called polarisation. By tuning this property, they managed to eliminate the need for adding elements like carbon or iron—impurities that are usually introduced to stabilize the device but often degrade performance. This is the first time in India that microwave power transistors have been demonstrated using GaN-on-silicon without these intentional impurities. The success of this fully indigenous project not only showcases India's growing capability in advanced semiconductor research but also lays the foundation for future home-grown technologies in the defence, aerospace, and telecom sectors. By removing the dependency on expensive imports, it opens up possibilities for affordable, large-scale production of high-frequency components that are vital for national security and digital infrastructure. This milestone aligns with the broader goal of developing a robust and self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem in India—an effort that has gained momentum with recent government initiatives and international collaborations. As GaN-on-silicon becomes more refined and scalable, it is poised to play a transformative role in India’s high-tech future.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:28:25World
In a move underscoring its strategic alliance with Israel, the U.S. government has officially approved the sale of advanced engines and support equipment for Israel’s Eitan armored fighting vehicles. Valued at approximately $180 million, this latest package includes 8V199TE21-D powerpack engines along with a suite of technical, engineering, and logistics support—significantly expanding on a prior $85.5 million agreement that did not require congressional notification. The U.S. State Department’s decision was announced through the Defense Security Cooperation Agency, which formally notified Congress of the proposed Foreign Military Sale earlier this week. The approved engines are intended to power the Eitan, Israel’s indigenously developed 8×8 wheeled armored personnel carrier that’s gradually replacing the aging M113 fleet. Designed to offer superior mobility, speed, and protection, the Eitan plays a key role in strengthening the Israeli Defense Forces (IDF), especially in urban warfare and high-threat environments. The latest deal does not include Major Defense Equipment (MDE) but offers significant advantages through U.S. government and contractor technical assistance, one-time engineering support, and other sustainment elements. Rolls-Royce Solutions America, headquartered in Novi, Michigan, has been selected as the principal contractor for the program. According to U.S. defense officials, this sale is expected to enhance Israel’s ability to confront modern battlefield challenges and respond swiftly to regional threats. By upgrading its armored ground vehicle fleet, Israel will be better equipped to safeguard its borders, protect critical infrastructure, and ensure the safety of its civilian population. The agreement also reinforces a cornerstone of U.S. Middle East policy—maintaining Israel’s “qualitative military edge” over potential adversaries. This concept ensures that Israel retains advanced defense capabilities compared to other countries in the region, and is a key principle guiding U.S. arms sales to its closest Middle Eastern ally. While no offset agreements were included in this transaction, such deals may be independently negotiated between the manufacturer and the Israeli government at a later stage. The Eitan program reflects Israel’s broader push to modernize its ground forces by incorporating cutting-edge technology and enhancing operational flexibility. With the backing of the United States, the Eitan platform is expected to become a cornerstone of Israel’s future armored mobility and border defense strategy.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:25:46World
Greece has taken another major step in strengthening its military capabilities by acquiring 16 Exocet MM40 anti-ship missiles from France. The agreement was formally signed in Athens by Greek Defence Minister Nikos Dendias and his French counterpart, Sébastien Lecornu, during an official diplomatic visit. While the cost of the deal remains undisclosed, the move marks a significant addition to Greece’s naval arsenal and reflects its ongoing commitment to defense modernization. The Exocet MM40 missiles are highly regarded for their advanced features and reliability in modern warfare. Designed for precision strikes at sea, these missiles have a maximum range of 250 kilometers and weigh approximately 780 kilograms. Measuring under six meters in length, they are compact but extremely powerful. The missile is guided by a combination of inertial navigation and an active electromagnetic seeker, allowing it to follow complex flight paths and engage targets even beyond the line of sight. One of the key strengths of the Exocet MM40 is its stealth-oriented design. It can fly at very low altitudes over the sea, reducing the chance of detection by enemy radar systems. Its low radar, visual, and infrared signatures make it harder to intercept. The missile’s advanced seeker system can distinguish targets even in cluttered environments and is resistant to electronic countermeasures. With GPS functionality, the Exocet can also engage coastal land targets, making it a flexible asset in various combat scenarios. This acquisition fits within a broader strategic push by Greece to modernize its armed forces. Athens has been consistently increasing its defense budget, and this year alone, it has more than doubled its military spending to €6.13 billion ($6.6 billion). The country stands out in NATO for its high defense expenditure—allocating over 3 percent of its GDP, a figure only matched by a few other member states such as Poland, Estonia, and Latvia. By 2036, Greece plans to invest approximately €26 billion ($28 billion) in new military systems. This long-term effort includes the procurement of advanced air and naval platforms. Earlier this year, Greece received its 30th upgraded F-16 Viper fighter jet from Lockheed Martin, enhancing the Hellenic Air Force’s combat capabilities. Around the same time, the country also welcomed the final delivery of 24 Rafale fighter jets from France’s Dassault Aviation—another milestone in the Greek-French defense partnership. The purchase of the Exocet MM40 missiles comes at a time when tensions in the Eastern Mediterranean remain a concern, particularly regarding maritime boundaries and energy exploration. With these new missiles, Greece is not only improving its deterrence but also reinforcing its position as a capable and modern naval power in the region.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:23:56World
In a significant show of allied strength and evolving defense cooperation, the U.S. Marines from the 3rd Marine Littoral Regiment (3d MLR) have deployed the advanced Navy-Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) to the Philippines for Exercise Balikatan 25. This marks the first time the system has ever been brought to the country, and it highlights the growing depth of the U.S.-Philippines military alliance. The deployment was officially confirmed by U.S. Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth during his visit to Manila on March 28. This moment not only strengthens military ties but also adds a powerful new layer to the Philippines' coastal defense strategy. Strengthening the Alliance through Exercise Balikatan 25 Exercise Balikatan 25, running from April 21 to May 9, is the latest installment in the annual joint exercise series between the United States and the Philippines. The name "Balikatan" means "shoulder-to-shoulder" in Filipino, symbolizing the strong partnership between the two nations. This year’s edition involves multiple training events, such as: Integrated Air and Missile Defense Maritime Key Terrain Security Operations in Northern Luzon and the Batanes Islands Counter Landing Live Fire Exercises in Cagayan Maritime Strike Exercises at sea The NMESIS system will be a key component of the Maritime Key Terrain Security Operations segment, although it will not be live-fired during this exercise. Tactical Movement and Joint Deployment During the exercise, U.S. Marines from the 3d Littoral Combat Team’s Medium-Range Missile Battery, along with the Philippine Marines from the 4th Marine Brigade, will jointly transport NMESIS launchers using U.S. Army and Air Force aircraft. These launchers will be relocated from Northern Luzon to various islands in the Batanes chain. Once in place, both forces will set up a Fires Expeditionary Advanced Base (EAB). The system will be used for simulated fire missions, allowing both sides to test coordination, mobility, and targeting procedures in a realistic but non-live environment. Supporting this operation, the AN/TPS-80 Ground/Air Task-Oriented Radar (G/ATOR) will be deployed in Northern Luzon. It will track air movements and feed targeting data into the system, ensuring high-level situational awareness for future joint operations. What is NMESIS? The Navy-Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) is a powerful and mobile anti-ship missile system designed to deny enemy ships access to strategic maritime zones. Key Specifications: Missile Type: Naval Strike Missile (NSM) Range: Approximately 185 kilometers (115 miles) Guidance: GPS and infrared homing Launcher Vehicle: Remotely operated JLTV-based launcher platform (Rogue Fires) Role: Anti-ship and land-target strike capability Mobility: High, air-transportable by C-130, CH-53, and other military aircraft Crew Requirements: Minimal due to semi-autonomous launcher NMESIS represents a leap in distributed lethality, enabling small Marine units to launch powerful precision-guided missiles at sea targets from remote island outposts, a concept central to the U.S. Marine Corps’ Force Design 2030 vision. Why This Matters for the Philippines The Philippines is a key strategic location in the Indo-Pacific region, and the deployment of NMESIS helps strengthen its maritime defenses at a time of rising regional tensions. This year marks the third consecutive time the 3d MLR has joined Exercise Balikatan. In previous years, they introduced advanced systems like the AN/TPS-80 radar and conducted security operations on islands like Itbayat, Batan, and Mauvulis. Now, with NMESIS, the collaboration is entering a more advanced phase. The system provides extended-range sea-denial capability, enhances coastal defense, and helps integrate land-based assets with naval operations — a crucial asset in archipelagic warfare. A Step Forward in Allied Readiness U.S. and Philippine forces continue to build trust, technical interoperability, and operational readiness through Balikatan. The inclusion of NMESIS this year shows that both nations are preparing for a more connected, agile, and responsive defense posture. As Colonel John G. Lehane of 3d MLR stated, “The AFP are some of our closest and strongest Allies, and we look forward to exercising alongside and learning from our Philippine Marine Corps counterparts.” With such advanced systems now being integrated, the partnership is not only strengthening but also transforming into a more modern and dynamic force capable of meeting future security challenges in the Indo-Pacific.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:22:05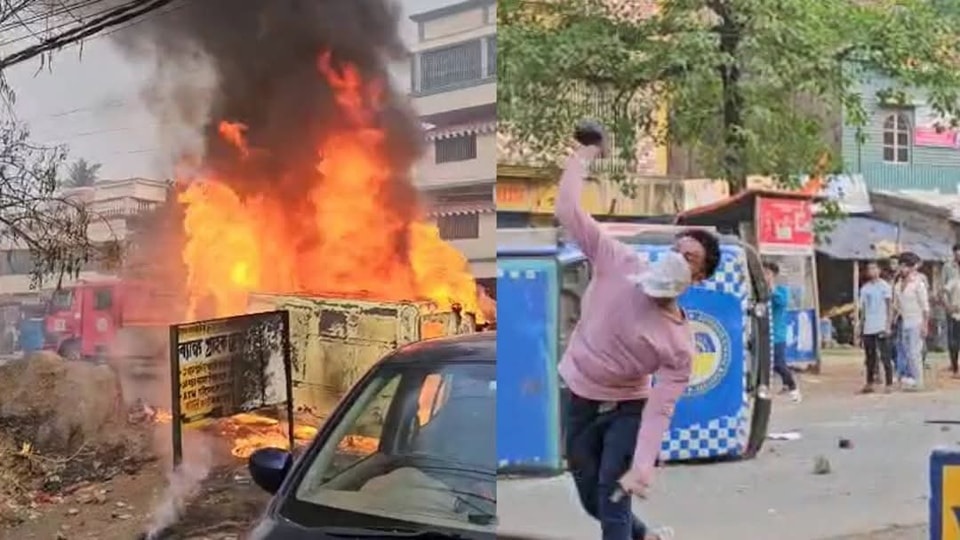
Bangladeshi Radicals Linked to Murshidabad Violence with Alleged Local Leaders Support: Intel Report
India
A recent intelligence report has raised serious concerns over the involvement of Bangladeshi radicals in the deadly violence that shook West Bengal’s Murshidabad district. According to sources familiar with the report, members of two notorious extremist groups from Bangladesh — Jamaat-ul-Mujahideen Bangladesh (JMB) and Ansarullah Bangla Team (ABT) — played a direct role in inciting the riots, allegedly with the help of local political leaders. The violence erupted last week during protests against the amended Waqf Act, a law that has sparked anger in several parts of West Bengal. What began as demonstrations quickly escalated into violent clashes, especially in areas like Suti, Dhulian, Jangipur, and Shamsherganj, resulting in the death of at least three individuals and injuries to several others. Sources said the intelligence report highlights how Bangladeshi operatives had crossed the border and participated in organizing the mobs, with backing from local leaders of a particular political party. This development has caused alarm in security circles and has drawn strong attention from the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, which is now actively monitoring the region. To prevent further escalation and infiltration, the Border Security Force (BSF) has been directed to maintain heightened vigilance along the India-Bangladesh border. Central paramilitary forces such as the CRPF and Rapid Action Force (RAF) have also been deployed across sensitive locations in the district. Following the outbreak of violence, Union Home Secretary Govind Mohan held a virtual meeting with top officials of the West Bengal government, including the chief secretary and the state’s director general of police. In the meeting, the Centre urged the state to step up surveillance in Murshidabad and in other potentially volatile districts. Security forces on the ground report that calm is slowly being restored. No new incidents of violence have been reported in the past 48 hours. Shops have begun reopening, and many families who had fled during the clashes are returning home. However, officials are continuing to assess the situation carefully, especially in areas considered vulnerable to further unrest. The involvement of foreign radical elements in internal unrest has added a new layer of complexity to the already sensitive law and order situation in West Bengal. As investigations continue, authorities are also exploring whether this incident is part of a broader pattern of cross-border radical influence in border regions. The intelligence inputs have sparked concerns not just about local law and order, but also national security. Analysts warn that the alleged cooperation between foreign extremists and local actors could pose a long-term threat if not addressed swiftly and firmly. As the situation unfolds, both the state and central governments are working in coordination to ensure peace returns to the region, and that such incidents do not recur.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:18:50World
The Italian Navy has officially added the ninth FREMM (European Multi-Mission Frigate) to its fleet, as the warship Spartaco Schergat (F598) was handed over by Orizzonte Sistemi Navali, a joint venture between Italian defense giants Fincantieri and Leonardo. This new vessel represents another key step in modernizing Italy’s naval capabilities and strengthening its presence across a wide range of maritime missions. The FREMM program—short for Fregata Europea Multi-Missione—is one of the most advanced and versatile naval projects in Europe. Designed to be highly modular, each FREMM frigate can be tailored for specific missions like general-purpose operations, anti-submarine warfare (ASW), and air defense. The Spartaco Schergat will primarily focus on both general-purpose and ASW duties, enhancing the Italian Navy’s flexibility and readiness in multiple combat environments. What makes this ninth FREMM particularly special is its technological edge over its predecessors. It features upgraded systems for modern sea control operations, including improved communication systems to better protect maritime lines and advanced tools for naval interdiction. These improvements are aligned with current and emerging naval threats, ensuring that Italy’s fleet remains capable in both traditional and hybrid conflict scenarios. The Schergat will be based in La Spezia, a key naval hub on Italy’s Ligurian coast. From there, it will undertake patrols, training missions, and active deployments as part of Italy’s wider maritime defense strategy. Measuring 145 meters long and capable of carrying up to 200 personnel, this warship brings both size and strength to the table. Technologically, the Spartaco Schergat is outfitted with cutting-edge sensors and weapons. It includes an active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar for tracking air and surface threats, hull-mounted and towed sonars for submarine detection, naval guns, autocannons, torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, and air defense systems. Additionally, it has space for two maritime helicopters—typically the SH90 type—and a rigid hull inflatable boat (RHIB) for special operations or search and rescue. The propulsion system of the FREMM class is equally impressive. Each ship is powered by a combination of one gas turbine, two electric motors, and four diesel generators, giving it a range of 6,000 nautical miles and speeds exceeding 30 knots (approximately 56 km/h). This blend of speed and endurance ensures the FREMM can operate effectively in both coastal and blue-water missions. Looking ahead, the FREMM fleet will continue to expand. Another hybrid-configuration frigate—designed to counter both surface and undersea threats—is expected to be delivered to the Italian Navy by August 2025. Beyond that, construction has already begun on two new-generation FREMM vessels, which are slated for delivery in the early 2030s. These next-gen ships will incorporate even more advanced combat systems and digital technologies to meet future maritime challenges. The FREMM design is not exclusive to Italy. Its proven performance and modularity have led to its adoption by the navies of France, Egypt, and Morocco, demonstrating the international appeal and credibility of the platform. With the induction of the Spartaco Schergat, the Italian Navy reinforces its commitment to maintaining a modern, capable, and flexible naval force—ready to protect national interests and contribute to international stability in waters near and far.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:15:40India
India is stepping into a new era of strategic defence with the development of the K-5 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), a powerful addition to its nuclear arsenal designed to ensure a credible second-strike capability from beneath the oceans. With a range of over 5,000 kilometres—and the potential to extend beyond 8,000 km with a lighter payload—the K-5 significantly enhances India’s reach, marking a milestone in its journey toward full-spectrum nuclear deterrence. The K-5 is being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) as the successor to the K-4 SLBM, which has a range of approximately 3,500 km and is already in service on the Arihant-class nuclear submarines. While the K-4 ensures deterrence against regional threats, the K-5 pushes India’s strategic capabilities well beyond, enabling it to target adversaries situated deep inland or across vast oceans. Strategic Reach and Range With a standard payload, the K-5 is expected to hit targets over 5,000 km away. This covers critical regions such as the entire Middle East, Central Asia, East Asia (including China’s eastern coast, Japan, and South Korea), and parts of Europe. When equipped with a lighter warhead—potentially around 500 kg—the missile’s range could extend up to 8,000 km. This extended reach would allow it to cover northern Australia, Moscow, and even the NATO-Russia frontier, vastly expanding India's deterrence zone. Most operational concepts suggest the missile would be launched from Indian Ocean waters south of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands—an ideal stealth zone for India’s Arihant-class nuclear-powered submarines. From this strategic location, the missile could cover a significant portion of the globe, sending a strong message to potential adversaries that any attack on India would invite assured retaliation from an undetectable underwater platform. Specifications and Technological Advancements The K-5 SLBM is believed to be a three-stage, solid-fuel missile featuring: Range: 5,000 km with standard warhead; up to 8,000 km with reduced payload Warhead Type: Likely nuclear, with potential for Multiple Independently targetable Reentry Vehicles (MIRVs) Payload Capacity: Estimated between 1,000–2,000 kg Launch Platform: Arihant-class (currently) and future S5-class nuclear submarines Guidance: Likely advanced inertial navigation with potential satellite-based corrections Propulsion: Solid-fuel rocket motors enabling cold-launch capability from underwater If the K-5 incorporates MIRV technology, a single missile could simultaneously strike multiple targets, further boosting its deterrent value. Sea-Based Second-Strike Capability The importance of sea-based deterrence lies in survivability. Submarines, especially nuclear-powered and stealthy ones, are the hardest platforms to detect and destroy. This makes them ideal for India’s "no first use" nuclear doctrine, ensuring that even if India were struck by a nuclear first strike, a devastating counterstrike could still be launched from underwater. This development completes India’s nuclear triad—the capability to launch nuclear weapons from land, air, and sea—bringing it in line with major nuclear powers like the United States, Russia, and China. Only a handful of nations possess the technological ability to develop and deploy SLBMs with ranges exceeding 5,000 km, making the K-5 a symbol of India’s rising strategic stature. Context of Regional Security China’s growing military presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and the expansion of its long-range nuclear missile fleet have been key factors in India accelerating SLBM development. China’s JL-3 SLBM, reportedly with a 10,000 km range, and its DF-41 land-based ICBM, have reshaped the strategic balance in Asia. India’s answer is the K-5—a deterrent not just aimed at parity, but strategic resilience. Beyond China, the K-5 also serves as a stabilising factor in India’s broader regional and global strategic posture. Its range potentially extends to Europe and Southeast Asia, reinforcing India's status as a responsible power that can independently secure its interests without reliance on external alliances. Future Plans and Submarine Platform Evolution The full impact of the K-5 will only be realised with adequate submarine platforms capable of carrying and launching multiple missiles. Current Arihant-class submarines are believed to carry four vertical launch tubes for SLBMs. However, the upcoming S5-class submarines, expected to enter service in the early 2030s, are projected to be larger and capable of carrying up to 12 K-series missiles, giving India a more formidable sea-based deterrent. These submarines will allow India to maintain continuous deterrence patrols, ensuring that at least one submarine is always on station, armed, and ready. However, maintaining this posture will demand careful balancing of crew rotation, submarine maintenance, and stealth operations in the deep sea. Challenges and Technological Mastery Developing an SLBM of this calibre is no small feat. It demands: Miniaturisation of nuclear warheads Complex three-stage solid-fuel propulsion systems Extremely reliable and accurate guidance systems Advanced materials to handle re-entry speeds and high temperatures Moreover, integrating the missile into submarines while maintaining stealth and safety standards adds another layer of complexity. If MIRVs are indeed integrated, it would represent a significant leap in both missile and warhead technology. Conclusion The K-5 SLBM is not just another missile—it is a message. A message that India is prepared, capable, and determined to maintain a credible and survivable nuclear deterrent. As India steps into this new strategic realm, it joins a select group of nations capable of global nuclear reach from the deep sea. In doing so, India reinforces its security, asserts its strategic autonomy, and contributes to maintaining peace through credible deterrence in an increasingly uncertain world.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:12:41India
The Italian-made Black Shark heavyweight torpedo has once again taken center stage as a top contender for the Indian Navy’s critical submarine warfare requirements. After a prolonged period of uncertainty and past controversy, the torpedo is now gaining renewed traction, especially following the exit of key competitors from the bidding process. A Technological Powerhouse in Underwater Warfare Developed by Leonardo (previously known as WASS), the Black Shark torpedo represents one of the most advanced submarine-launched weapon systems in the world. It is an evolved version of the earlier A184 model, equipped with state-of-the-art enhancements that significantly boost its performance against both underwater and surface threats. At the core of its superiority lies a fibre-optic guided system coupled with advanced electronic counter-countermeasures (ECCM) and multi-frequency sonar capabilities. These features allow for precise target identification and tracking, even in environments saturated with countermeasures and decoys. Key Specifications of the Black Shark Maximum Speed: 50 knots (approximately 93 km/h) Effective Range: 50 kilometers Propulsion System: Aluminium-silver oxide (Al-AgO) battery paired with a contra-rotating brushless motor Warhead: 350 kg high-explosive charge Standards Compliance: Built according to NATO’s STANAG 4439 and MURAT-2 safety and performance standards The use of a non-gas-emitting propulsion system ensures silent and emission-free operation, giving submarines better stealth and endurance at deep sea levels. A Comeback After Controversy The Black Shark's journey to the Indian Navy has not been without setbacks. During the 2008–2013 procurement process, the torpedo was part of a high-profile deal that was eventually cancelled due to allegations of procedural irregularities. This led to an investigation by India's Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), and the torpedo was shelved for several years. Now, however, the tides are turning in its favor. With Germany’s ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS) recently pulling out of the competition to supply torpedoes for the Indian Navy’s Kalvari-class submarines, only France’s Naval Group remains as a competitor. According to internal assessments, the Italian Black Shark is more cost-effective, giving it a clear advantage. Strategic Edge for the Indian Navy India is looking to procure 48 heavyweight torpedoes to strengthen its submarine fleet, and the Black Shark’s modern capabilities and long operational lifespan—estimated to remain relevant for at least 30 more years—make it an ideal choice. Its combination of high speed, extended range, deep-sea capability, and robust electronic systems makes it not just a weapon, but a force multiplier for any modern navy. For the Indian Navy, which is aiming to modernize and expand its underwater combat strength, the Black Shark could provide a much-needed edge in the Indian Ocean region and beyond. As the procurement decision nears, the Black Shark stands poised not just to re-enter the Indian defence arena, but to dominate it.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-16 14:08:13World
In a surprising public statement, Italy’s Defence Minister Guido Crosetto has criticized the United Kingdom for not fully sharing technology in a multi-nation fighter jet program, signaling growing tensions within the Global Combat Air Programme (GCAP). The project, which includes Italy, the UK, and Japan, aims to develop a next-generation stealth fighter jet by 2035, blending cutting-edge AI, hypersonic capabilities, advanced radar, and electronic warfare systems. Crosetto expressed deep concern that the UK is being reluctant in transferring critical technologies, even as all three nations invest heavily in the joint effort. He emphasized that genuine partnerships are built on equal trust and cooperation, not on retaining strategic advantages. “There is no longer anyone who can be considered first and second class,” he said, pointing out that Italy and Japan had already lowered such “barriers of selfishness,” but the UK had not yet done so. Although Crosetto did not identify which specific technologies Britain was allegedly holding back, his remarks hint at issues that may involve advanced software, avionics, or stealth systems being developed by British defense firms like BAE Systems. These are vital components for what is supposed to be one of the most advanced aircraft ever built. GCAP is not just a military initiative but also a strategic alliance aimed at competing with U.S. and Chinese advancements in aerial combat technology. The joint company overseeing the project includes BAE Systems from the UK, Leonardo from Italy, and Japan’s JAIEC, each holding an equal 33.3% stake. However, such balance in ownership does not seem to be reflected in the sharing of intellectual property, at least from Italy’s viewpoint. Crosetto also welcomed the idea of bringing Saudi Arabia into the fold. He believes Riyadh’s participation could provide additional resources and accelerate technological development. According to him, Saudi Arabia’s inclusion would mirror the strategic importance of Japan’s entry and could help expand the scope of GCAP beyond just Europe and Asia. For now, the British Ministry of Defence has not publicly responded to Italy’s concerns. However, behind-the-scenes discussions are likely underway as all three nations understand the importance of maintaining unity and trust to keep the ambitious program on track. If these tensions continue to simmer, the project could face not only delays but also a potential weakening of alliance cohesion—something that could undermine Europe and Asia’s collective efforts to stand up to global superpowers in the defense technology race.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:57:27World
In a bold move to lead the global race in artificial intelligence (AI) video generation, Chinese tech giant Kuaishou has unveiled the upgraded version of its video-generating model, Kling AI 2.0. At a corporate event in Beijing, the company claimed that Kling is now the “world’s most powerful” video generation model, challenging international rivals such as OpenAI’s Sora and Google DeepMind’s Veo. Kuaishou, known as a major competitor to ByteDance's TikTok in China, has rapidly positioned itself as a serious player in the AI space. According to Kuaishou senior vice-president Gai Kun, Kling AI 2.0 brings significant upgrades, including better understanding of user prompts, improved realism in generated content, and higher visual quality for both imagery and movement. Gai described it as the “most powerful video-generation model available for public use.” Since its initial release in mid-2024, Kling has gained immense popularity, with over 22 million users globally creating more than 168 million video clips and 344 million images. The new Kling AI 2.0 is already accessible online and offers users greater control over motion, resulting in more dynamic and refined video outputs. The release comes amid a surge of interest in AI-generated content across China. Major Chinese tech firms such as ByteDance, Alibaba, Tencent, Zhipu AI, and Shengshu Tech are all aggressively investing in video-generating tools, aiming to outpace Western leaders in this field. This AI race has been described by Gai as a “run for life,” reflecting the urgency and intensity of the competition. What sets Kling apart is its performance on a global scale. According to third-party evaluator Artificial Analysis, the previous generation of Kling already held the top spot for image-to-video models worldwide and was second only to Google’s Veo 2 in text-to-video generation. With Kling AI 2.0, Kuaishou aims to close that gap—or even take the lead. Kuaishou is also supporting creative communities through its new "NextGen" initiative. This project is designed to provide artists and filmmakers with funding, technical support, and visibility to produce film-quality content using Kling’s tools. This move reflects the company’s broader ambition not just to provide AI tools, but to shape the future of digital storytelling. While Chinese chatbots are widely available for public use, AI video generators like Kling are typically offered under a freemium model. Users can access basic features for free but must pay to unlock more advanced capabilities. With Kling AI 2.0, Kuaishou is not just keeping pace with global competitors—it is attempting to lead. As AI-generated content continues to evolve, the battle for technological dominance is becoming more fierce, with Chinese tech giants determined to reshape the future of media, creativity, and entertainment on a global scale.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:52:25World
The Italian Army is entering a new era of mobility and firepower with the unveiling of the VBM 30 NG (New Generation), the most advanced version of its 8×8 wheeled Armoured Infantry Fighting Vehicle (AIFV) – the Freccia. Developed by the CIO consortium (a collaboration between IDV and Leonardo), this new model is more than just an upgrade; it's a total transformation that brings the Italian Army’s medium brigades in line with modern NATO standards. Evolution of the Freccia: From VBM to VBM 30 NG In the early 2000s, Italy introduced the VBM (Veicolo Blindato Medio) to equip the “Pinerolo” and “Aosta” brigades with medium-weight, fast-moving, and highly mobile armoured vehicles. The Freccia vehicles were first deployed in Afghanistan in 2010, proving their worth in real combat conditions. While earlier versions went through a Mid-Life Upgrade (VBM Plus) to extend service life, the VBM 30 NG represents a whole new generation of capabilities. Stronger, Smarter, Safer: Key Upgrades in VBM 30 NG ???? Redesigned Hull for Superior Protection The hull of the VBM 30 NG has been entirely redesigned with a focus on survivability. Wheel arches have been removed, and a V-shaped underbelly has been introduced to better deflect blasts from mines or IEDs. Inspired by IDV’s VBA amphibious vehicle (also used by the US Marines as the ACV), the internal floor is now decoupled from the seating structure, reducing the impact of explosions on troops and preventing leg injuries. ????️ Ballistic Protection and Materials Ballistic protection has been elevated by at least one level based on NATO STANAG 4569 standards. The use of advanced materials, similar to those in the Centauro II and VBA, enhances the vehicle's ability to withstand modern battlefield threats, including high-velocity projectiles and explosive blasts. ⚙️ Powerful Performance The VBM 30 NG is designed to handle an increased gross vehicle mass of up to 35 tonnes. Its engine, the IDV 6V TCA Commonrail turbocharged diesel, has been boosted from 550 hp to 720 hp, delivering a torque of 2,500 Nm. Despite the weight increase, the vehicle maintains impressive mobility: Max speed: 105 km/h Range: 800 km Climb capability: 60% gradient Side slope: 30% Hydropneumatic McPherson suspension and improved shock absorbers ensure smoother rides and better stability on rough terrain. ???? Turret Technology: Enhanced Firepower with Leonardo’s Innovation The VBM 30 NG’s new turret, developed by Leonardo, introduces a leap in digital battlefield capability. It features: 30 mm X-Gun with airburst ammunition (ABM) – offering superior lethality and Counter-UAS capability. Janus-D panoramic sight with laser rangefinder – effective even against small aerial targets. LOTHAR SD digital gunner sight – stabilized and independent from the cannon for higher precision. Over 200 ready-to-fire rounds – with under-armour reloading for added safety. +60° elevation / -10° depression – allowing for high-angle firing against drones and hidden targets. The turret's aluminium base structure is protected by upgraded modular armour, ensuring survivability while keeping weight manageable. ???? Smarter Systems: Command, Control & Navigation The VBM 30 NG integrates Leonardo’s latest C2D/N EVO digital battlefield management system. The crew now benefits from three independent displays (instead of two), improving situational awareness and command efficiency. All systems are NGVA-compliant, meaning they can be easily upgraded in the future with new digital or electronic modules. The vehicle also features: New-generation GPS/Galileo-compatible receiver Enhanced intercom system SWave VQ1 multi-band radio system Harris AN/PRC-152A SATCOM integration These upgrades enable seamless communication across all operational levels, ensuring the VBM 30 NG remains future-proof and network-ready. Conclusion The VBM 30 NG is not just an upgraded Freccia – it is a reimagined AIFV designed for 21st-century warfare. With unmatched mobility, stronger protection, and cutting-edge digital systems, the Italian Army now has a platform that can stand shoulder-to-shoulder with NATO’s best. The first batch of 76 vehicles, ordered in December 2024, marks the beginning of a new chapter in Italy’s mechanized forces, ensuring that its medium brigades remain agile, lethal, and protected in any combat environment.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:48:22World
In a startling development underscoring the rising maritime tensions in the South China Sea, the Philippine military has revealed that at least one of five underwater drones recovered by local fishermen sent a signal back to mainland China. The discovery, made between 2022 and 2024, has raised serious concerns about foreign surveillance and the potential for underwater warfare in strategically sensitive Philippine waters. These drones, capable of far more than mere navigation, were found in key maritime chokepoints across the archipelago. According to Rear Admiral Roy Vincent Trinidad, spokesperson for the Philippine Navy on South China Sea affairs, the drones had capabilities that could aid in detecting undersea threats, conducting surveillance, and testing underwater weaponry. "This is not just about exploring the sea. This is about the possibility of undersea conflict,” Trinidad emphasized during a media briefing. While the Philippine military refrained from officially naming the country responsible for deploying these devices, several drones bore Chinese markings. More tellingly, a forensic analysis of a SIM card found on one of the drones confirmed its last communication was traced to mainland China. One drone was recently discovered off San Pascual, Masbate, on December 30, 2024, by local fisherfolk and has since been handed over to the Philippine Navy. Photos released by the police regional office show a sleek, torpedo-shaped device — designed to blend into deep waters and avoid detection. In total, three of the drones were found off northern Luzon, including two near the Balintang Channel — a vital waterway just south of Taiwan. The remaining two were recovered near Masbate Island in the central region and close to Mindanao in the south. All locations are considered critical for both national defense and international maritime navigation. This revelation comes at a time of increasing military readiness. The Philippines is preparing for its annual joint military exercise with the United States, dubbed Balikatan or "shoulder to shoulder." This year’s drills, set from April 21 to May 9, will involve around 10,000 troops and for the first time include a test of integrated air missile defense systems. Brigadier General Mike Logico, speaking about the exercises, stated, “We are treating exercises as rehearsals. This is a continuation of long-planned joint operations with our allies.” Defense Secretary Romeo Brawner also highlighted that northern Luzon would host the bulk of the drills due to its strategic significance, hinting at potential threat scenarios in the area. “These are the areas where we perceive the possibility of an attack,” Brawner said, adding that the country must prepare without creating unnecessary panic. The discovery of these drones is the latest chapter in a tense standoff between Manila and Beijing over contested waters and sovereignty claims in the South China Sea. It also adds a technological layer to the conflict — one that now stretches below the waves, as nations use advanced unmanned systems to expand their reach and gather critical intelligence. As regional dynamics shift, the presence of foreign underwater drones in Philippine waters underscores the growing risks of covert surveillance and the need for greater maritime vigilance.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:43:30
Netherlands Plans to Acquire New Stealth Submersible Delivery Vehicles for Special Forces Operations
World
The Netherlands is preparing to upgrade its special forces’ underwater capabilities by acquiring new Submersible Delivery Vehicles (SDVs). The Dutch Ministry of Defence, through its procurement division COMMIT (Materiel and IT Command), has released a Request for Information (RFI) to gather details from manufacturers on available SDV systems that meet modern operational needs. These vehicles are intended for the elite Netherlands Maritime Special Operations Forces (NLMARSOF). Why the Netherlands Needs New SDVs Currently, the NLMARSOF uses Diving Propulsion Devices (DPDs) from the American company STIDD. These smaller systems are versatile and can be launched from land, ships, and submarines like the Walrus-class. For deeper and longer missions, NLMARSOF uses the Shadow Seal SDV—originally designed by Dutch firm Ortega Submersibles BV before it was acquired by the UK-based JFD. However, as operational requirements evolve, the Royal Netherlands Navy is now seeking more advanced SDVs that offer greater range, speed, stealth, and environmental adaptability. What the Netherlands is Looking For The new SDVs must be able to carry between four to eight combat divers, including all their gear and mission equipment. A key requirement is the integration of internal rebreather systems with a capacity of at least 240 minutes of breathable air per person—crucial for long-duration underwater missions. Key Specifications Demanded in the RFI The Royal Netherlands Navy is looking for SDVs with advanced technical capabilities: Surface range: Minimum 80 nautical miles Submerged range: Minimum 25 nautical miles Surface speed: At least 30 knots Submerged speed: Minimum of 5 knots Operating depth: Certified for 30 meters, though safety margins suggest capability for deeper depths Temperature range: Operational in air temperatures from +50°C to -15°C and seawater temperatures from +35°C to -2°C Stealth: Extremely low acoustic signature when submerged to avoid detection Sea state operation: Capable of operating up to sea state 4, allowing missions in moderately rough sea conditions Potential Candidates and Deployment The RFI's high demands significantly narrow the field of potential SDVs. Notably, SDVs like the Mark 11 SEAL Delivery Vehicle (SDV Mk 11) are unlikely to qualify due to design limitations. Viable candidates may include: JFD’s Carrier Seal SubSea Craft’s Victa Newer variants of the Shadow Seal The Navy plans to procure three SDVs capable of launching from Landing Platform Docks (LPDs) and nine new DPDs for submarine deployment. Although the current plan does not specifically mention SDVs compatible with submarines, future integration—especially with the upcoming Orka-class submarines—remains a possibility. These new submarines will be larger than the current Walrus-class, providing more flexibility for SDV operations. Regional Trends and Strategic Outlook This move comes at a time when other NATO allies are also modernizing their special forces capabilities. For instance, the Belgian Navy is also exploring similar underwater delivery platforms for its combat divers. This signals a broader regional trend in reinforcing maritime special operations in response to evolving security challenges. The Netherlands’ planned SDV acquisition reflects a shift towards more advanced, stealthy, and long-range underwater transport solutions for its elite frogmen. These new vehicles will allow the NLMARSOF to carry out missions with enhanced precision, deeper penetration, and reduced risk of detection—reinforcing the Netherlands’ role in NATO’s maritime security efforts.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:40:12World
Russia has introduced a modernized version of its well-known “Chekan” Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) vehicle, often referred to as the “Wagner’s wagon.” Originally developed for the Wagner Group, this vehicle is now actively being used by both Russian regular forces and paramilitary units across conflict zones, including Ukraine. Built on the reliable Ural-4320 heavy-duty truck chassis, the Chekan is a six-wheeled armored vehicle designed to offer strong protection and mobility in hostile environments. One of its key features is the V-shaped hull, specifically engineered to deflect the blast from landmines and improvised explosive devices (IEDs), which are common threats in modern warfare. Key Features and Specifications: Chassis Base: Ural-4320 6×6 truck platform Armor Level: BR5 standard (protects against small arms fire and shrapnel) Maximum Payload: Up to 6,000 kilograms Primary Armament: 14.5mm KPVT heavy machine gun Secondary Armament: 7.62mm PKT coaxial machine gun Role Variants: Troop carrier, logistics support, and command variants Manufacturer: LLC AVD, Saint Petersburg Users: Russian airborne units, irregular forces, and Wagner-aligned elements One of the most significant upgrades in the latest version is the inclusion of an electronic warfare (EW) system. This advanced equipment is designed to jam or disrupt enemy drones, reflecting Russia’s effort to counter the widespread use of UAVs for surveillance and precision attacks on the battlefield. The turret of the Chekan is adapted from the BTR-80 armored personnel carrier, giving it powerful offensive capabilities. The presence of a heavy machine gun and secondary armament allows it to engage both infantry and light armored threats effectively. Deployment and Strategic Use Field reports and visuals from the Ukrainian frontlines show the Chekan being used in a variety of roles. It has been spotted accompanying airborne troops and paramilitary fighters, especially in areas where Wagner-affiliated units are still active. Its robust design, heavy armor, and offensive capabilities make it a valuable asset in high-risk operations. The Chekan’s roots in the Wagner Group—designated as a terrorist organization by several nations, including the United States—highlight the overlapping lines between Russia’s formal military structures and its shadowy private military networks. Despite this, Russia promotes the vehicle as a domestically produced and adaptable solution for modern combat needs. With its blend of protection, firepower, and new-age electronic countermeasures, the updated Chekan MRAP is a clear indicator of how Russia is adapting its ground forces to confront emerging threats in modern warfare.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:36:49World
In a groundbreaking step toward modernizing battlefield technology, Duality AI has partnered with the U.S. Army’s XM30 Programme to advance artificial intelligence (AI) in counter-drone warfare. This collaboration is part of a broader initiative to develop the next-generation replacement for the M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicle, with a heavy focus on leveraging AI for soldier protection. Duality AI is best known for developing Falcon, a powerful digital twin simulation platform. The U.S. Army, through its XM30 Advanced Capabilities team, is utilizing Falcon to build and train an AI Target Detection and Recognition (AiTDR) system. This AI-driven system is being designed to identify, track, and respond to hostile drones before they become a threat to military personnel. Why Counter-Drone AI Matters With drones becoming an increasingly common part of modern warfare — from surveillance to carrying out direct attacks — it's vital that frontline vehicles like the upcoming XM30 are equipped with fast, accurate, and adaptable AI systems. The AiTDR system, therefore, plays a critical role in enhancing the vehicle's situational awareness and defense capabilities. Falcon: The Heart of Virtual AI Training Falcon’s digital twin simulation technology creates realistic battlefield scenarios using virtual sensors and environments. This allows AI models like AiTDR to be trained using synthetic data — digitally generated information that mimics real-world conditions. This approach is especially valuable because gathering real-world data for every possible combat situation is nearly impossible. Through Falcon, the Army can: Simulate various types of drones, terrain, and lighting conditions. Experiment with sensor configurations without needing physical hardware. Produce vast amounts of accurate training data in a fraction of the time and cost of traditional methods. According to Duality AI’s co-founder and Chief Product Officer Michael Taylor, “Falcon’s complete control over simulation environments gives the Army the ability to train and test the AiTDR model in complex conditions, explore varied drone detection scenarios, and validate potential solutions before field testing.” Project Linchpin and the Army Research Lab's Role The AI model is being developed under the U.S. Army's Project Linchpin, with technical support from the Army Research Lab (ARL). The use of Falcon during the initial stages is expected to: Speed up development timelines Reduce field testing costs Improve AI model accuracy and resilience under pressure This digital-first methodology signals a shift away from traditional defense development, allowing for faster innovation with reduced risk. Building on Proven Success Duality AI’s expertise in synthetic data generation has already been demonstrated in programs like DARPA’s RACER challenge. These successes show that AI trained on high-quality synthetic data can perform at or above the level of systems trained on real-world data. In the XM30 project, Falcon’s simulation suite is helping to create and refine the AiTDR model in multiple phases. The first phase focuses on integrating the AI model with Falcon’s simulator. Future phases will see the model evolve alongside continuous upgrades to the virtual training environment, guided by Duality’s engineers. A Vision for the Future Beyond the current focus on drone threats, the collaboration opens the door to a wider use of digital twin simulations across the Army’s AI training programs. This could include systems for vehicle navigation, automated threat assessment, and intelligent decision-making on the battlefield. Apurva Shah, Duality’s CEO, summed up the significance of the partnership: “The XM30 digital-first approach to AI model deployment is farsighted and precisely the type of system development approach for which Falcon’s digital twin workflows have been designed.” As the XM30 programme pushes forward, the integration of advanced simulation technology like Falcon stands to redefine how military systems are built and deployed — setting a new benchmark for AI-driven defense innovation.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:32:31World
The United Kingdom has officially handed over one of its retired Duke-class frigates to Turkey, marking another step in the Royal Navy's effort to modernize its fleet while ensuring the ethical disposal of aging vessels. The warship in question, HMS Monmouth (F235), served for over three decades before being decommissioned and sold to a Turkish ship recycling firm. Commissioned in 1993, HMS Monmouth was the sixth vessel of the Duke-class, also known as the Type 23 frigates. These ships were originally designed for anti-submarine warfare but were eventually upgraded to serve multi-role purposes. Over time, the aging Monmouth had surpassed its expected service life, making it increasingly expensive and impractical to refit or redeploy for modern naval duties. The ship has now been sold to Leyal Gemi Söküm Sanayi ve Ticaret, a ship recycling company based in Izmir, Turkey. This move aligns with the UK's broader initiative to promote sustainable and responsible disposal of military assets. The Turkish firm was selected through a competitive bidding process among European recycling yards. Richard Whalley, Head of Exports and Sales at UK Defence Equipment & Support — and a former lieutenant on HMS Monmouth — expressed personal sentiments about the transfer. While acknowledging the sadness of seeing a once-proud naval asset head for dismantling, he emphasized the importance of ethical recycling. “The sale of HMS Monmouth for recycling in Turkey will provide an ethical and responsible method of recovering metals and other valuable assets which provides a financial return for the Royal Navy,” Whalley said. The Duke-class, introduced in the late 1980s, originally consisted of 16 frigates. With advancing naval technology and changing defense needs, these vessels are now being phased out. In their place, the UK is investing in next-generation platforms — specifically the Type 26 and Type 31 frigates. The Type 26, also called the City-class frigate, is currently under construction by BAE Systems in Glasgow. These new warships are being designed with enhanced anti-submarine capabilities, improved support for carrier strike groups, and modern features suited to contemporary threats, including cyber and electronic warfare. The lead ship, HMS Glasgow, is already undergoing sea trials. To complement the City-class, the Royal Navy is also building five Inspiration-class (Type 31) frigates. These vessels will fill the general-purpose roles once held by the Type 23s, such as maritime security, intelligence gathering, and support operations for allied forces. Together, the Type 26 and Type 31 frigates represent a future-proof fleet set to carry the Royal Navy through the 2030s and beyond. The transfer of HMS Monmouth to Turkey is not just a farewell to a warship but also a reflection of the Royal Navy’s shift towards sustainability, modernization, and global partnerships. It’s a symbolic end of an era — and the beginning of a new chapter in British naval power.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:28:41India
The Indian Army is undergoing a profound transformation, embracing next-generation technologies to strengthen its combat effectiveness in the modern digital battlespace. At the heart of this shift lies a focused effort to modernise electronic warfare (EW) capabilities through the integration of indigenous systems like SAMBHAV, Samyukta, and Himshakti, alongside cutting-edge artificial intelligence platforms. These advancements are not only enhancing traditional battlefield capabilities but also enabling the Army to gain superiority in the electromagnetic and information domains—an increasingly decisive factor in contemporary warfare. SAMBHAV: A Secure Communication Game-Changer SAMBHAV (Secure Army Mobile Bharat Version) is a major leap forward in secure communication for the Indian Army. Built with advanced encryption and designed for 5G-ready networks, this mobile ecosystem enables soldiers to maintain secure connectivity even during movement, significantly improving real-time coordination and reducing the vulnerabilities of traditional mobile systems. With more than 35,000 SAMBHAV units slated for deployment in two phases, the Army aims to ensure end-to-end encrypted communication in operational zones. This secure mobile system has been developed in collaboration with Indian academia and industry experts, reflecting the country’s growing emphasis on indigenous defence solutions. SAMBHAV also supports the Indian government’s vision of “civil-military fusion,” leveraging public mobile infrastructure while layering military-grade security over it. Cyber Units: Expanding the Army's Digital Footprint Complementing this rollout is the establishment of Command Cyber Operations Support Wings (CCOSWs), specialised cyber units designed to fortify the Army's cyber defence posture. These wings, stationed across operational commands, are tasked with defending digital infrastructure, conducting cyber surveillance, and ensuring that advanced communication systems like SAMBHAV remain secure from electronic espionage or disruption. Each CCOSW is trained in state-of-the-art cyber warfare tactics and is integrated into broader operational planning, reflecting the growing role of cyber warfare as a tactical and strategic tool. This approach ensures layered protection of critical infrastructure and enables rapid cyber counteraction during both peacetime and conflict. Samyukta and Himshakti: Indigenous EW Powerhouses India's focus on self-reliance is also evident in the successful development of Samyukta and Himshakti—homegrown electronic warfare platforms tailored to India’s operational needs. Samyukta is designed to detect, intercept, and jam enemy electronic communications in the tactical battlefield environment, making it a key asset for battlefield dominance. Himshakti, on the other hand, is optimized for high-altitude operations, particularly suited for mountainous terrains like the Northern borders. These systems enable the Army to map, exploit, and dominate the electromagnetic spectrum, disrupting enemy communications while protecting its own. Such indigenous systems are a testament to India’s growing capability to design and manufacture complex defence technologies in-house, reducing dependence on imports and building long-term strategic autonomy. AI: The Brain Behind the Digital Frontier Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a cornerstone of India’s military modernisation drive. From surveillance to decision-making, AI-powered systems are rapidly redefining the way threats are identified and addressed. Motion Detection & Target Identification Systems powered by AI are now deployed along sensitive borders, capable of real-time alerts using data from thermal cameras, night vision sensors, and long-range optics. Another groundbreaking advancement is the AI-driven "Continuously Observing Ubiquitously Available Surveillance System," which operates without requiring constant human oversight. It addresses limitations like line-of-sight issues and energy dependency, while providing uninterrupted, smart surveillance in volatile regions. Furthermore, AI algorithms are being embedded into EW systems to improve jamming efficiency, electromagnetic spectrum analysis, and rapid countermeasure deployment. These AI tools enhance decision-making speed, precision targeting, and situational awareness, all crucial in today’s high-velocity conflicts. Strategic Vision: Multi-Domain Operations and 2025 Reforms All these initiatives are part of a broader roadmap set by the Ministry of Defence, which has declared 2025 as the "Year of Reforms." This declaration signifies an institutional push toward technology-driven transformation, integrated theatre commands, and multi-domain operations (MDO). MDO aims to synchronise military efforts across land, sea, air, space, and cyberspace, establishing a unified combat approach. India’s electronic warfare doctrine is also evolving based on global conflict lessons. The Indian Army is studying models like Israel’s operations against Hezbollah, where precision electronic warfare combined with psychological tactics created massive disruption without full-scale military engagement. These insights are shaping India's approach to integrated non-kinetic warfare. Joint military exercises now routinely simulate cyber-electronic warfare scenarios, highlighting the growing emphasis on readiness in contested electromagnetic environments. Conclusion The Indian Army’s modernisation push—spearheaded by systems like SAMBHAV, Samyukta, Himshakti, and AI-based platforms—is transforming how India prepares for and fights wars. With an increased focus on indigenous development, real-time surveillance, AI-enabled decision-making, and digital dominance, the Army is not only bridging the gap between conventional and modern warfare but also preparing to lead in the future battlefield. These initiatives form the backbone of India's move toward a combat-ready, technologically empowered force capable of securing its interests across all domains. While challenges persist in integrating these technologies seamlessly and training personnel to their full potential, the ongoing commitment and strategic clarity ensure that the Indian Army is on a strong path to achieving information and electronic superiority in the 21st century.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:19:46India
India is gearing up for one of its most significant defence purchases yet — a direct government-to-government (G2G) deal with France for 110 additional Rafale fighter jets. The move, expected to be initiated later this year, comes at a time when the Indian Air Force (IAF) urgently needs to replenish its shrinking squadron strength due to delays in earlier procurement efforts. Instead of waiting on the long-stuck Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender — which has been in limbo since 2018 — India is now leaning toward a faster, more streamlined route. The MRFA process, meant to bring in 114 fighter jets, has been bogged down by complications like technology transfer demands and stiff competition between global defence giants. As a result, little progress has been made even after years of deliberation. By opting for a G2G deal with France, the Indian government hopes to skip the bureaucratic red tape and take advantage of the well-established ecosystem already created around the Rafale jets. India currently operates 36 Rafales in the IAF and has just cleared a ₹63,000 crore deal for 26 Rafale Marine jets for the Indian Navy, intended for the INS Vikrant aircraft carrier. With existing training systems, maintenance setups, and supply chains already in place, adding more Rafales through the same route becomes a logical and cost-effective step. A crucial development tied to this potential deal is French aircraft manufacturer Dassault Aviation’s growing interest in taking full ownership of Dassault Reliance Aerospace Limited (DRAL), a joint venture located in Nagpur. Set up in 2016 with Reliance Aerostructure, the DRAL facility has been manufacturing Rafale components like wings and fuselage sections. Now, Dassault is reportedly pushing for complete control over DRAL to streamline production and ensure quality — something that became a sticking point during earlier Rafale negotiations with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). Dassault believes direct ownership would enable it to maintain high production standards and potentially position the facility to cater to export orders in the future. The French company claims that if it gains full control, the Nagpur unit could produce up to two jets per month, theoretically delivering all 110 jets within five years. However, some defence analysts are cautious, pointing out that Dassault only managed to build 13 Rafales in France in 2023, falling short of its own target. Still, in line with India’s “Make in India” initiative, Dassault has reportedly committed to sourcing a large portion of aircraft parts from Indian suppliers. The earlier Rafale deal already established a robust supply chain involving major Indian defence players like L&T, Mahindra, Godrej & Boyce, and the Kalyani Group. The company is expected to deepen these partnerships in the new deal, with DRAL potentially acting as the central hub for final assembly and integration. However, there are concerns within India’s Ministry of Defence about the actual level of indigenous production. Some officials fear that DRAL could end up being more of an assembly line for kits shipped from France rather than a true manufacturing hub, raising questions about meaningful technology transfer. Achieving a 70–75% local content target is seen as a steep challenge, especially given the Rafale’s complexity, involving over 40,000 unique parts. There’s also unease about the possibility of full foreign ownership of DRAL. Critics argue that this could sideline public-sector entities like HAL and consolidate control over advanced defence technologies in the hands of a few private players. If the deal goes through, India’s total Rafale fleet would rise to 172 — 36 jets already in service with the IAF, 26 for the Navy, and 110 new additions. This would make India the second-largest operator of Rafale jets after France itself, significantly boosting India’s air power at a time when regional security dynamics are evolving rapidly. With China deploying stealthy J-20 fighters and Pakistan reportedly eyeing advanced jets like the J-35, India’s decision to strengthen its air combat fleet with Rafales could be a game-changer in maintaining strategic balance in the region. While negotiations are still in early stages, the intent is clear: India is moving swiftly to address its air defence needs, and bypassing tender delays in favour of a direct Rafale deal may be the fastest route to readiness.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 15:05:41World
Thales has been awarded a critical new contract by NATO to deliver the third phase of its long-running NATO Common Operational Picture (NCOP) programme. This phase, officially titled “NCOP-BMD”, introduces enhanced Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) features aimed at countering the increasing threat posed by ballistic missiles to European and allied territories. It marks a major step forward in how NATO commanders will view, understand, and respond to complex threats on the battlefield. For over a decade, Thales has worked closely with NATO on developing and evolving the NCOP system, which has already been rolled out to around 30 command centres across member nations through previous phases—Increment-1 and Increment-2. These systems provided a standardized operational picture across all participating units, enabling joint operations involving land, sea, and air forces to work from a single, shared perspective. Now, with Phase 3, the programme is entering a new level of strategic capability. What makes this phase especially significant is the introduction of advanced BMD tools. These will give NATO commanders an enhanced understanding of missile threats in real time, including detection, tracking, and potential response options. As ballistic missile risks have grown in recent years—both from rogue state actors and potential regional conflicts—this capability is seen as essential to ensuring Europe's defense posture remains strong and proactive. Thales has engineered a secure and flexible software architecture for NCOP-BMD, allowing different layers of military operations to tap into a dynamic and comprehensive Common Operational Picture (COP). These COPs gather data from numerous tactical systems used by NATO’s member states, integrating information such as troop positions, equipment readiness, air and naval movement, and now—ballistic missile tracking—into a single view. This unified picture enables better coordination, quicker decision-making, and a more efficient deployment of NATO’s collective response. Importantly, it also accounts for interoperability among NATO’s diverse systems, a challenge that Thales has spent years mastering. Each real-time COP generated by NCOP-BMD includes detailed insights on ongoing missions, logistics chains, the status of friendly and opposing forces, and recommended coordinated action plans. For commanders, this means the ability to respond rapidly not just to traditional military threats, but also to time-sensitive missile attacks where every second matters. According to Gérard Herby, Vice President of Protection Systems at Thales, the third phase is built on lessons learned from the previous phases and is designed to address NATO’s evolving operational needs. “Thales will be providing new functionalities for ballistic missile defence in order to improve the situational awareness of NATO Commanders,” he stated. “This third contract will draw on our deep expertise in NATO interoperability developed since 2015.” This project forms part of NATO’s broader digital transformation and modernization of its command-and-control capabilities. As security environments grow more complex—with hybrid warfare, cyber threats, and missile risks converging—systems like NCOP-BMD will be central to NATO’s efforts to maintain strategic awareness and ensure collective defense across the alliance. In essence, Thales’ continued role in delivering this technology ensures that NATO will have the tools it needs to detect, assess, and act against missile threats in real time—making European skies and battlefields safer, smarter, and more secure.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 14:59:30World
Ukraine has taken a significant leap in modern warfare with the unveiling of its advanced uncrewed surface vehicle (USV) named Alligator-9, a powerful multi-role naval system designed to operate in high-threat environments. This next-generation war machine brings together the capabilities of precision laser weaponry and drone swarm technology, offering unmatched flexibility in naval operations. A New Era of Naval Warfare The Alligator-9 isn’t just any robotic boat—it’s a modular combat platform with multiple mission profiles. It’s been developed by Ukraine’s Unmanned Systems Force to meet a range of operational needs at sea, combining offensive strike power, surveillance capability, electronic warfare, and air defense—all in one system. This USV features three primary configurations, making it adaptable for various combat situations: Strike Configuration: Capable of launching six to ten Alligator-5 ToD (Torpedo Drones) to attack enemy ships or surface targets with high precision. Electronic Warfare Configuration: Equipped to deploy three to five Alligator-5 EW drones for jamming enemy radars, conducting surveillance, clearing mines, and supporting navigation for friendly forces. Hybrid Configuration: Likely to be a flexible mix of both strike and EW capabilities, depending on mission requirements. Armed with the Tryzub Laser System One of the most impressive features of the Alligator-9 is its Tryzub (Trident) laser system, a state-of-the-art directed energy weapon that can neutralize aerial threats with pinpoint accuracy. This laser system has reportedly already seen combat use and adds a cutting-edge layer of defense to Ukraine’s growing arsenal. Key capabilities of the Tryzub laser on the Alligator-9 include: Destruction of attack drones, bombs, and cruise or ballistic missiles from distances of up to 3,000 meters (9,842 feet). Engagement of aircraft and reconnaissance drones at ranges reaching 5,000 meters (16,404 feet). Disruption or disabling of airborne targets at distances up to 10,000 meters (32,808 feet). This makes the Alligator-9 not just a threat to sea-based targets, but also a formidable air defense platform in coastal and open water zones. Modular and Mission-Ready While specific details like the dimensions, top speed, and operational range of the Alligator-9 remain classified, the design is known to be modular, allowing quick reconfiguration depending on the mission. This modularity provides operational flexibility for the Ukrainian Navy to adapt to rapidly changing battlefield conditions. With stealthy design elements, potential autonomous navigation, and remote-control capability, the Alligator-9 is expected to play a key role in asymmetric naval warfare, especially in Ukraine’s fight to defend its coastline and challenge enemy naval forces in the Black Sea. Final Thoughts The introduction of the Alligator-9 marks a bold step for Ukraine’s defense innovation, especially as it continues to blend artificial intelligence, drone warfare, and laser weapons into its military strategy. As traditional naval assets become more vulnerable to fast, smart, and unmanned threats, the Alligator-9 could become a game-changer in both defensive and offensive naval operations.
Read More → Posted on 2025-04-15 14:56:49Search
Top Trending
-
 Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
-
 India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
-
 Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
-
 Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
-
 What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
-
 China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
-
 China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
-
 India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
Top Trending in 4 Days
-
 Rostec's UVZ Unveils Revolutionary T-90 Tank Design Without Turret to Boost Survivability in Modern Warzones
Rostec's UVZ Unveils Revolutionary T-90 Tank Design Without Turret to Boost Survivability in Modern Warzones
-
 DRDO Successfully Test 30 KW First Laser Weapon Against Aircraft, Missiles, and Drones
DRDO Successfully Test 30 KW First Laser Weapon Against Aircraft, Missiles, and Drones
-
 India’s ‘Surya’ Laser Weapon: DRDO to Develop 300kW Directed-Energy System with 20km Range by 2027
India’s ‘Surya’ Laser Weapon: DRDO to Develop 300kW Directed-Energy System with 20km Range by 2027
-
 Zelensky Claims Chinese Nationals Fighting for Russia in Ukraine, Warns of War Expansion
Zelensky Claims Chinese Nationals Fighting for Russia in Ukraine, Warns of War Expansion
-
 North Korea Sends Ballistic Missiles to Russia in Alarming Arms-for-Defense Deal
North Korea Sends Ballistic Missiles to Russia in Alarming Arms-for-Defense Deal
-
 Indian Army Neutralises Chinese Drone Near LoC Using DRDO’s Indigenous Laser Weapon
Indian Army Neutralises Chinese Drone Near LoC Using DRDO’s Indigenous Laser Weapon
-
 Bangalore’s EtherealX Unveils Razor Crest MK-1 — The World’s First Fully Reusable Medium-Lift Rocket
Bangalore’s EtherealX Unveils Razor Crest MK-1 — The World’s First Fully Reusable Medium-Lift Rocket
-
 IAF Charts Path from Chaos to Clarity: Plans to Replace Mixed Fighter Fleet with Unified Indigenous Powerhouse
IAF Charts Path from Chaos to Clarity: Plans to Replace Mixed Fighter Fleet with Unified Indigenous Powerhouse