World
North Korea, often characterized by its reclusive nature and aggressive military posturing, possesses one of the largest militaries in the world. Recent reports have intensified interest in its military capabilities and international partnerships, particularly in light of accusations that North Korea has dispatched thousands of troops to Russia for potential involvement in the Ukraine conflict. This move marks a significant potential overseas deployment for the North Korean military since the Vietnam War, raising questions about the country's military influence and its historical collaborations.The Scale of North Korea's MilitaryThe Korean People's Army (KPA) stands as a formidable force, boasting an estimated 1.3 million active personnel, making it one of the largest military organizations globally, second only to countries like China and the United States. In addition to active troops, North Korea has around 600,000 reservists and approximately 5.7 million in the Worker/Peasant Red Guards. This massive reserve gives the country a substantial manpower pool, reinforcing its military readiness.The KPA comprises various branches, including the army, air force, navy, and strategic forces equipped with ballistic missiles capable of carrying nuclear warheads. Conscription is mandatory for men aged 17 to 30, ensuring a continuous influx of personnel into the military ranks. The air force consists of about 110,000 personnel, while the navy includes around 60,000.North Korea's Military ArsenalNorth Korea's military strength is not only quantified by troop numbers but also by its arsenal. The country is recognized as one of the nine nations possessing nuclear weapons. Its missile development program has produced a variety of missiles, from short-range tactical options to intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) that can potentially reach the continental United States. Although much of North Korea's conventional military hardware is outdated, including over 6,900 tanks primarily derived from Soviet-era designs, the KPA continues to prioritize modernization and technological advancement.The air force is equipped with more than 400 fighter aircraft, but many of these are aging and may not be combat-ready. Similarly, the Korean People's Army Naval Force (KPANF) has around 470 surface vessels and 70 submarines, which include antiquated models. Recent efforts have been made to enhance naval capabilities, introducing new technologies such as an underwater drone and missile submarines, indicating a strategic pivot towards naval power.Military Partnerships: Historical ContextNorth Korea's military alliances have historically extended beyond its borders, establishing partnerships with various countries. Notably, during the Vietnam War, North Korea dispatched over 1,000 troops to assist North Vietnam, including pilots who engaged U.S. forces. The military cooperation aimed to bolster North Vietnam's efforts against the United States, which saw North Korea utilizing its air force effectively during the conflict.In Egypt, North Korea provided military advisers and personnel during the Yom Kippur War in 1973, reflecting a commitment to support allied nations against perceived threats. This partnership stemmed from a military assistance pact forged by Kim Il Sung and Egypt’s Hosni Mubarak.Similarly, in Libya, North Korea established a military alliance under Muammar Gaddafi, solidified by a ten-year treaty emphasizing mutual defense. The cooperation included training and military exchanges, with North Korea reportedly exploring ways to leverage Libya as a strategic location for its military interests.Syria has long been a close ally, with North Korea playing a crucial role in developing missile technology and chemical weapons. Reports have emerged indicating that North Korean military personnel were actively involved in Syria's civil conflict, although these claims were often met with denials from Pyongyang.The Current Landscape of AlliancesIn recent years, North Korea's partnerships have evolved, particularly with Iran, where both nations, under international sanctions, have engaged in nuclear and missile development collaboration. Reports of technical exchanges and shared resources underscore a growing military relationship that could have profound implications for regional stability.Africa has also seen North Korean involvement, particularly in nations like Zimbabwe and Uganda, where military training and arms sales have been prevalent since the Cold War. However, relations have soured in light of tightening U.N. sanctions, leading to reduced military cooperation in recent years.North Korea's military capabilities and its network of alliances paint a complex picture of a nation striving to assert its influence despite its isolation. The potential deployment of troops to Russia marks a pivotal moment in its military strategy, hinting at a willingness to project power beyond its borders. As the world watches closely, the evolving dynamics of North Korea's military partnerships and capabilities will undoubtedly remain a focal point in international relations and security discussions.This intricate web of military strength, historical collaborations, and current strategic moves underscores the critical role North Korea plays in the geopolitical landscape, raising important questions about the future of global security and stability.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 15:20:46World
On October 23, 2024, the British Army made significant strides in its mechanized capabilities by successfully testing the water-fording capabilities of the Boxer 8x8 armoured vehicle at Instow Beach in North Devon. This trial marked a pivotal moment for the 38.5-tonne vehicle, which showcased its stability and control while navigating through seawater. The test was overseen by the Amphibious Trials and Development Wing (ATDW), confirming that the Boxer is poised to become the primary mechanised infantry vehicle (MIV) for the British Army.The Boxer armoured vehicle is part of a broader effort by the British Army to enhance its operational flexibility and adaptability in various combat scenarios. The £2.8 billion contract secured in 2019 included the acquisition of 523 Boxer vehicles, with production shared between the UK and Germany. This investment is critical to the Mechanised Infantry Vehicle program, which aims to fortify the capabilities of the Army’s Strike Brigades, designed for rapid deployment across diverse terrains. The latest trial underscores the Boxer’s robust amphibious capabilities, allowing it to operate effectively in challenging coastal environments.The Boxer is being delivered in several configurations, such as troop carriers, command vehicles, ambulances, and specialist vehicles. This modularity is a key feature, allowing the Army to adapt the vehicle for various roles. In 2022, the UK government furthered its commitment by exercising an option to order an additional 100 Boxers, bringing the total to 623 units. Among the diverse configurations being produced are infantry carrier vehicles, engineer section vehicles, reconnaissance platforms, and mobile fire support variants, including the Boxer RCH 155, which will serve as a mobile fire platform.The British Army has conducted extensive testing of the Boxer since mid-2023, including mobility assessments over rough terrain and long-distance maneuvers to ensure rapid deployment capabilities. These trials also involve role-specific tests for different variants of the Boxer, such as the infantry carrier and command vehicle. A notable part of the assessment process was a live-fire trial, which aimed to evaluate how well the vehicle can integrate with various weapon systems, from heavy machine guns to anti-tank missiles.The recent fording tests hold critical importance for the Boxer’s operational capabilities. Being able to ford water up to 1.5 meters deep without special preparation enhances the vehicle's mobility, allowing it to traverse rivers and flooded areas effectively. This flexibility is essential in military operations, where encountering water obstacles is a common challenge. The Boxer’s design includes high ground clearance and a robust drive system, ensuring that it maintains traction and stability even in difficult, waterlogged conditions.Moreover, the ability to cross water obstacles without external support reduces vulnerability and speeds up operations in contested areas. It allows the British Army to operate with greater logistical reach, enabling forces to maintain momentum and avoid being bogged down by challenging terrains. The fording capability also ensures the protection of the crew and onboard systems from water ingress, maintaining functionality in critical areas such as the engine and weapon systems.As the British Army continues to integrate the Boxer into its Brigade Combat Teams alongside platforms like the Ajax infantry fighting vehicle and the Challenger 3 main battle tank, it is clear that the Boxer will play a vital role in modernizing the Army’s capabilities. While the Warrior infantry fighting vehicle will remain in service until new capabilities are fully operational, the Boxer is expected to assume an increasingly significant role in future operations.In summary, the successful testing of the Boxer 8x8 armoured vehicle’s water-fording capabilities not only highlights its operational versatility but also enhances the British Army’s readiness to deploy effectively in diverse combat environments. As the Boxer continues to undergo rigorous testing and evaluation, it reaffirms its position as a crucial asset in the British Army’s evolving mechanized force structure.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 15:15:34Space & Technology
In a significant leap for space communications, the French Defence Innovation Agency (AID) has announced the successful launch and operation of the Keraunos satellite, marking what is claimed to be the world's first stable Optical-Laser Infrared (OLI) communication link between a low-orbit nanosatellite and a ground station. This ambitious project was developed in collaboration with two pioneering French space companies, Cailabs and Unseenlabs, and falls under the umbrella of France's Military Programming Law for 2024-2030. The Keraunos satellite is part of a broader initiative, which also includes projects named Toutatis and Yoda, all aimed at enhancing the country's military communication capabilities.In September 2024, a joint announcement highlighted the successful test of this groundbreaking technology, which took place during the summer. The test demonstrated the potential of OLI communications for transferring data at unprecedented speeds, laying the groundwork for future military and commercial applications. While there have been other advancements in the field by NASA, China, and other nations, this test stands out as the first commercial endeavor to successfully implement such a high-speed communication link.To appreciate the implications of this technology, it's essential to understand how OLI communications differ from traditional radio frequency (RF) systems. Both methods are part of the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum, but they occupy distinct frequency ranges and bandwidths. RF systems, which utilize lower energy photons, typically operate within the range of 3 KHz to 300 GHz, while OLI communications, using infrared light, function at significantly higher frequencies (300 GHz to 400 THz). This fundamental difference allows OLI systems to transmit data at much higher speeds—up to 200 Gb/sec, which is a staggering 40 times faster than conventional RF systems. In practical terms, it means that complex data sets, like a full-resolution map of Mars, could be transmitted in nine days using OLI instead of nine weeks with RF.The military implications of OLI communications are profound. Not only does it offer speed, but it also enhances security, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. The narrow beam width of OLI communications makes them more difficult for adversaries to detect and jam. This precision can provide a significant tactical advantage, particularly in military operations where secure and reliable communication channels are paramount. Furthermore, the components of OLI systems tend to be lighter and less voluminous, allowing for easier integration into existing infrastructures without the need for traditional, bulky antennas. This flexibility translates into lower setup costs and improved logistics for military operations.However, OLI systems are not without their limitations. The narrow focus of their communication beam means that any misalignment between the transmitter and receiver can lead to transmission loss. Additionally, environmental factors, such as rain and cloud cover, can disrupt communication links. Fortunately, the innovative technologies developed by Cailabs and Unseenlabs are designed to address these challenges, with adaptive ground receivers capable of mitigating some of the issues associated with atmospheric disturbances.The AID has expressed its commitment to integrating OLI communications into next-generation military satellites, targeting a range of platforms across land, sea, and air. This technology could significantly enhance communication capabilities for European land forces, ensuring resilience in a rapidly evolving battlefield landscape. The successful validation of OLI communications through the Keraunos test marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of space-to-ground communication, setting the stage for broader applications in both military and civilian sectors. As the world embraces this innovative technology, it is likely that OLI will become a cornerstone of future communication infrastructures, complementing existing RF systems without completely replacing them.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 15:12:09India
In a groundbreaking move towards sustainable energy, NTPC, one of India's largest power companies, has teamed up with the Indian Army to establish a Solar Hydrogen-based Microgrid in Chushul, Ladakh. This collaboration is not just about meeting immediate energy needs but represents a significant leap toward enhancing energy security while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.The initiative was formalized through a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed by Mr. Mohit Bhargava, the CEO of NTPC Renewable Energy Ltd. (NTPC REL), and Lt. General Rajinder Dewan of the Indian Army. This partnership is particularly crucial as it aims to provide a reliable power supply of 200 kW, specifically designed to function under the harsh winter conditions of Ladakh, where temperatures can drop to extreme levels. The need for continuous power in such an environment is vital for military operations and local communities.The design and development of this innovative renewable energy project will fall under NTPC REL's expertise, focusing on solar and wind energy solutions that cater to the unique demands of the Indian Army. Utilizing a Build, Own and Operate (BOO) model, NTPC will take responsibility for the entire project lifecycle, from inception to operation. This approach not only ensures a seamless execution of the project but also aligns with NTPC's commitment to sustainable energy practices.This collaboration is a part of India's broader vision for decarbonization and energy independence. By shifting away from traditional diesel generators, which have long been the mainstay in remote and off-grid areas, this project highlights a pivotal transition toward cleaner energy sources. The microgrid system will leverage hydrogen as an energy storage medium, a step that showcases NTPC's commitment to advancing hydrogen technologies.NTPC has a history of engaging in hydrogen-related projects, including hydrogen blending with natural gas and exploring hydrogen-based mobility solutions. By integrating hydrogen technology in this microgrid project, NTPC is positioning itself at the forefront of the renewable energy revolution in India. This initiative not only strengthens military capabilities but also sets a precedent for similar projects in remote locations across the country.In conclusion, the partnership between NTPC and the Indian Army symbolizes a significant stride towards a sustainable future. By harnessing the power of green hydrogen and renewable energy, they are not only addressing immediate power needs but also paving the way for energy independence and resilience in the face of climate change. This innovative project in Ladakh serves as a model for future endeavors that prioritize sustainability while meeting the demands of critical infrastructure.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 15:06:58World
Germany’s Rheinmetall has delivered an additional 20 Marder infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) to Ukraine as it continues its defense against Russian forces. This delivery, completed by the end of Q3 2024, adds to the steady flow of support from Germany and marks a significant milestone: nearly 200 Marder IFVs have now been supplied directly to Ukraine or via the “Ringtausch” (ring exchange) program. This exchange program, coordinated with Germany's allies, allows NATO countries to provide Ukraine with urgently needed resources while backfilling those sent from Bundeswehr reserves. The Marder vehicles sent are primarily the Marder 1A3 model, known for its effectiveness in high-intensity combat.Specifications and Enhancements of the Marder 1A3The Marder 1A3 is a heavily armored IFV designed to transport troops safely into combat zones while providing robust firepower support. Originally developed for the Bundeswehr in the 1970s, the Marder has been progressively modernized. The 1A3 variant features an upgraded armor system for enhanced protection against mines, IEDs, and ballistic threats, making it a reliable choice for both defense and offensive maneuvers. One of the standout features of the Marder 1A3 is its firepower. The vehicle is equipped with a 20mm Rheinmetall MK 20 Rh202 automatic cannon, effective against light armored vehicles, infantry, and low-flying aerial targets. The addition of a laser rangefinder in this model significantly boosts its target accuracy, allowing operators to engage targets efficiently over longer distances. Furthermore, the Marder 1A3’s firing system is stabilized, giving it a critical advantage for firing on the move—a vital feature for Ukraine’s mobile defense strategies.These IFVs also come equipped with a 7.62mm MG3 machine gun mounted as a coaxial weapon to supplement the main cannon. The Marder 1A3 can carry a squad of six soldiers, along with a crew of three (commander, gunner, and driver). Its 600-horsepower engine allows for top speeds of up to 65 km/h (40 mph), ensuring agility across diverse terrains.Supporting Ukraine’s Defense with Renewed VehiclesTo meet urgent battlefield needs, Rheinmetall has been refurbishing these Marders from older Bundeswehr stocks since the spring of 2022. Initially financed by the company, these refurbishments include comprehensive overhauls at Rheinmetall’s facilities in Unterlüß and Kassel, Germany. This process not only ensures that the vehicles are operational but also prepares them for the specific challenges of the Ukrainian front lines, which range from urban combat to open-field engagements.Germany’s funding of the recent batch of Marders, which carries a mid double-digit million euro price tag, underscores its commitment to supporting Ukraine with highly effective land combat vehicles. This delivery also adds to the ring exchange arrangement, where countries willing to provide more direct aid to Ukraine are compensated with German-made systems in return. This cooperative approach has helped NATO allies address logistical and operational gaps in supporting Ukraine.The Legacy of the Marder Amid Modern Combat VehiclesThe Marder has proven to be a versatile and durable IFV, but it is being gradually phased out within Germany’s own military. The Bundeswehr is replacing the Marder with the more advanced Puma IFV, a vehicle with enhanced mobility, firepower, and protection. However, with over 300 Marders still active in Germany, they remain a valuable asset within NATO’s arsenal. While newer systems like the Puma represent the future of German armored capabilities, the Marder continues to serve effectively in both Germany and Ukraine, highlighting its long-standing reputation as a reliable combat vehicle.As Ukraine continues its defensive and offensive operations, these additional Marder 1A3 IFVs will strengthen its armored vehicle fleet and bolster its defense lines. With enhanced combat features and extensive refurbishments tailored to Ukraine's needs, the Marders offer vital support to Ukraine's military at a critical time in the ongoing conflict.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 15:03:08India
In a notable stride for India’s defense sector, Chennai-based TridenTech Engineering Pvt Ltd, in collaboration with partners such as IIT Madras, Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Research and Analysis Laboratory (RAL), and BILVA Technologies, has successfully test-fired an indigenously developed 80mm unguided rocket. This achievement reflects India’s growing emphasis on self-reliance in defense technology, particularly through public-private partnerships that leverage expertise across various fields. The successful test of the 80mm rocket not only strengthens India's defense capabilities but also showcases the country’s potential to develop robust and cost-effective rocket systems in-house.The development of the rocket was a collaborative effort with each partner bringing specialized expertise. TridenTech Engineering Pvt Ltd led the project from initial concept and design to final testing, reflecting the central role that private-sector firms can play in defense innovation. Their work in developing the physical structure, propulsion systems, and stabilizing mechanisms of the rocket has been essential to its functionality.Academic and Industrial CollaborationIIT Madras, under the guidance of Professor Ramakrishna, offered a wealth of academic and research support. Their work focused on rocketry, propulsion systems, and material science, providing essential theoretical backing and simulation data that helped refine the rocket's initial designs. BEL, represented by Abhishek Hegde, added substantial expertise in electronic and defense systems, which proved critical to developing performance-assurance components essential for field reliability.RAL and BILVA Technologies also played key roles, particularly in materials research and control system development. These components ensure the rocket's structural integrity under high-stress launch conditions and its consistency in propulsion, making sure it performs as expected in a range of scenarios. The resulting 80mm unguided rocket offers the Indian military an effective tool for rapid, area-based fire support in battlefield conditions, especially useful in scenarios where quick saturation fire is required.Performance and Operational AdvantagesAlthough an unguided system, the 80mm rocket is designed for battlefield suppression, where its ability to deliver a large payload rapidly is valuable. The recent test fire evaluated basic stability and performance metrics, affirming the design's reliability. These rockets, despite lacking guidance systems, can still cover a defined area effectively, making them an asset for scenarios that do not require pinpoint accuracy. The system has a scalable design that can be adapted or upgraded to meet different combat requirements, which makes it both versatile and economical.The success of this test marks only the beginning, as further trials will continue to refine key performance metrics such as range, accuracy, and payload capacity. The potential to add guidance features in future variants could transform this rocket into a precision weapon, expanding its use cases. A guided version would provide a new level of accuracy and control, ideal for missions where precision targeting is essential.Future OutlookThe upcoming phases of testing will assess various deployment scenarios and may lead to adjustments in payload flexibility, accuracy, and speed of deployment. With a successful track record in testing, this indigenous rocket could eventually enter larger-scale production. Further refinements could even open up the possibility of export, positioning India as a producer of competitive defense technology. This successful demonstration underscores the ability of India’s private sector to meet stringent defense standards, providing the Indian military with options tailored to national defense needs and suited to rapid, cost-effective deployment. Through such indigenous advancements, India is positioning itself for a more self-reliant defense landscape, with private players like TridenTech Engineering setting the stage for innovation in the years to come.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 14:58:51World
German Defence Minister Boris Pistorius has set his sights on a significant upgrade for Germany’s missile capabilities. He plans to acquire 600 new Taurus Neo cruise missiles, an advanced variant of Germany’s existing Taurus missiles. This initiative comes as Ukraine intensifies its appeals for Germany to provide such long-range weapons, which could be instrumental in targeting Russia’s deep-seated military installations. Despite his ambitions, Pistorius faces significant financial hurdles, with no confirmed funding yet to launch the project.Currently, Germany possesses around 600 Taurus missiles in its inventory. These weapons, manufactured by MBDA, can reach over 500 km (311 miles), designed to penetrate high-value targets well behind enemy lines. From the air, these missiles can be deployed by aircraft like the Tornado and F-15, giving the German forces a robust counterstrike option. Each Taurus missile is specifically designed for precision attacks on critical infrastructure: command centers, ammunition depots, airstrips, bridges, and other strategically vital points. The effectiveness of the Taurus is partly due to its bunker-busting capability, which enables it to destroy hardened targets and reduce the adversary’s ability to coordinate or resupply.This capability becomes increasingly critical as Russia continues its missile campaign in Ukraine, often targeting civilian infrastructure. In contrast, Ukraine’s response capacity is limited by the lack of comparable long-range weapons. Pistorius’s interest in the Taurus Neo is thus timely but may take time to materialize. The new variant, Taurus Neo, promises enhanced capabilities and is expected to cost around €2.1 billion for 600 units. Pistorius aims to start securing funding by 2025, initially needing €350 million to get the project moving. If the budget allows, the bulk of the payments would be scheduled to flow starting in 2029, with the first deliveries anticipated that same year.While Germany’s inventory already holds hundreds of Taurus missiles, Ukraine’s persistent requests for long-range weapons have placed the German government in a difficult position. Chancellor Olaf Scholz has repeatedly declined to send Taurus missiles to Ukraine, citing the risk that their extended range might be used to strike within Russian borders, potentially escalating the conflict. The Kremlin has already expressed concern over the possibility of Germany or any Western allies providing Ukraine with such long-range capabilities, warning that such a move could lead to increased "spiraling tension" in the region.Other NATO allies, including Britain and France, have recently supplied Ukraine with Storm Shadow and Scalp missiles—long-range options that Kyiv’s forces have successfully adapted to Soviet-era aircraft. This demonstrates Ukraine's determination and adaptability in modernizing its military arsenal, even if only with limited assistance from the West. But Germany has thus far remained cautious, mindful of the potential consequences of directly arming Ukraine with weapons capable of deep strikes within Russian-held territory.The debate over providing long-range missiles to Ukraine continues to test Germany’s political stance, particularly as both domestic and international pressures grow. Pistorius's push for the Taurus Neo underscores Germany's commitment to bolstering its defense capabilities. However, the significant financial outlay and the complex political implications make this a challenging goal. Whether the project will secure the required budget in 2025 remains uncertain, but it clearly reflects Germany’s intent to keep its defenses well-prepared and modernized, even as geopolitical tensions rise.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 14:54:58India
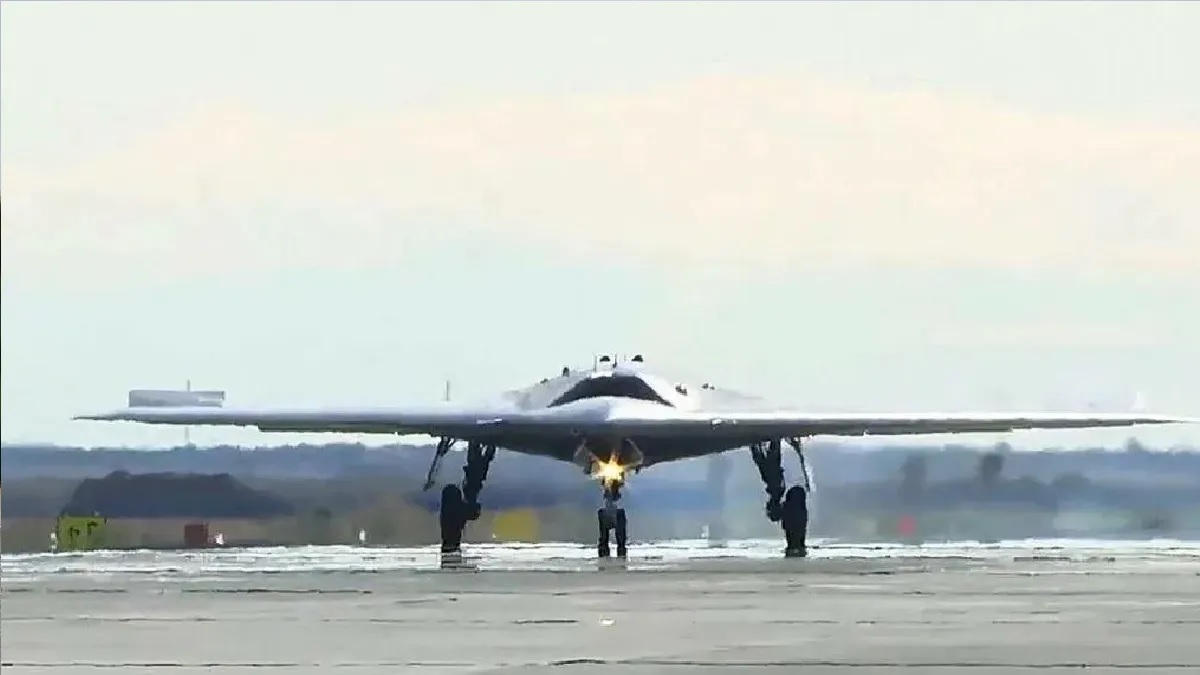
In a major leap forward for India's defense capabilities, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has received approval from the Indian Air Force (IAF) to transform its experimental Stealth Wing Flying Testbed (SWiFT) into a fully operational unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV). Originally designed as a technology demonstrator, SWiFT will now evolve into a 1-ton stealthy UCAV, uniquely tailored for precision mini-bomber roles as well as intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations. This move marks India’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of stealth technology and expanding its aerial combat and surveillance capabilities.The Evolution of SWiFT from Demonstrator to UCAVThe SWiFT project initially aimed to test essential technologies that would eventually feed into larger UCAV programs. Key areas of focus included stealth, aerodynamics, and unmanned flight capabilities, particularly for operations where human involvement is high-risk. By proving these technologies in SWiFT, DRDO planned to pave the way for a new generation of stealthy unmanned systems, an approach now coming to fruition with this recent IAF nod.This progression to a full-scale UCAV not only reflects SWiFT’s technical maturity but also highlights the IAF’s growing emphasis on integrating stealthy unmanned platforms. With this green light, the SWiFT UCAV is expected to join the forefront of India's aerial combat strategy, where its operational flexibility and precision will provide substantial support in high-stakes scenarios.Advanced Features: Stealth, Payload, and Engine PowerThe newly approved SWiFT UCAV is designed to handle a wide array of missions, with advanced features engineered to meet the rigorous demands of modern combat. To maintain its stealth profile, SWiFT will feature an internal weapons bay, a sophisticated element typically reserved for advanced stealth aircraft. This internal bay minimizes radar signatures by housing weapons within the body, rather than external mounting, which would make the aircraft more detectable. This design enables SWiFT to carry precision-guided munitions while staying under radar detection thresholds, allowing it to carry out deep strikes undetected.Powering SWiFT is the Small Turbo Fan Engine (STFE), a compact yet powerful engine previously deployed in the Nirbhay cruise missile. Developed in India, the STFE is celebrated for its reliability and efficiency, which makes it an excellent fit for SWiFT’s stealthy, agile design. This engine provides the necessary thrust to support extended flight operations, facilitating missions that range from precision bombing to extended ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) without compromising stealth or endurance.Combat Versatility and ISR CapabilitiesThe SWiFT UCAV's 1-ton payload capacity further enhances its versatility on the battlefield. As a mini-bomber, it can engage high-value targets in contested territories where manned aircraft might be more vulnerable. This will allow the IAF to execute precise strikes while minimizing human risk. The UCAV’s ISR capabilities are equally impressive: equipped with advanced sensors, it is designed to conduct surveillance operations and provide real-time intelligence. This information is critical for ground commanders, allowing them to make informed decisions in fast-evolving combat scenarios.Stealth UCAVs like SWiFT bring significant strategic advantages, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region, where various military powers are advancing their air defense capabilities. For India, SWiFT represents not just a technological advancement, but also a shift in tactical options, allowing the military to gather vital intelligence or launch attacks even in heavily defended airspace.A Growing Global Trend in Unmanned CombatThe shift towards stealthy UCAVs aligns India with the global trend of incorporating unmanned systems capable of executing "dull, dirty, and dangerous" missions. With advancements in artificial intelligence and autonomous flight, UCAVs are now critical assets in modern warfare, especially in environments where human pilots may face intense hazards. Defense analysts predict that these unmanned systems will be invaluable in future conflicts, allowing militaries to maintain operational flexibility and maximize impact while minimizing personnel exposure to risk.DRDO’s ongoing work on SWiFT, coupled with its successful integration of the STFE engine, is evidence of India’s commitment to leading in unmanned combat systems. The project signifies a strong move towards operational self-reliance and innovation in defense technology, and it signals India's intent to be a key player in the realm of stealth and unmanned aerial capabilities. With SWiFT, India is not only advancing its defense technology but also shaping a new chapter in aerial warfare, where UCAVs will likely play a transformative role.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 14:52:48World
Defense manufacturer X-Bow Systems recently celebrated a successful test launch of its Bolt rocket, a key milestone in the company's efforts to advance solid rocket motor (SRM) technology. This test demonstrated the potential of X-Bow’s SRM propulsion system, which could offer a faster and more scalable alternative to traditional rocket propulsion. It marked a critical step in X-Bow’s broader ambition to provide reliable, rapid, and cost-effective solid rocket solutions for both commercial and military applications.The launch of the Bolt rocket generated crucial data that will support the continued analysis of the SRM’s performance, helping engineers evaluate its effectiveness and reliability in flight conditions. This data is also essential for assessing the feasibility of large-scale SRM production, with applications that could range from commercial satellite deployment to military operations. According to X-Bow’s CEO Jason Hundley, the company’s unique approach enables “unprecedented speed, precision, and scalability” in designing, producing, and testing SRMs.The Advantages of Solid Rocket MotorsUnlike liquid rocket engines, SRMs are designed to combine fuel and oxidizer in a solid-state, which gives them several advantages, particularly in shorter or booster-assisted launches. Because the fuel and oxidizer are premixed, solid rocket motors are simpler and can be stored for long periods without the risk of degradation. This characteristic makes them suitable for military applications and situations where rockets need to be launch-ready with minimal preparation time.While SRMs are excellent for specific missions like launching into Low Earth Orbit (LEO) or providing booster support, they aren’t as efficient for longer missions that require extensive propulsion control. In these situations, liquid rockets, which store fuel and oxidizer separately, are preferred for their controllability and extended burn time. However, liquid-fueled rockets also come with challenges, including higher maintenance needs and the risk of propellant degradation over time.X-Bow’s Innovative Manufacturing ApproachOne of the most striking aspects of X-Bow’s SRM development is its use of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing. The Bolt rocket, for example, is partially manufactured using 3D-printed components for both the motor casing and propellant. This approach allows X-Bow to streamline production while reducing costs and making rapid improvements. Compared to conventional manufacturing methods, which can be time-consuming and costly, additive manufacturing provides the flexibility to upgrade rocket components quickly, keeping pace with evolving technological demands.The ability to manufacture SRMs on-demand could be a game-changer for X-Bow, especially as it continues work on projects like the Mk 72 and Mk 104 solid rocket motors under a contract awarded by the U.S. Navy. This partnership aligns with the Navy’s need for a consistent, reliable supply of SRMs that can be quickly produced and deployed for a variety of missions.Looking Ahead: Commercial and Military ApplicationsThe successful Bolt rocket test points to X-Bow’s capacity to deliver scalable SRM solutions, a capability that could extend the company’s reach into both government and private-sector markets. As solid rocket motor technology continues to evolve, applications are likely to expand beyond traditional uses in military and defense. Commercial satellite launches, rapid payload deployment, and even potential rescue missions could benefit from the efficiency and reliability of SRMs like those developed by X-Bow.In an industry where speed and adaptability are paramount, X-Bow Systems stands out with its innovative approach to rocket design and manufacturing. By leveraging modern technologies and new manufacturing methods, the company is making strides in SRM technology, shaping the future of rapid, cost-effective rocketry.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 14:45:25India
The Indian Air Force's Tejas Mk1A fighter jet, part of India’s ambitious homegrown fighter program, has just gained a significant capability boost with the integration of the Joint Direct Attack Munition-Extended Range (JDAM-ER). Known for its agility and versatility as a light combat aircraft, the Tejas Mk1A now benefits from the precision and range offered by JDAM-ER, underscoring India’s commitment to outfitting its defense systems with top-tier technology. This upgrade puts the Tejas Mk1A squarely in the multirole combat fighter class, capable of smart, long-range precision strikes that were previously achievable only by more expensive, heavier fighters in the IAF’s fleet.What the JDAM-ER Brings to the Tejas Mk1AJDAM-ER kits, which began arriving from the United States following a 2022 order, are designed by Boeing to convert standard unguided bombs into highly accurate, precision-guided munitions. The "ER" in JDAM-ER denotes “Extended Range,” an essential upgrade that stretches the effective range of the munition to over 70 kilometers. This extended reach allows the Tejas Mk1A to strike from a safer distance, minimizing the risk of exposure to enemy defenses and giving pilots a critical advantage in contested airspaces.The JDAM-ER kits utilize GPS guidance, offering pinpoint accuracy and allowing for precise targeting in various weather conditions. This precision is crucial in modern combat, where minimizing collateral damage and maximizing strike effectiveness are key goals. For the Tejas Mk1A, which was initially conceived as a lightweight, multirole fighter, this new capability marks a transition towards performing more demanding strike roles alongside other established aircraft.Complementing the Tejas Mk1A’s Versatile ArsenalJDAM-ER is not the Tejas Mk1A's only smart weapon. The fighter already carries a selection of advanced munitions from partners like Israel and France, enhancing its versatility for diverse combat missions:1. Griffin Laser-Guided Bombs (LGB): Provided by Israel’s Elbit Systems, the Griffin LGB offers high-precision targeting and is lightweight enough for the Tejas Mk1A to carry multiple bombs, enhancing its strike potential on each sortie. With laser guidance, it can hit designated targets with remarkable accuracy, making it suitable for both moving and stationary targets.2. AASM Hammer: Developed by France's Safran Electronics & Defense, the Armement Air-Sol Modulaire (AASM) Hammer adds yet another layer of capability with its modular guidance options. The AASM can be equipped with GPS, laser, or infrared guidance, and offers a range of up to 60 kilometers. This flexibility allows the Tejas Mk1A to perform precision strikes on fixed and moving targets, regardless of the weather or time of day.With JDAM-ER joining this arsenal, the Tejas Mk1A now has the potential to conduct both short and long-range precision strikes, providing the IAF with tactical flexibility in a variety of combat scenarios. The aircraft’s capacity to carry and deploy munitions from multiple global sources – Israel, France, and now the United States – demonstrates India’s strategic defense relationships and its commitment to sourcing top-of-the-line technology.Expanding Tejas Mk1A's Mission CapabilitiesThis JDAM-ER integration is part of India’s broader vision to make the Tejas Mk1A not only a multirole fighter but also an adaptable platform capable of taking on evolving missions. As a lightweight fighter initially designed for air defense and close air support, Tejas Mk1A can now undertake roles that involve deeper strikes into contested areas, previously handled by heavier, legacy platforms like the MiG-21, which the Tejas Mk1A is set to replace.Equipped with precision-guided munitions like JDAM-ER, Griffin LGBs, and AASM Hammer, the Tejas Mk1A is expected to play a frontline role in IAF operations, from rapid-response strikes to more complex, planned assault missions. The aircraft’s evolution from a light multirole fighter to a smart-strike platform reflects India’s commitment to developing a versatile, indigenous fighter fleet equipped to meet the complex demands of modern air warfare.The Tejas Mk1A program showcases not only the expanding technical abilities of Indian aerospace engineering but also highlights the importance of international defense partnerships. Each upgrade, whether sourced from Israel, France, or the United States, enhances the operational flexibility of this indigenous fighter. With JDAM-ER now in its arsenal, the Tejas Mk1A cements its status as a cutting-edge aircraft, capable of executing precision strikes that meet the IAF’s tactical needs for years to come.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-25 14:40:16World
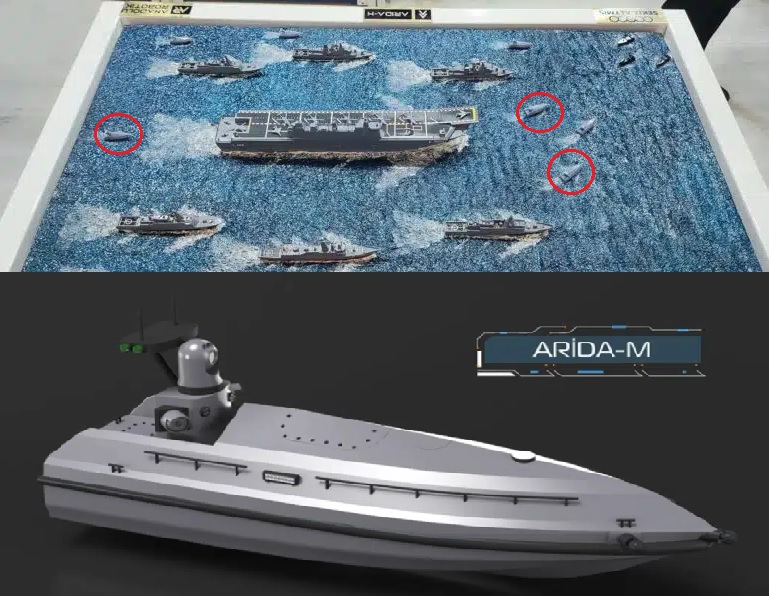
At the SAHA EXPO 2024, Anadolu Robotik showcased a groundbreaking defense innovation: the Arida-M counter-kamikaze unmanned surface vehicle (USV) system. This state-of-the-art system is designed to detect and neutralize kamikaze USVs that target naval assets. As maritime warfare continues to evolve, the Arida-M presents a solution that addresses the growing asymmetric threats faced by naval forces worldwide.The backbone of the Arida-M system is the "Muhafız" USVs, which translates to "Guard" in English. These compact yet powerful vessels are engineered for speed and agility, designed to act as sentinels patrolling the waters around strategic maritime assets such as ports, coastal installations, and naval ships.The "Muhafız" USV: The Heart of Arida-MAt first glance, the Muhafız USVs may appear small—each vessel is just 4.5 meters long and 1.3 meters wide, weighing a mere one ton. But these USVs pack a punch. Despite their compact size, they boast a payload capacity of 30 kilograms, primarily consisting of advanced sensors and communication systems. The speed of the Muhafız USVs is one of their key strengths, capable of reaching over 50 knots, allowing them to intercept fast-moving kamikaze USVs with precision. Propelled by diesel engines and waterjets, they can operate in sea conditions up to sea state 4, making them versatile in various maritime environments.One of the most impressive aspects of the Muhafız USVs is their explosive payload, a critical component in their counter-kamikaze mission. The vessels carry 50 kilograms of explosives mounted at the bow, ready to neutralize enemy USVs through direct impact. Combined with their electro-optical (EO) sensors, which enable threat detection and navigation, these USVs are equipped to swiftly intercept hostile targets.System Architecture: Layers of DefenseThe Arida-M system is not just about intercepting kamikaze USVs—it represents a holistic, multi-layered approach to maritime defense. It integrates a control center, long-range infrared electro-optical sensors, and the Muhafız USVs into a single cohesive system. This structure ensures a rapid, efficient response to potential threats while maintaining full situational awareness.The process begins with radar and EO systems scanning the maritime environment for incoming threats. Once a hostile USV or another potential danger is detected, the system automatically assesses the threat level and deploys the Muhafız USVs. These unmanned vessels, equipped with RF and satellite communication systems, rapidly intercept the hostile USV, using their onboard explosives to neutralize the threat. The Arida-M’s robust architecture can adapt to various threat types, including kamikaze USVs, small boats, and even naval mines, making it a versatile defense solution for diverse operational needs.Testing and PartnershipsThough the Arida-M system is still under development, Anadolu Robotik has made significant strides toward full operational capability. Initial tests using 1/30 scale models have already been conducted, with full-scale sea trials expected to begin soon. The partnership with Turkish defense company Sekiz Altmis has been instrumental, particularly in providing the communication systems that enable real-time coordination and control of the Muhafız USVs. Additionally, the system’s communication capabilities can be enhanced with LTE systems, depending on the customer’s requirements.Responding to an Evolving ThreatThe necessity for such advanced systems became clear during the recent Russia-Ukraine conflict, where the effectiveness of kamikaze USVs was highlighted. These low-cost, high-impact weapons posed a serious threat to even the most advanced naval vessels, raising concerns about how to effectively counter them. Traditional naval defense systems, which rely on guided or unguided weapons, can quickly become overwhelmed during swarm attacks—where multiple hostile USVs or UAVs strike simultaneously.This is where the Arida-M system shines. By incorporating autonomous USVs into the defense strategy, naval forces can augment their existing weapon systems, forming a multi-layered defense. AI-driven USVs like Muhafız are capable of early detection and interception, alleviating the burden on a ship’s primary weapons and significantly improving the chances of neutralizing threats before they reach critical infrastructure.The Future of Naval DefenseWhile the Arida-M system is still in its testing phase, its potential to revolutionize naval defense is undeniable. By combining advanced robotics, communication systems, and explosive payloads, it offers a highly adaptable and scalable solution to counter asymmetric maritime threats. As the system continues to undergo trials and improvements, there’s little doubt that it will be in high demand—not just in Turkey, but among international clients facing similar security challenges.In the evolving arena of naval warfare, where kamikaze USVs and swarm tactics have become prominent, systems like Arida-M represent the next generation of defense. With continued development, this innovative countermeasure has the potential to set new standards in maritime security, providing navies with the tools they need to defend against the growing array of modern threats.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:56:02World
Russia is preparing for a significant boost in its defense spending, marking one of the most notable shifts in its military budget since the Soviet era. With its ongoing military offensive in Ukraine, the Kremlin has prioritized bolstering its military, approving a near 30% rise in defense expenditure for 2025. The budget was passed in its first reading by the State Duma, Russia's lower house of parliament, with an overwhelming majority and only one dissenting vote. The second reading is scheduled for November 14, when the budget will undergo further scrutiny.This defense spending surge reflects Moscow’s strategic choice to pump vast financial resources into the Ukraine conflict, which has stretched beyond initial expectations. Russia has already been churning out large quantities of missiles and drones, while paying substantial salaries to its soldiers deployed on the front lines. The Kremlin's focus on defense has led to increased spending not only on traditional military expenses but also on areas classified under "domestic security," many of which are linked to the ongoing war effort.By 2025, defense spending is projected to reach 13.5 trillion rubles (approximately $145 billion), a figure that surpasses combined expenditures on welfare and education. In fact, around 40% of Russia's total government budget will be dedicated to defense and security, out of a total government expenditure estimated at 41.5 trillion rubles. This immense allocation illustrates how deeply the war has impacted Russia's fiscal priorities.What makes this even more significant is that some military-related expenses, including those categorized as "top secret" by the government, are not part of the official defense budget. These additional expenditures include items like intelligence operations and specialized equipment, further inflating the total resources committed to the conflict. Many of these classified outlays are expected to supplement the war effort, demonstrating Russia's commitment to sustaining its military campaign for the foreseeable future.Moscow's military campaign has progressed notably in eastern Ukraine, with Russian forces making steady advances and seizing towns and villages from outnumbered Ukrainian troops. This territorial progress, however, comes at a high cost—both in terms of lives and resources. The Russian government has framed its military build-up as essential to the success of its war goals, even as critics argue that the heightened defense spending has crowded out essential social programs.Despite promises from the Russian government to increase investment in social welfare and infrastructure, the reality shows a different picture. Planned spending on “national defense” is more than double what is allocated for social policies, such as welfare and public services. This imbalance highlights the economic sacrifices being made to sustain Russia’s military operations. Ordinary Russians are seeing fewer resources directed to social benefits, while the military garners a greater share of the nation's budget.The massive increase in military expenditure reflects the Kremlin’s determination to secure a strategic advantage in Ukraine, even as the international community keeps a close eye on how long Russia can sustain such heavy investments. For now, the new budget provides a clear indication of Moscow's long-term intentions: winning the war in Ukraine, regardless of the economic trade-offs at home.Russia's defense spending in 2025 is set to break records, illustrating the extent to which the Ukraine conflict has reshaped the country's political and economic landscape. As Moscow continues to prioritize military power, the future will likely see continued strain on other sectors of the Russian economy, with no clear end to the war in sight.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:51:59India
In a major leap for India’s defense capabilities, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has given the green light to fully develop the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Stealth Wing Flying Testbed (SWiFT) program. Originally conceived as a technology demonstrator, SWiFT has now transitioned into a full-scale project aimed at producing a 1-ton Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle (UCAV). This UCAV is set to play a vital role in India’s future air combat strategies, with a focus on stealth, intelligence, and precision strike capabilities.The SWiFT program is no longer just a testbed; it’s evolving into a full-fledged unmanned aircraft with serious combat potential. The IAF’s approval signifies a broader strategic push towards enhancing unmanned capabilities in line with modern warfare requirements. The project’s elevation from a mere demonstrator to a sophisticated combat-ready UCAV signals India’s intent to develop unmanned systems that are capable of performing deep strike missions, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations, and combat support tasks—all while evading enemy detection.Stealth and Precision: Core Features of the SWiFT UCAVThe SWiFT UCAV is being designed to carry out a range of high-risk missions, especially in environments that are heavily defended by advanced air defense systems. To achieve this, the platform’s stealth characteristics are critical. One of its standout features will be the internal weapons bay, a common trait in modern stealth aircraft. By carrying weapons like precision-guided bombs inside the fuselage, SWiFT minimizes its radar cross-section, maintaining its low observable profile during combat.This internal configuration is key to ensuring that the UCAV remains hidden from enemy radar while still packing a punch in terms of firepower. The ability to deliver precision-guided munitions without compromising stealth makes SWiFT an ideal platform for penetrating hostile airspace, where traditional manned aircraft could face significant risks.Powered by India’s Own Small Turbo Fan Engine (STFE)At the heart of the SWiFT’s capabilities is the Small Turbo Fan Engine (STFE), which has already proven itself in India’s Nirbhay cruise missile program. The STFE is a compact yet powerful engine, designed to meet the specific demands of unmanned aircraft. Its integration into SWiFT will provide the thrust necessary for the UCAV to perform a range of missions, from deep strikes on enemy infrastructure to extended ISR operations.The engine’s compact size complements the UCAV’s stealth design, ensuring that SWiFT remains agile and can stay undetected while flying at high speeds. The STFE’s proven reliability in the Nirbhay missile makes it a natural choice for SWiFT, offering long endurance and enough power to carry out a variety of missions.A Versatile Combat PlatformThe SWiFT UCAV is not just about stealth—it’s about versatility. With a payload capacity of 1 ton, the aircraft can be configured for different roles depending on the mission. In its mini-bomber configuration, it can strike deep into enemy territory, delivering high-precision attacks on critical targets. In ISR mode, SWiFT will be able to provide real-time intelligence to military commanders, giving them the information they need to make swift, informed decisions on the battlefield.The drone’s ability to switch between offensive and reconnaissance roles makes it a multi-purpose asset for the IAF, capable of operating in complex, contested airspace where manned aircraft might face greater risks. In contested environments, SWiFT will be able to carry out high-risk missions, gather critical intelligence, and perform strikes without endangering the lives of human pilots.Strategic Importance of Stealth UCAVs for the IAFThe development of stealth UCAVs like SWiFT marks a strategic shift in India’s defense strategy, particularly in how it approaches future aerial combat. As air defense systems become more advanced, the need for aircraft that can operate undetected is more critical than ever. The SWiFT’s stealth capabilities give the IAF a significant advantage, especially in situations where survivability and precision are paramount.By investing in stealth unmanned platforms, India is preparing itself for a future where UCAVs will play a key role in not just gathering intelligence but also in delivering strikes deep within enemy lines. The SWiFT program positions India alongside other major military powers that are increasingly relying on unmanned systems to perform complex missions in high-threat environments.The decision to move SWiFT into full-scale development reflects the growing importance of unmanned, stealthy combat aircraft in modern warfare. With its stealth features, versatile mission capabilities, and the reliable STFE engine, SWiFT represents a crucial step forward in India’s quest for an advanced aerial combat fleet that can take on a wide range of threats, all while reducing the risk to human pilots.The Indian Air Force’s decision to fully back the SWiFT program represents a major milestone for India’s defense capabilities. By transitioning the platform from a technology demonstrator to a fully operational UCAV, the DRDO and IAF are embracing a future where stealth, precision, and unmanned systems play an increasingly important role. With the SWiFT UCAV in its arsenal, India will be better equipped to tackle modern threats and maintain a competitive edge in aerial warfare.The SWiFT UCAV is set to be a game-changer, providing India with an indigenous, stealthy, and versatile platform capable of performing a range of critical missions. As the program moves forward, it will likely serve as a cornerstone of India’s future air combat strategies, ensuring that the nation remains at the forefront of unmanned aerial technology.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:49:06World
At the SAHA 2024 defense exhibition in Istanbul, Meteksan Defence showcased its groundbreaking radar system, the MILSAR SAR/MTI. This cutting-edge radar is rapidly becoming a game-changer for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) operations, particularly in the realm of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). With its ability to detect drifting mines in the volatile Black Sea, the MILSAR has demonstrated its operational capabilities in a real-world conflict zone, marking a crucial milestone in military radar technology.Developed under the Turkish Defence Agency (SSB) project, MILSAR is built to provide superior intelligence-gathering for both military and non-military missions. The radar’s sophisticated integration of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Moving Target Indicator (MTI) functionalities sets it apart, enabling it to operate efficiently across various weather conditions, day or night. This is particularly crucial in Türkiye, where cloud cover and other visibility challenges persist for much of the year.One of the highlights of this system is its ability to function in conjunction with drones like the Bayraktar TB2, Aksungur, and ANKA. The MILSAR's multi-mode capability—offering both Stripmap and Spotlight modes—enables wide-area surveillance as well as precise target imaging. In Stripmap mode, the radar can scan vast expanses, providing real-time, high-resolution images with up to 30-centimeter accuracy. This makes it an invaluable tool for missions requiring detailed reconnaissance over large territories. In contrast, Spotlight mode allows for highly focused, pinpoint imaging, crucial for operations that demand precision in identifying specific targets, even in poor visibility conditions such as fog, rain, or nighttime operations.The ability to detect moving targets, whether on land or at sea, is another key feature of MILSAR. Ground Moving Target Indication (GMTI) allows for tracking vehicles or personnel on the ground, while Maritime Moving Target Indication (MMTI) and Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) extend these capabilities to detect and monitor vessels in maritime environments. These functionalities make MILSAR highly versatile, suitable for both military engagements and missions like border surveillance or coastal patrols.Perhaps the most compelling aspect of MILSAR is its role in detecting drifting mines in the Black Sea, a task born out of necessity due to the ongoing conflict between Ukraine and Russia. The radar, installed on UAVs like the Aksungur, has been able to identify and classify drifting mines with remarkable accuracy, even before fully completing its research and development phase. This success underscores the radar’s operational maturity and its critical role in addressing emerging maritime threats. In tandem with electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) systems, MILSAR enhances the UAV's ability to gather intelligence and improve situational awareness for naval forces operating in contested waters.Beyond mine detection, the MILSAR radar system has a wide array of potential applications. Its ability to perform under adverse weather conditions, combined with its low weight (less than 30 kg) and minimal power consumption, makes it a valuable asset for a variety of UAV platforms. Its lightweight design also opens doors for integration into drones of various sizes, offering significant flexibility for both military and civilian applications. Countries like Pakistan, with its Shahpar-1 and Shahpar-2 UAVs, could benefit immensely from MILSAR’s capabilities, especially in challenging environments where visibility is often poor, and real-time intelligence is critical.Meteksan Defence is not stopping here. The company continues to innovate and enhance MILSAR's capabilities. One of the upcoming features in development is "Change Detection," a tool that leverages artificial intelligence to compare current and historical images, identifying changes in terrain or objects. This feature could be crucial for missions such as detecting improvised explosive devices (IEDs) or monitoring unauthorized human activity. Additionally, MILSAR’s capacity to assist in non-military operations, such as forest fire monitoring, shows its versatility in addressing diverse threats.As seen at SAHA 2024, MILSAR’s future looks bright, with its proven success in the Black Sea only scratching the surface of its potential. By bridging the gap between radar and electro-optical technologies, Meteksan’s innovation is set to redefine ISR operations across the globe.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:45:24World
In a significant move to bolster India’s growing space economy, the Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the establishment of a ₹1,000 crore venture capital (VC) fund specifically aimed at nurturing the space sector. This initiative is seen as a crucial step in fostering innovation, creating jobs, and solidifying India’s position in the global space industry.The VC fund, which will be overseen by IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center), is part of the government’s broader reforms introduced in 2020 to encourage private sector participation in space activities. With the space economy expected to grow from its current valuation of ₹8.4 billion to ₹44 billion by 2033, the government is laying the foundation for sustained growth through this timely financial intervention.A Catalyst for Space StartupsThe fund will have a deployment period of up to five years, offering critical financial backing to startups across the space value chain. The Cabinet has outlined that the fund will deploy between ₹150-250 crore annually, based on the investment opportunities and funding requirements of the sector. The aim is to ensure that budding companies in areas like satellite manufacturing, space exploration, and advanced space technologies can access the capital needed to expand and innovate.A key focus of the fund is to prevent the loss of talent and innovation to other countries by supporting Indian startups at various stages of their development. Investments will range from ₹10 crore to ₹60 crore, with the lower end supporting early-stage companies and the higher end reserved for more established, late-growth startups. According to government estimates, the fund will support around 40 startups, providing the much-needed infusion of capital that will help them scale operations and contribute to national space capabilities.Driving Innovation and Economic GrowthThe approval of this fund comes at a time when India’s space sector is witnessing unprecedented growth. Over 250 space startups have emerged in recent years, creating a vibrant innovation ecosystem. However, many of these startups face funding challenges, which often leads to the migration of talent and businesses to countries with more robust financial support systems.By setting up this government-backed VC fund, the Cabinet aims to not only bridge this financial gap but also boost investor confidence. The fund’s capital infusion will act as a multiplier, attracting private investment and creating a ripple effect that will benefit the entire industry. This approach is designed to accelerate the development of space technologies, increase India’s global competitiveness in space exploration, and ensure that Indian companies remain at the forefront of this rapidly evolving sector.The Bigger Picture: India’s Space AmbitionsIndia’s space ambitions have grown exponentially, with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) making significant strides in satellite launches, deep space missions, and collaborative international projects. This VC fund aligns with the government’s long-term vision to transform India into a global space hub, tapping into the country’s vast talent pool and innovation potential.Moreover, the government’s focus on space startups is not just about scientific exploration but also about economic growth. The space sector offers immense opportunities for job creation, advanced technological research, and new business models. By investing in these startups, the government is effectively laying the groundwork for a future where India can compete with leading spacefaring nations like the US, Russia, and China.In summary, the Cabinet’s approval of the ₹1,000 crore venture capital fund marks a pivotal moment for India’s space industry. It demonstrates the government’s commitment to fostering a robust and competitive space ecosystem, one that is capable of driving technological advancements, boosting the economy, and creating high-value jobs. With this fund, India is positioning itself for a bright future in the space sector, one that promises to be full of exciting innovations and breakthroughs.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:41:13India
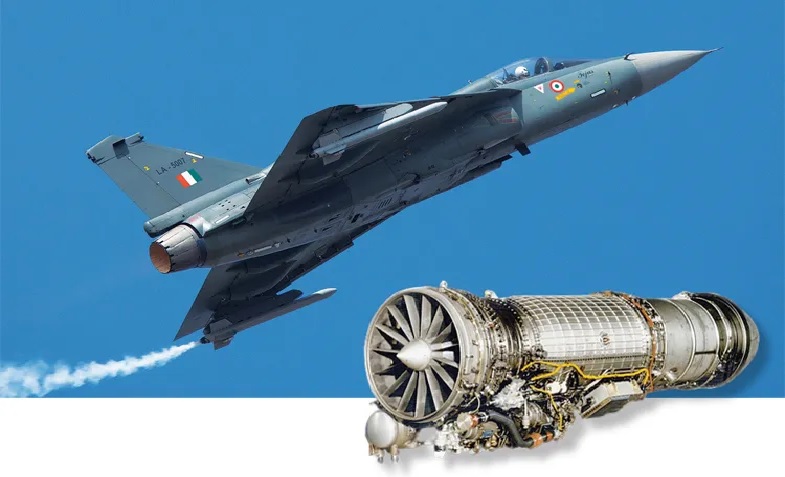
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has opted to take a long-term view in its partnership with GE Aerospace, waiving contractual penalties despite a significant delay in the delivery of F-404 engines, crucial to powering India’s Tejas Mk1A fighter jets. Originally set under a 2021 contract, GE was scheduled to supply 99 F-404 engines to HAL, but the company has been hampered by global supply chain disruptions, resulting in a delay of nearly 10 months.The F-404 engines are vital for the Tejas Mk1A, a fighter jet developed indigenously for the Indian Air Force. The aircraft is key to India's defense modernization efforts, and the delays have naturally caused concern. However, instead of taking punitive measures, HAL has chosen a more strategic route. Sources close to the situation report that HAL's decision to waive penalties stems from its focus on fostering a long-term partnership with GE Aerospace, which could bear fruit in future projects, particularly the next-generation Tejas MkII.The delay in engine deliveries highlights the broader challenges facing the global aerospace industry. The COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with supply chain bottlenecks, has severely impacted the availability of critical raw materials and components, leading to delays in production. GE Aerospace, like many others in the industry, has been struggling to keep up with its commitments due to these external factors. While frustrating, HAL appears to have acknowledged the wider context and is betting on future cooperation rather than immediate financial recourse.What makes this partnership particularly important for HAL is the potential for collaboration beyond the F-404 engines. The Tejas Mk1A program is not the only one relying on GE's technological prowess. HAL is eyeing a much more advanced partnership when it comes to the F-414 engines, which will be the powerplant for the future Tejas MkII. These engines are expected to provide even greater thrust and performance, necessary for the next phase of India's indigenous fighter jet program.In fact, one of HAL's strategic aims is to secure a transfer of technology (ToT) agreement with GE for the local manufacturing of the F-414 engines in India. Such an arrangement would be a significant step in enhancing India's defense self-reliance and advancing its capabilities in aerospace manufacturing. HAL's decision to forgo penalties could play a crucial role in ensuring these negotiations remain on track, as penalizing GE might have soured the relationship just when HAL needs GE's cooperation the most.Despite the delays, GE Aerospace has assured HAL that deliveries of the F-404 engines will begin soon, possibly within this month. The company has also committed to an accelerated production schedule to make up for the lost time. If all goes according to plan, GE aims to ramp up production to meet both the Tejas Mk1A and Tejas MkII programs by 2026, which is when demand for engines will be at its peak.The Tejas Mk1A itself is a lightweight, multi-role fighter designed to replace India's aging fleet of MiG-21s. It features numerous upgrades over its predecessor, the Tejas Mk1, including an advanced radar system, mid-air refueling capabilities, and a higher payload capacity. Powered by the GE F-404 engines, it is expected to significantly enhance the Indian Air Force’s operational capabilities. The Mk1A’s successful deployment is crucial to India's defense strategy, and HAL’s focus on securing a stable supply chain of engines reflects just how critical this project is.By opting for a more collaborative approach, HAL is looking beyond immediate issues and laying the groundwork for a robust partnership with GE Aerospace. This strategy is aimed not just at delivering the F-404 engines but also at ensuring that the more advanced F-414 engines, and possibly future technologies, can be co-developed or manufactured locally in India. Such a move would be a game-changer for the Indian defense industry, furthering the nation's goals of self-reliance under the "Make in India" initiative.In summary, HAL's decision to forgo penalties in favor of long-term cooperation with GE Aerospace may turn out to be a strategic masterstroke. By focusing on the bigger picture, HAL ensures that India’s fighter jet programs remain on course, while simultaneously strengthening its ties with a key global aerospace player.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:37:13World
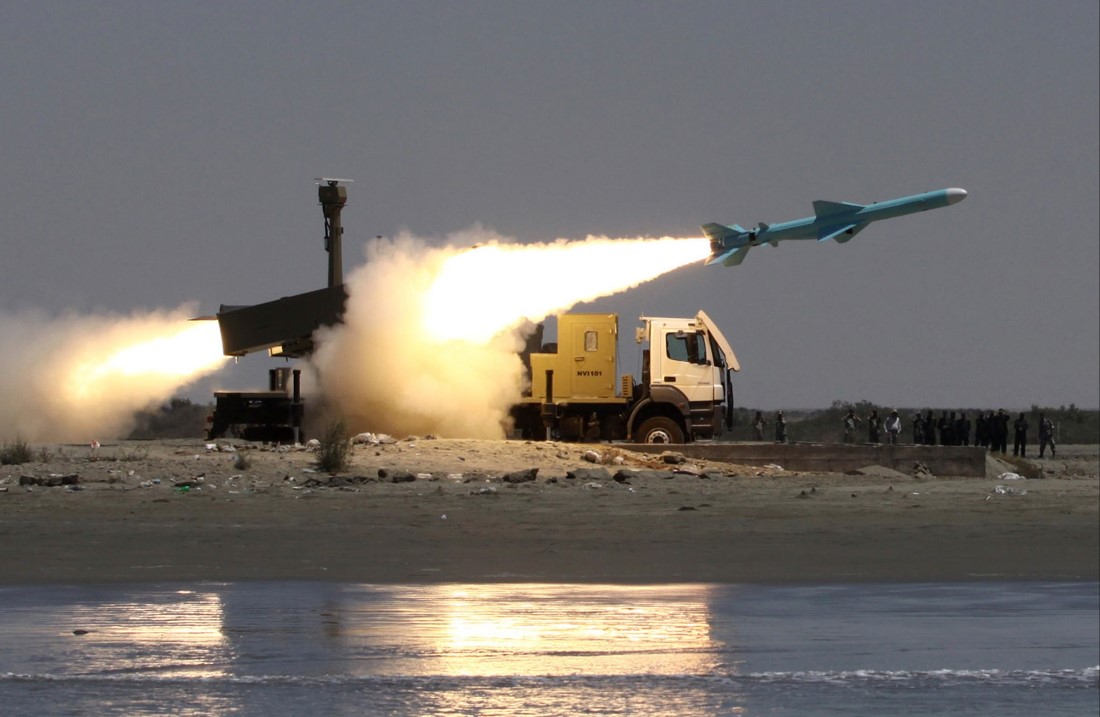
Iran has unveiled its latest naval weapon, the CM-300 anti-ship cruise missile, marking a significant leap in its maritime defense capabilities. This advanced missile, designed to target medium and large warships, is a clear demonstration of Iran’s focus on fortifying its coastal defense and extending its military influence over vital maritime zones such as the Persian Gulf and the Strait of Hormuz. With its long-range capabilities and versatile launch systems, the CM-300 represents a growing challenge to the naval forces of potential adversaries in the region.The CM-300’s standout feature is its impressive range, reaching up to 300 kilometers. This allows Iran to strike targets far beyond its coastline, giving it an edge in any naval confrontation. Such reach ensures that Iran can effectively control key maritime chokepoints and assert its dominance over strategic waterways. Given the rising tensions in the region, particularly around the Strait of Hormuz—a critical passage for global oil shipments—this missile offers Iran a powerful tool to deter foreign navies.One of the CM-300’s most important characteristics is its flexibility. It can be launched from a variety of platforms, including both naval warships and land-based trucks. This dual-launch capability gives Iran the tactical advantage of quick deployment in various combat scenarios. Whether defending its waters or launching an offensive strike, Iran can rapidly mobilize these missiles, enhancing its readiness in the face of naval threats. The mobility provided by truck-mounted launchers also ensures that the missile can be positioned strategically along Iran’s coastline, ready to respond to potential incursions.The technology behind the CM-300 is equally formidable. Equipped with an advanced radar guidance system and inertial navigation, the missile can accurately track and destroy moving targets with minimal risk of interception. This high level of precision, combined with the missile's speed of 0.8 to 0.9 Mach, ensures that large naval targets like destroyers or even aircraft carriers are within its strike range. The CM-300's ability to evade detection and engage such significant targets demonstrates Iran’s growing technological prowess in missile development.Additionally, the missile carries a powerful 165-kilogram warhead, which is designed to incapacitate or destroy large vessels with a single strike. Its propulsion system, featuring a solid rocket booster for initial launch followed by a turbojet engine for sustained flight, enables it to maintain high-speed, long-range operations. The missile itself is over six meters long and weighs around 770 kilograms, making it a formidable asset in Iran’s naval arsenal.One of the CM-300’s most vital components is its integrated radar and command system. Radar vehicles scan the seas for potential threats and relay this data to the missile's launch platforms, ensuring that the missile is directed precisely at its intended target. The mobile launch trucks, which are used to deploy the missile, offer the Iranian military the flexibility to rapidly position and withdraw these assets in response to changing battlefield conditions. Pre-launch testing equipment further ensures that each missile is combat-ready, reducing the likelihood of malfunctions during critical operations.This missile’s introduction is part of a broader strategy by Iran to modernize its defense systems, especially its naval capabilities. By developing weapons like the CM-300, Iran is not only bolstering its ability to defend its shores but also projecting its power over key regional waterways. In the broader context of Middle Eastern geopolitics, the CM-300 serves as a deterrent to foreign naval forces, signaling that Iran is prepared to defend its maritime interests with cutting-edge technology.The CM-300 anti-ship missile marks a significant shift in regional naval power. With the capability to strike at long distances and destroy large enemy ships, it provides Iran with a strategic advantage that could alter the balance of power in the Persian Gulf. As Iran continues to upgrade its military capabilities, the CM-300 stands out as a symbol of its commitment to defending its waters and maintaining control over one of the world's most crucial maritime routes.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:33:11World
In a bold move to strengthen the Pentagon’s counter-China strategy, Saronic Technologies has revealed its largest and most advanced unmanned vessel yet: the 24-foot Corsair. This third autonomous surface vessel (ASV) from the Texas-based defense tech startup is the latest addition to the US Navy’s growing fleet of unmanned systems designed to maintain maritime dominance and deter potential adversaries like China. The unveiling of Corsair comes as tensions continue to escalate in the Indo-Pacific region, with the US and its allies closely monitoring China's military expansion, especially in the South China Sea and near Taiwan. The Pentagon’s Replicator program, focused on acquiring swarms of low-cost, expendable unmanned platforms, aims to counter the increasing threat of a possible invasion of Taiwan. Saronic’s Corsair is a key component of this program, which envisions deploying thousands of these autonomous vessels to form a hybrid fleet with traditional manned warships.Saronic Technologies has rapidly expanded its capabilities in the ASV market, with Corsair following the release of the smaller 14-foot Cutlass and 6-foot Spyglass earlier in the year. However, Corsair stands out not just because of its size but its extensive capabilities. The vessel can operate autonomously for over 1,000 nautical miles (1,852 kilometers) without needing to refuel, at a blistering top speed of over 35 knots (65+ kilometers per hour). This endurance and speed make it ideal for long-range, high-speed missions across vast oceanic distances.One of the standout features of Corsair is its payload capacity. It can carry up to 1,000 pounds (453 kilograms) of equipment, allowing it to perform a variety of missions. These range from maritime domain awareness, which involves monitoring and securing critical waterways, to delivering kinetic (physical) or non-kinetic (cyber or electronic) effects in combat situations. Its versatility in mission roles underscores how crucial unmanned platforms like Corsair are becoming for modern naval warfare.What sets Corsair apart from traditional vessels is its cost-effective scalability. Saronic has integrated advanced artificial intelligence, software, and hardware systems into the design, which enables the company to produce the vessel at a fraction of the cost of manned counterparts. The streamlined production process means Saronic can manufacture hundreds, or even thousands, of these vessels quickly to meet the rising demand. According to Saronic’s co-founder and CEO, Dino Mavrookas, the company is already working on five Corsair prototypes, with full-scale production set to ramp up next year.“We’re not just building one or two of these,” Mavrookas emphasized. “We’re building hundreds and hundreds of Corsairs, with the ability to scale that number into the thousands. This will give the Navy and our allies the ability to deploy large numbers of these vessels to create a significant strategic advantage.”Corsair’s design is also geared towards ease of deployment. As an "attritable" asset, meaning it's built to be cost-efficient enough that losing some in combat won’t cripple operations, Corsair can be delivered to the battlefield in large numbers. Despite its expendability, Saronic has not compromised on reliability or performance. With the integration of state-of-the-art technologies, the platform is designed to be both durable and flexible, capable of performing in a wide range of maritime conditions.In line with the Pentagon’s vision of a hybrid fleet, Corsair is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of naval warfare. By combining traditional manned warships with autonomous platforms, the US Navy aims to create a force that is not only more resilient but also more unpredictable—an essential factor in countering China's growing naval strength. The combination of manned and unmanned systems allows for a more distributed and agile naval presence, which could significantly impact potential conflicts, particularly in the contested waters around Taiwan and the South China Sea.The Corsair is just the latest example of how unmanned systems are revolutionizing modern warfare. As the US continues to invest heavily in autonomous technologies, Saronic Technologies is positioning itself as a leader in the field. With its plans to produce these vessels at scale, the company is poised to meet the growing demand for unmanned platforms, not just for the US Navy but for allied forces as well.Saronic’s ambitious production goals, coupled with Corsair’s advanced capabilities, signal a major shift in how naval forces will operate in the future. As geopolitical tensions continue to rise, particularly with China, platforms like Corsair will be crucial in maintaining the strategic balance and deterring potential threats. In the years to come, it’s clear that autonomous vessels like Corsair will be at the heart of the US military’s efforts to adapt to an increasingly complex and contested maritime environment.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:26:05Space & Technology
China has officially stepped into the high-stakes race to explore Venus, joining India and the United States in an ambitious effort to unravel the mysteries of Earth's closest planetary neighbor. The country's newly revealed plans, outlined in its National Space Science Medium- and Long-Term Development Plan (2024–2050), include a Venus atmospheric sample return mission—a move that signals China's growing determination to be a leader in space exploration by mid-century.Unveiled on October 15, 2024, by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the China National Space Administration (CNSA), and the China Manned Space Engineering Office (CMSEO), the roadmap details China's strategic approach to space exploration over the next few decades. The plan highlights the nation's intention to deepen its space science capabilities, culminating in the collection of atmospheric samples from Venus—an achievement that would mark a major milestone in planetary exploration.### China's Venus AmbitionThe mission to Venus is part of a broader, three-phase strategy that will guide China's space efforts up until 2050. The most exciting aspect of this plan is the second phase (2028–2035), where China will focus on sending a spacecraft to Venus to collect atmospheric samples and bring them back to Earth. This is no small feat, given Venus’s hostile environment, with scorching surface temperatures that can melt lead and thick clouds of sulfuric acid that blanket the planet. Yet China’s plan showcases the technological innovation it has cultivated over the years.The Venus sample return mission may involve some advanced engineering: a spacecraft would descend into the planet’s atmosphere, potentially using a balloon to collect gases and particles. The ascent vehicle would then launch from the Venusian atmosphere to an orbiter that would ferry the precious cargo back to Earth. If successful, it would be the first mission to return atmospheric samples from another planet, giving scientists unprecedented access to Venus’s secrets.### Why Venus MattersVenus has long been a subject of fascination due to its similarities to Earth in size and composition, but it presents stark differences in terms of climate and habitability. The planet is often referred to as Earth’s "evil twin" because of its extreme conditions. Yet, recent discoveries have renewed interest in the possibility of life, particularly the detection of phosphine gas in Venus's upper atmosphere. This gas, on Earth, is associated with biological activity, sparking debates about whether microbial life could exist in Venus’s clouds. China’s sample return mission aims to delve deeper into these questions. By capturing and analyzing samples from Venus’s atmosphere, scientists hope to better understand the planet's climate, its potential for habitability, and the broader mechanisms at work in planetary evolution. Understanding Venus could also shed light on the future of Earth’s climate, as both planets may have shared similar conditions early in their histories before diverging dramatically.### A Global Race to VenusChina’s ambitious plan comes at a time when other space powers are also preparing for Venus missions. India has already greenlit its Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM), which is set to launch in 2028, aiming to study the planet’s atmosphere, surface, and interactions with solar winds. Meanwhile, NASA is gearing up for its VERITAS mission, which will focus on mapping Venus’s surface and uncovering its geological past, possibly solving the mystery of whether Venus once had conditions suitable for life.China’s involvement adds a competitive edge to the global race to Venus. The U.S. has long been a leader in planetary exploration, and India's recent strides in space technology—demonstrated by its successful missions to Mars and the Moon—make it a formidable competitor. With China now joining this race, the competition is heating up, and the stakes are high. The insights gained from Venus could revolutionize our understanding of planetary systems, including our own.### China’s Broader Space AmbitionsThe Venus mission is just one part of China’s expansive vision for space exploration. In the first phase of the roadmap (2024–2027), China is focusing on completing crewed lunar landings and maintaining operations on its Tiangong space station. The third phase (2036–2050) will target even more advanced missions, possibly including explorations beyond our solar system. China’s long-term goal is to solidify its position as a dominant force in space, challenging the current dominance of the U.S. and emerging players like India and the European Space Agency.China’s determination to explore Venus underscores its growing ambitions to lead the next era of space exploration. As the global competition intensifies, missions like this could pave the way for remarkable scientific breakthroughs, positioning China as a key player in humanity's quest to explore the cosmos.### The Road AheadBy committing to a Venus atmospheric sample return mission, China is not just following in the footsteps of other space-faring nations—it is setting the stage for a new era of planetary exploration. The mission’s success could answer some of the most profound questions about the origins and evolution of planets, including our own. And as China, India, and the United States race to unlock Venus’s secrets, the world watches with anticipation, eager to see what the next great chapter in space exploration will bring.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:22:58India
In a major step towards self-reliance in defense manufacturing, India's "Make in India" initiative is set to reach a new milestone with the complete indigenization of AK-203 rifles by December 2024. The breakthrough comes from the Small Arms Factory (SAF) in Kanpur, which has successfully developed a metal that meets Russia’s stringent GOST (Gosstandart) standards—an achievement that will allow the full production of AK-203 rifles on Indian soil.The AK-203, a modern variant of the legendary Kalashnikov assault rifle, has long been regarded as one of the most reliable and effective small arms in the world. It combines the battle-proven design of the AK-47 with updated features such as improved accuracy, lighter weight, and compatibility with modern attachments. With its rugged design and capacity to withstand harsh conditions, the AK-203 has been chosen as the future standard issue rifle for the Indian Armed Forces. Over 770,000 of these rifles are planned to be produced, and the move towards complete indigenization is critical to ensuring supply chain security and reducing dependence on foreign components.For years, while the assembly of AK-203 rifles has taken place in India at the Indo-Russian Rifles Private Limited (IRRPL) facility in Amethi, key components, particularly metal parts, were imported from Russia. This limited the degree to which the rifles could be truly labeled as “Made in India.” The recent breakthrough in Kanpur changes that, making it possible for all components, including barrels and springs, to be produced domestically. Surendra Pati Yadav, General Manager of SAF, described the achievement as a "Eureka moment" for his team, marking the end of their long quest to develop metal that meets the exacting GOST standards required for the AK-203.The GOST certification is essential because it ensures the high quality and durability of Russian-designed firearms. Russian weapons, known for their robustness and reliability, have historically set a global benchmark in military hardware. Replicating the exact specifications of these materials was no easy task, requiring meticulous research, testing, and multiple adjustments before achieving success. This metal, now developed entirely in India, will be used in all future production runs of the AK-203 rifles, starting in December 2024.This development not only marks a major technical achievement for India’s defense sector but also significantly boosts the country’s strategic autonomy. By eliminating the need for imported materials, India is taking a step closer to building a self-sustaining defense industry—one that can supply its armed forces with the equipment they need without being reliant on foreign sources. This is especially important in a geopolitical landscape where supply chains can easily be disrupted by international tensions or sanctions.The rifles themselves are designed to meet the needs of modern warfare, with features like a collapsible stock for better maneuverability, rails for mounting sights or scopes, and enhanced accuracy over its predecessors. The AK-203 can fire 7.62x39mm rounds at a rate of 600 rounds per minute and has an effective range of around 300 meters, making it suitable for a wide range of combat scenarios.The IRRPL facility in Amethi, which is a joint venture between India's Advanced Weapons and Equipment India Limited (AWEIL) and Russia's Kalashnikov Concern, will continue to be at the center of this production effort. The plant is expected to meet the growing demands of the Indian Army, as well as potentially providing exports in the future. The complete indigenization of the AK-203 rifles will ensure a more stable and cost-effective supply of these critical weapons.While the first batches of AK-203 rifles produced in India did include some Russian components, this will no longer be the case moving forward. Yadav emphasized that by December 2024, the rifles will be entirely Indian-made, from the smallest springs to the most crucial metal parts. The capability to manufacture all components locally signifies a historic moment for India's defense manufacturing capabilities and represents a key success in the government's push for self-reliance in critical military hardware.As the Indian Armed Forces gear up to receive these fully indigenized rifles, the benefits of this project will extend beyond just military readiness. The domestic production of such a high-volume order will likely spur further developments in India’s defense industrial base, creating jobs, fostering technological innovation, and enhancing the country’s ability to produce more advanced weaponry in the future.The AK-203 project stands as a testament to India’s growing capabilities in defense manufacturing and engineering. The success of this initiative will be watched closely not only in India but also around the world, as it could serve as a model for other nations looking to reduce their dependence on foreign suppliers and bolster their domestic defense industries.By December 2024, India will not just be assembling AK-203 rifles—it will be producing them entirely from materials and components made within its borders, symbolizing a significant leap forward in its defense self-sufficiency goals.
Read More → Posted on 2024-10-24 15:17:54Search
Top Trending
-
 Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
-
 China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
-
 Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
-
 India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
-
 China’s Super Radar Detects Mysterious Plasma Bubble Over Giza Pyramids
China’s Super Radar Detects Mysterious Plasma Bubble Over Giza Pyramids
-
 India's Indigenous Kaveri Engine Program with New Focus on Thrust and Performance
India's Indigenous Kaveri Engine Program with New Focus on Thrust and Performance
-
 Isro Draws up Ambitious Plan for 2024, says will Launch at Least 12 Missions
Isro Draws up Ambitious Plan for 2024, says will Launch at Least 12 Missions
-
 Successful Hypersonic Missile Test by U.S. Department of Defense
Successful Hypersonic Missile Test by U.S. Department of Defense
Top Trending in 4 Days
-
 South Korea’s K239 Chunmoo Rocket Artillery Spotted in Saudi Arabia
South Korea’s K239 Chunmoo Rocket Artillery Spotted in Saudi Arabia
-
 Russia Launches Massive Missile and Drone Attacks on Ukraine's infrastructure
Russia Launches Massive Missile and Drone Attacks on Ukraine's infrastructure
-
 Russia Fires Intercontinental Ballistic Missile at Ukraine
Russia Fires Intercontinental Ballistic Missile at Ukraine
-
 Peru to Acquire South Korea's K2 Black Panther Tanks
Peru to Acquire South Korea's K2 Black Panther Tanks
-
 Advancing Space Tech for Defense: ICEYE Leads Finland's F-35 Industrial Participation Program
Advancing Space Tech for Defense: ICEYE Leads Finland's F-35 Industrial Participation Program
-
 Russia Reports Interception of 44 Ukrainian Drones Including 20 over Novgorod region
Russia Reports Interception of 44 Ukrainian Drones Including 20 over Novgorod region
-
 Ukraine Scales Up Neptune Missile Production: Over 100 Units Manufactured with Enhanced Range
Ukraine Scales Up Neptune Missile Production: Over 100 Units Manufactured with Enhanced Range
-
 India-Israel AI-Enhanced Weaponry Makes Combat Debut in Gaza
India-Israel AI-Enhanced Weaponry Makes Combat Debut in Gaza