India
India’s defense landscape is undergoing rapid transformation, and at the heart of this modernization is the push for indigenous loitering munitions. Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently witnessed the unveiling of the Nagastra-3, an advanced loitering munition system being developed under the Medium Range Precision Kill System (MRPKS). This system is designed to provide the Indian Armed Forces with a versatile, high-endurance, precision-strike capability over a range exceeding 100 kilometers. Technical Specifications and Capabilities The Nagastra-3 is a next-generation loitering munition built to offer long-range reconnaissance and strike capabilities against high-value targets. The system's defining features include: Range: Over 100 km, allowing deep-strike operations beyond enemy lines. Endurance: More than 5 hours, enabling prolonged surveillance and target acquisition before committing to a strike. Guidance System: GPS and Inertial Navigation System (INS) for precise targeting, coupled with Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven target identification. Warhead: Designed for precision strikes, the Nagastra-3 can carry a high-explosive (HE) warhead, anti-tank shaped charge, or fragmentation warhead based on mission requirements. Launch Platform: It is a canister-launched system, deployable from mobile platforms, providing rapid launch capability. Operational Altitude: Capable of flying at medium altitudes to evade enemy radar detection. Stealth and Survivability: Built with a low radar cross-section (RCS) and capable of performing evasive maneuvers to avoid interception. Data Link: Secure, encrypted communication with ground control stations for real-time video feed and manual target confirmation. Role in Modern Warfare The introduction of the Nagastra-3 into India’s arsenal strengthens its ability to conduct asymmetric warfare. Loitering munitions like the Nagastra-3 bridge the gap between traditional cruise missiles and UAV-based airstrikes. The capability to hover over a battlefield, select targets in real time, and execute precision strikes makes it an invaluable asset for: Neutralizing Enemy Air Defenses: The ability to engage high-value air defense systems and radar installations before a full-scale aerial attack. Tactical Battlefield Support: Providing real-time reconnaissance and engaging enemy troop concentrations, armored formations, or command centers. Urban Warfare and Counter-Terror Operations: Reducing collateral damage by allowing precise engagement of targets in densely populated areas. Strategic Implications The Nagastra-3's development aligns with India's push for self-reliance under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative. The loitering munition not only reduces India's dependence on imported weaponry but also positions the country as a key player in unmanned aerial warfare. With regional threats evolving, the ability to conduct precise, time-sensitive strikes without risking pilot lives enhances India’s strategic deterrence capabilities. Future Prospects Given its promising features, the Nagastra-3 is likely to undergo further refinements, including AI-assisted autonomous targeting, swarming capabilities, and enhanced electronic warfare countermeasures. The successful integration of this system into India's military framework will mark a significant leap in the nation’s offensive and defensive combat strategies. As the world moves towards network-centric warfare, loitering munitions like the Nagastra-3 will play a pivotal role in shaping future battlefields, giving India a critical edge in modern warfare scenarios.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-30 15:15:04India
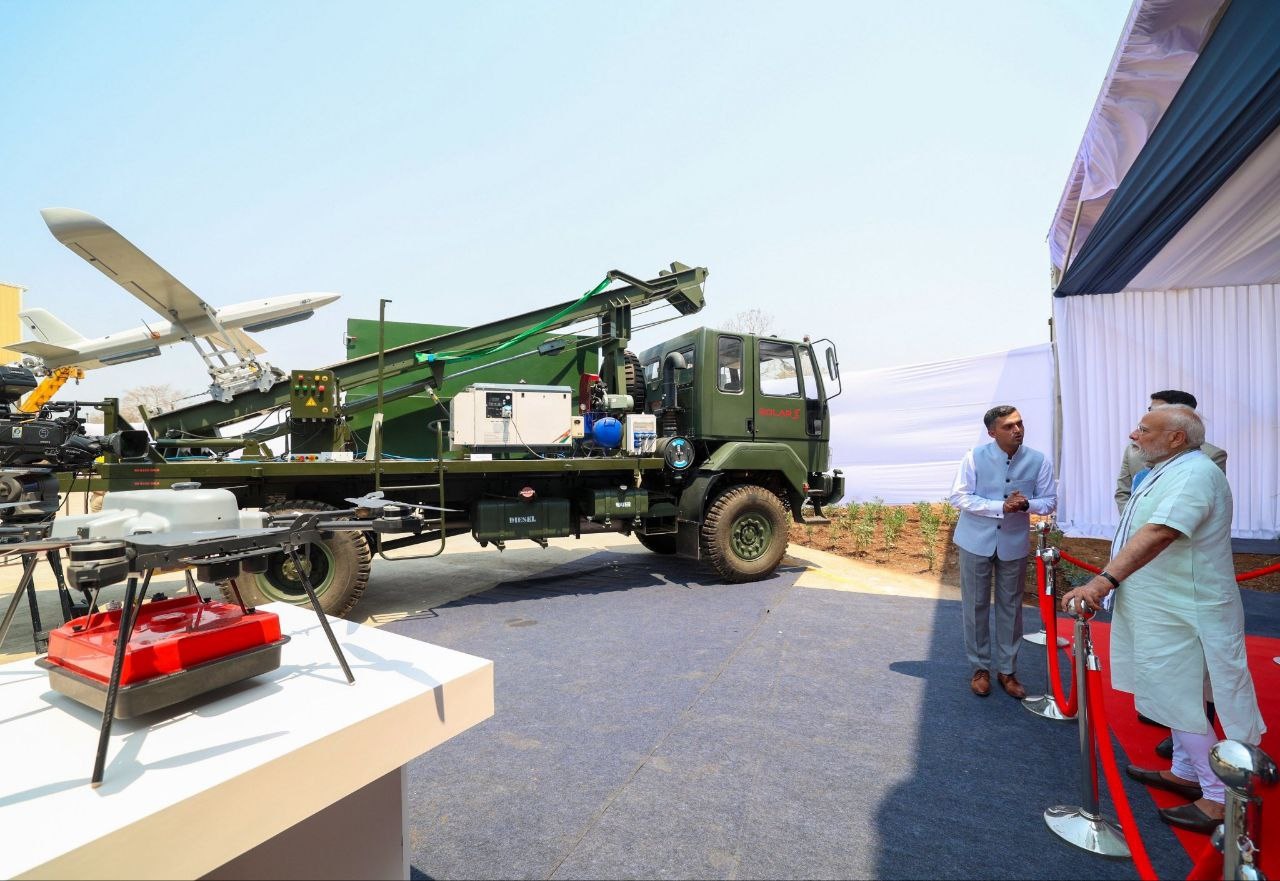
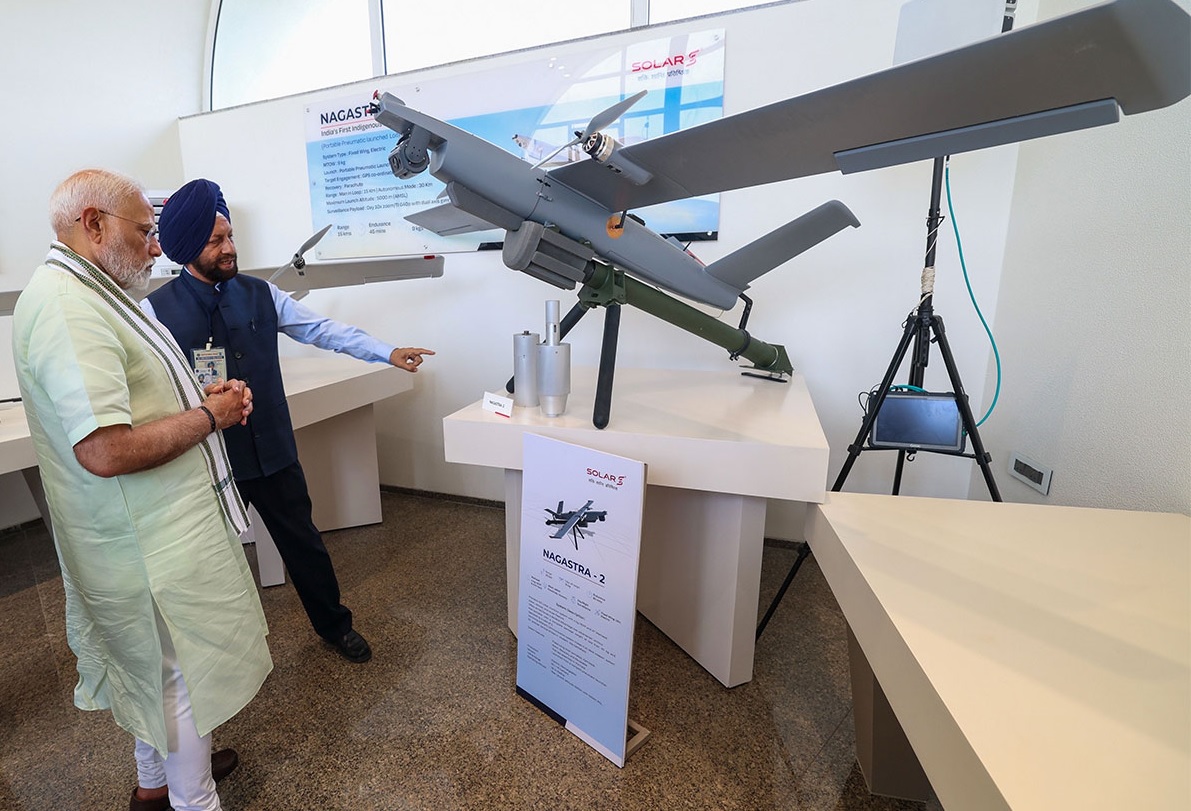
Prime Minister Narendra Modi today inaugurated Solar Defence's expansive 1,080-acre facility in Nagpur, marking a significant advancement in India's defense capabilities. This state-of-the-art complex encompasses a Loitering Munition Test Range and a dedicated runway for testing Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) and High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Loitering Munition Test Range The Loitering Munition Test Range is designed to rigorously evaluate systems like the indigenous Nagastra series. The Nagastra-1, developed by Solar Industries in collaboration with Z-Motion Autonomous Systems Pvt Ltd, is a man-portable, fixed-wing electric UAV weighing approximately 9 kg. It offers a range of 15 km in manual mode and up to 30 km autonomously, with an endurance of 30 minutes. Equipped with day and night surveillance cameras and a 1 kg high-explosive fragmenting warhead, the Nagastra-1 boasts a GPS-enabled precision strike capability with an accuracy of up to 2 meters. A notable feature is its parachute recovery mechanism, allowing for mission abortion and reuse—a significant advantage over many existing systems. MALE/HALE UAV Test Runway The facility also includes a specialized runway for testing MALE and HALE UAVs. Solar Industries is developing MALE UAVs equipped with both surveillance and attack capabilities, aligning with the global recognition of drones as critical force multipliers in modern warfare. The development of these UAVs is part of the Ministry of Defence’s Indigenously Designed, Developed, and Manufactured (IDDM) category, emphasizing India's commitment to self-reliance in defense technology. The inauguration of this facility underscores India's strategic push towards enhancing its defense manufacturing capabilities and reducing reliance on foreign technology. By investing in indigenous development and testing infrastructure, India aims to position itself as a global leader in autonomous weaponized systems
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-30 15:10:40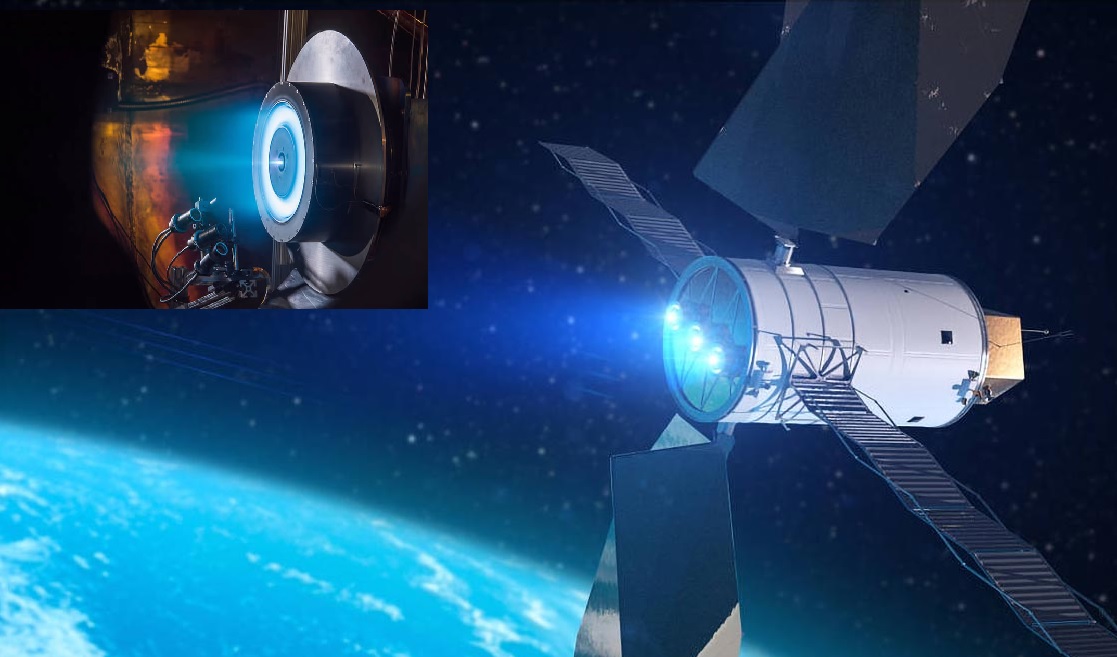
ISRO Successfully Completed 1,000-Hour Life Test of Stationary Plasma Thruster for Future Satellites
Space & Technology
On March 27, 2025, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully completed a 1,000-hour life test on its 300mN Stationary Plasma Thruster, a key component of the Electric Propulsion System (EPS) designed for future satellites. This achievement marks a significant step towards replacing traditional chemical propulsion with electric propulsion in ISRO's upcoming satellite missions. Advancing Satellite Propulsion Technology The Electric Propulsion System (EPS) is set to revolutionize ISRO’s satellite technology by enabling satellites to rely entirely on electric propulsion for orbit raising and station-keeping. Unlike conventional chemical thrusters, EPS offers higher efficiency and significant mass savings, allowing for increased payload capacity, particularly in communication satellites. The key advantage of this system lies in its Specific Impulse (Isp), which is a measure of propulsion efficiency. The electric thrusters boast an Isp that is at least six times higher than conventional chemical propulsion, making them far more fuel-efficient. Key Specifications of ISRO's 300mN Stationary Plasma Thruster Thrust Output: 300mN (millinewtons) Power Consumption: 5.4 kW Propellant Used: Xenon Vacuum Chamber Testing: Simulated space environment Erosion Monitoring: Periodic assessment of electrode liner wear Specific Impulse: At least 6 times higher than conventional propulsion Critical Testing and Performance Validation The 1,000-hour life test was conducted at full power levels in a vacuum chamber replicating space conditions. A crucial aspect of the test was monitoring electrode liner erosion, which helps predict the long-term durability of the thruster. The data obtained is essential for refining ISRO's future electric propulsion designs and ensuring their reliability in space operations. Future Deployment in ISRO Satellites With this successful test, ISRO plans to integrate and validate the Electric Propulsion System in its upcoming Technology Demonstration Satellite (TDS-01). The system will play a key role in orbit-raising maneuvers to the Geostationary Orbit (GEO), proving its capability before full-scale deployment in future missions. This milestone not only strengthens India's space capabilities but also aligns ISRO with global advancements in electric propulsion technology, paving the way for more efficient, cost-effective, and longer-lasting spacecraft.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-30 15:02:42World
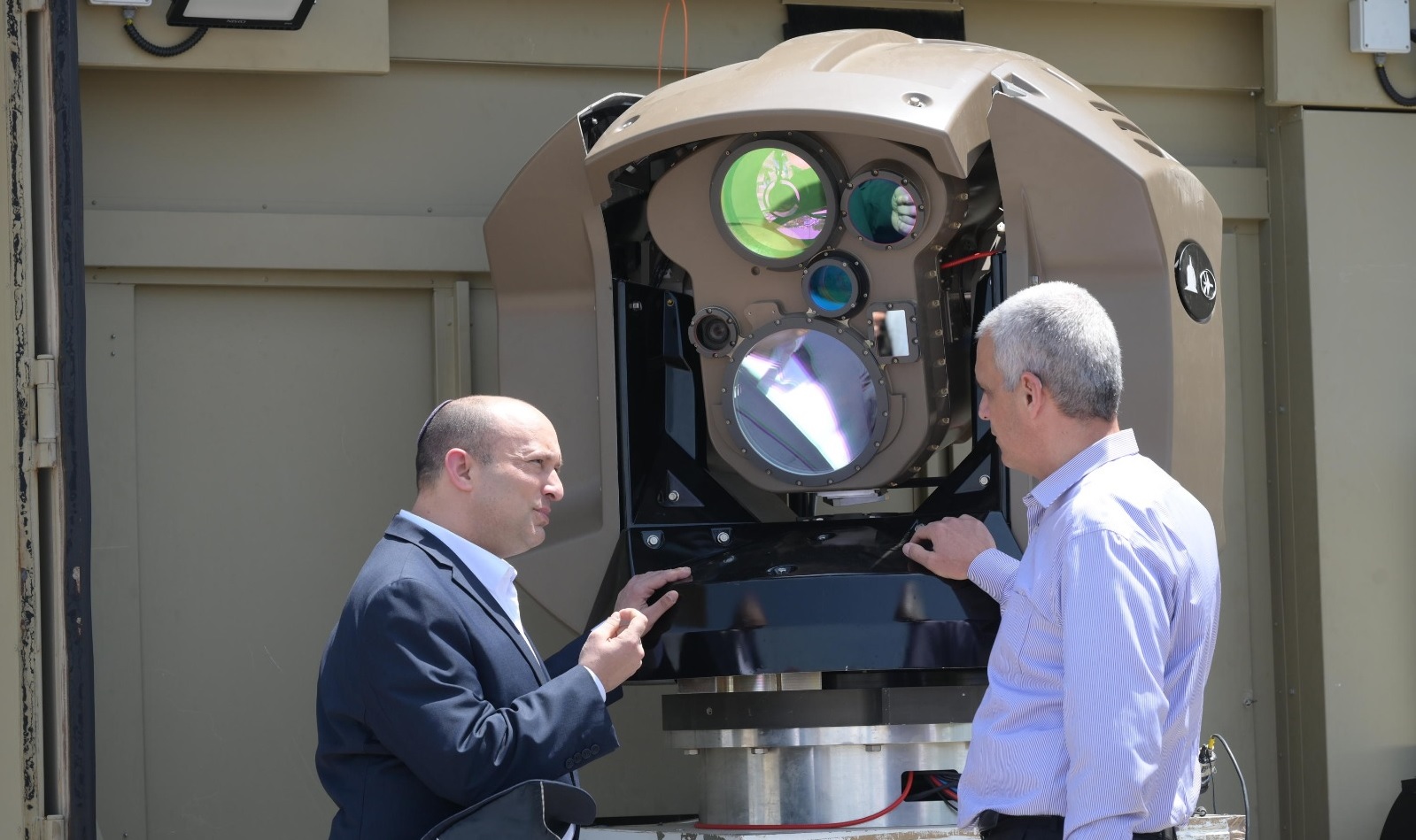
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems has officially announced that its Iron Beam, a high-energy laser air defense weapon, will become operational in 2025. This marks a major breakthrough in missile defense technology, as the system is set to provide an affordable and highly effective countermeasure against aerial threats. A Game-Changer in Air Defense Iron Beam is designed to work alongside Israel’s Iron Dome and other missile defense systems, offering a cost-effective solution for intercepting enemy rockets, drones, and mortar shells. Unlike traditional missile-based defenses, which rely on costly interceptors, Iron Beam uses directed energy to destroy threats at the speed of light. Rafael CEO Yoav Turgeman emphasized that the Iron Beam will significantly reduce operational costs while increasing interception efficiency. Currently, each Iron Dome interceptor costs around $30,000, whereas the Iron Beam’s laser-based approach is far cheaper, requiring only electricity to function. Key Specifications of Iron Beam Technology: High-energy laser-based air defense system Purpose: Neutralizes rockets, drones, and mortar shells Speed: Engages targets at the speed of light Cost Advantage: Far cheaper than missile-based interceptions Operational Range: Estimated to be several kilometers Integration: Works in conjunction with Iron Dome and other air defense systems Revolutionizing Air Defense Iron Beam’s operational deployment in 2025 will mark a global milestone in laser defense technology. With its instantaneous response time and lower operational costs, it is expected to transform Israel’s air defense strategy while setting a precedent for the future of military laser weapons worldwide.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-30 14:58:48World
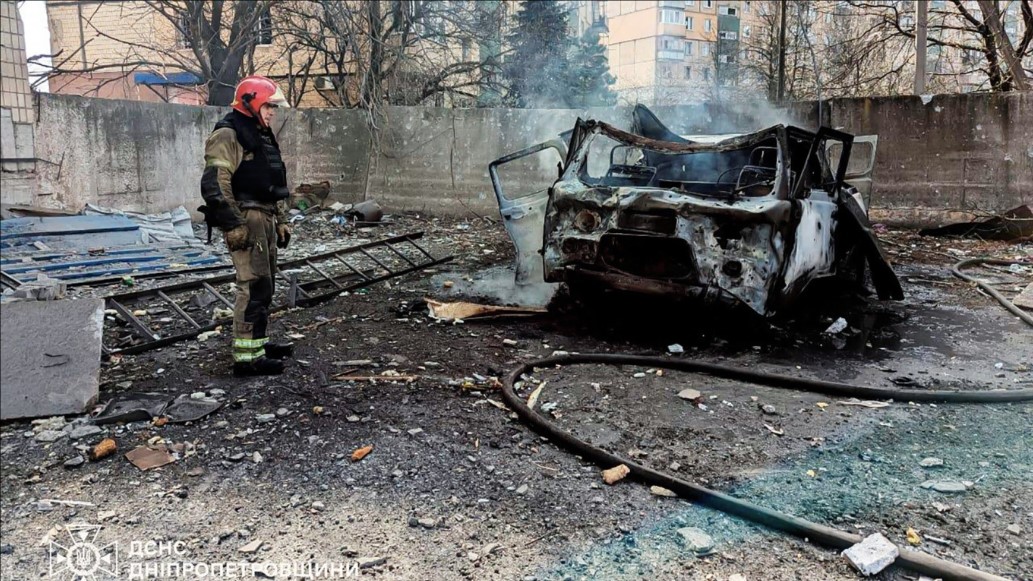
In a recent development, Russian forces have seized control of two additional villages in eastern Ukraine, marking a significant advancement in the ongoing conflict. The Russian Defense Ministry announced the capture of Lozova in the Kharkiv region and Krasnoye (known as Sontsivka in Ukraine) in the Donetsk region. The latter's proximity to the strategic hub of Kurakhove underscores the tactical importance of these gains. This progression aligns with Russia's intensified efforts to secure more territory in eastern Ukraine, particularly in the Donetsk and Zaporizhzhia regions. Ukrainian officials and military analysts anticipate a renewed Russian offensive in the coming weeks, aiming to exert pressure on Ukraine and strengthen Russia's position in potential ceasefire negotiations. President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has highlighted increased Russian troop movements, suggesting possible attacks in northeastern regions like Sumy and Kharkiv. The capture of these villages not only signifies territorial expansion but also serves as a strategic maneuver to encircle key resource hubs, potentially disrupting Ukrainian supply lines and fortifications. As both nations prepare for prolonged engagement, the international community remains watchful of the evolving dynamics and their broader geopolitical implications. Lockheed Martin Delivers First F-16 Block 70 Fighter Jet to Taiwan On March 28, Lockheed Martin hosted a formal ceremony at its Greenville facility in South Carolina to present the first serial production F-16D Fighting Falcon Block 70 aircraft to Taiwan. The event was attended by representatives from Lockheed Martin, the Taiwanese government, and members of the United States Congress. Taiwan becomes the fourth recipient of the F-16 Block 70/72 variant, following Bahrain, Slovakia, and Bulgaria. Under a government-to-government agreement signed in 2019, Taiwan ordered 66 new F-16C/D Block 70 aircraft, making it the largest customer of this configuration to date. Lockheed Martin has previously completed deliveries to Bahrain, and production is ongoing for orders from Slovakia and Bulgaria. The Taiwanese Air Force currently operates a fleet of upgraded F-16AM/BM aircraft brought to the F-16V standard, which will be complemented by the new-build Block 70 jets. Taiwan had initially expressed interest in acquiring F-35A fighters, but the United States declined to approve the sale, citing concerns over escalating tensions with mainland China. As a result, Taiwan proceeded with the advanced F-16 variant, which offers modern avionics, improved radar systems, and enhanced survivability despite being a fourth-generation platform. The delivery schedule was initially planned for completion by 2026, but delays in relocating the F-16 production line from Fort Worth to Greenville have pushed the timeline back by at least two years. Taiwan’s new aircraft are expected to replace aging Mirage 2000-5 and F-5 Tiger II fighters, strengthening its defensive capabilities. Lockheed Martin has received confirmed orders for 188 F-16 Block 70/72 aircraft. In addition to current customers, future sales may include countries such as Morocco, Jordan, Turkey, the Philippines, Vietnam, and Colombia, as interest in the proven platform continues to grow. In October 2024, Taiwan’s Defence Minister announced plans for further combat aircraft acquisitions from the United States. However, due to political sensitivities, approval for more advanced platforms like the F-35 remains unlikely in the near term.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-30 14:55:17World
On March 28, 2025, Lockheed Martin hosted a ceremony at its Greenville, South Carolina facility to commemorate the delivery of the first F-16D Fighting Falcon Block 70 aircraft to Taiwan. This event marks a significant milestone in Taiwan's ongoing efforts to modernize its air force and bolster its defensive capabilities. Taiwan's Acquisition and Strategic Implications In 2019, Taiwan entered into a government-to-government agreement with the United States to procure 66 new F-16C/D Block 70 aircraft, positioning Taiwan as the largest customer of this advanced configuration. This acquisition is part of Taiwan's broader strategy to replace its aging fleet of Mirage 2000-5 and F-5 Tiger II fighters, thereby enhancing its ability to safeguard its airspace amid regional security challenges. Delays and Adjusted Delivery Timeline The initial delivery schedule aimed for completion by 2026. However, delays associated with relocating the F-16 production line from Fort Worth, Texas, to Greenville have extended the timeline by at least two years. Despite these setbacks, the delivery of the first F-16 Block 70 underscores the commitment to strengthening Taiwan's defense capabilities. Advanced Features of the F-16 Block 70 The F-16 Block 70/72 represents the most advanced iteration of the Fighting Falcon, incorporating several state-of-the-art features: Advanced Radar Systems: Equipped with Northrop Grumman's APG-83 Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar, the Block 70 offers fifth-generation radar capabilities, providing pilots with enhanced situational awareness and all-weather targeting precision. Enhanced Battlespace Awareness: The aircraft features a high-resolution Center Pedestal Display (CPD), delivering critical tactical imagery and allowing pilots to fully exploit data from the AESA radar and targeting systems. Extended Structural Life: With an extended structural life of 12,000 hours, the Block 70 surpasses previous F-16 models by more than 50%, ensuring a reliable service life of at least 40 years without the need for extensive structural repairs. Automatic Ground Collision Avoidance System (Auto GCAS): This life-saving system is designed to prevent controlled flight into terrain incidents, a leading cause of aircraft losses and pilot fatalities. Global Interest and Future Prospects Beyond Taiwan, Lockheed Martin has secured orders for the F-16 Block 70/72 from countries including Bahrain, Slovakia, and Bulgaria, with confirmed orders totaling 188 aircraft. Additional nations such as Morocco, Jordan, Turkey, the Philippines, Vietnam, and Colombia have also expressed interest in this advanced platform, reflecting its growing global appeal. The delivery of the first F-16 Block 70 to Taiwan signifies a pivotal advancement in the island's defense modernization efforts. Despite initial delays, the incorporation of these advanced fighters is set to significantly enhance Taiwan's air defense capabilities, contributing to regional stability and security.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-30 14:50:30India
The Indian Air Force (IAF) has embarked on a significant modernization program for its frontline Su-30MKI fleet, integrating advanced indigenous and foreign technologies to counter emerging aerial threats. Among the key upgrades are the Virupaksha Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar, Astra MkIII beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM), and enhanced networking capabilities through airborne warning and control system (AWACS) support. These enhancements, according to IAF officials, could give the upgraded Su-30MKI a decisive edge over China's new-generation J-35A stealth fighter. Understanding the Upgrades: The Virupaksha AESA Radar The heart of the Su-30MKI's modernization is the integration of the Virupaksha AESA radar, developed by India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). This radar marks a generational leap over the older Russian-origin N011M Bars radar, offering: Greater Detection Range: Estimated to exceed 300 km for large aircraft and over 200 km for smaller targets like fighter jets. High-Resolution Tracking: Capable of simultaneously tracking multiple targets in air-to-air and air-to-ground modes, enhancing situational awareness. Electronic Warfare (EW) Capability: Equipped with advanced jamming resistance and passive detection features to counter stealth aircraft. Multi-Mode Operations: Supports synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging, moving target tracking, and terrain mapping, allowing strike missions to be more precise. This AESA radar significantly enhances the Su-30MKI’s ability to detect and engage enemy aircraft before they can close in for a dogfight, countering the advantages of stealth designs like the J-35A. Astra MkIII BVRAAM: India's Long-Range Punch The Astra MkIII is the next-generation air-to-air missile under development, designed to extend engagement ranges and enhance the lethality of IAF’s Su-30MKIs. It features: Ramjet Propulsion: Ensures a sustained high-speed trajectory, unlike traditional rocket-powered missiles. Range of Over 300 km: This allows Indian pilots to engage adversaries beyond the effective range of China’s PL-15 missile, which is estimated to have a range of 200-250 km. Advanced Guidance System: Equipped with dual-mode seekers and high anti-jamming resistance, ensuring effectiveness even in contested environments. No-Escape Zone: Expanded due to its superior energy retention at terminal engagement phases, increasing kill probability. When paired with the Virupaksha AESA radar, the Astra MkIII provides an enormous advantage, allowing Su-30MKIs to engage J-35A aircraft before they are detected, negating their stealth advantage. AWACS Network: Force Multiplier in Air Combat India’s airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) platforms, such as the DRDO-developed Netra and upcoming AEW&C Block-2, play a crucial role in countering stealth threats. These aircraft provide: Early Detection of Low-Observable Aircraft: Operating at high altitudes, they can spot stealth fighters using low-frequency radar bands and data fusion techniques. Beyond-Line-of-Sight Targeting: AWACS can provide targeting information to Su-30MKIs, allowing them to fire Astra MkIII missiles without switching on their own radar, reducing their electromagnetic signature. Network-Centric Warfare Capabilities: Enhancing coordinated responses, real-time data sharing, and increasing the survivability of combat aircraft. With AWACS support, the Su-30MKI gains the ability to engage adversaries while remaining hidden, a critical tactic against stealth aircraft like the J-35A. Comparing the Upgraded Su-30MKI and the J-35A Feature Upgraded Su-30MKI J-35A Radar Virupaksha AESA (300+ km detection range) Unknown AESA (est. 200-250 km) Missiles Astra MkIII (300+ km) PL-15 (~200-250 km) Stealth Moderate RCS Reduction Measures Advanced Stealth Features Maneuverability Thrust Vectoring (TVN) No TVN Sensor Fusion Integrated with AWACS & EW suite Advanced but lacks confirmed network capabilities The J-35A benefits from stealth characteristics, making it difficult to detect using conventional radars. However, the upgraded Su-30MKI, with its high-power AESA radar and AWACS support, can detect and engage it beyond visual range. Moreover, the Astra MkIII missile, with a superior engagement range compared to China’s PL-15, gives the Su-30MKI an advantage in a long-range missile duel. Tactical Advantages in a Combat Scenario Long-Range Detection and Engagement: The Su-30MKI can leverage AWACS data to detect the J-35A early and launch Astra MkIII before the Chinese fighter gets within its own missile range. Electronic Warfare Superiority: With onboard EW capabilities and jamming-resistant radars, the Su-30MKI can disrupt the J-35A’s fire-control radar, reducing the effectiveness of its PL-15 missiles. Supermaneuverability in Close Combat: If combat shifts to within-visual-range (WVR), the Su-30MKI's thrust vectoring and superior agility give it an edge over the J-35A. Saturation Strikes with AWACS Coordination: Multiple Su-30MKIs can engage J-35As simultaneously using networked targeting, overwhelming China’s fighter in a contested airspace. An Effective Counter to the J-35A The Su-30MKI’s modernization with the Virupaksha AESA radar, Astra MkIII missile, and AWACS support significantly enhances its ability to counter stealth threats. While the J-35A’s low-observability and modern avionics make it a formidable adversary, the combination of long-range detection, superior missile technology, and network-centric operations gives the IAF a crucial advantage. As India continues to refine its air combat doctrine and invest in indigenous technologies, the upgraded Su-30MKI will remain a potent force capable of challenging even next-generation adversaries like the J-35A. This development ensures that the IAF maintains air superiority in contested environments, safeguarding India's airspace against emerging threats.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:33:02World
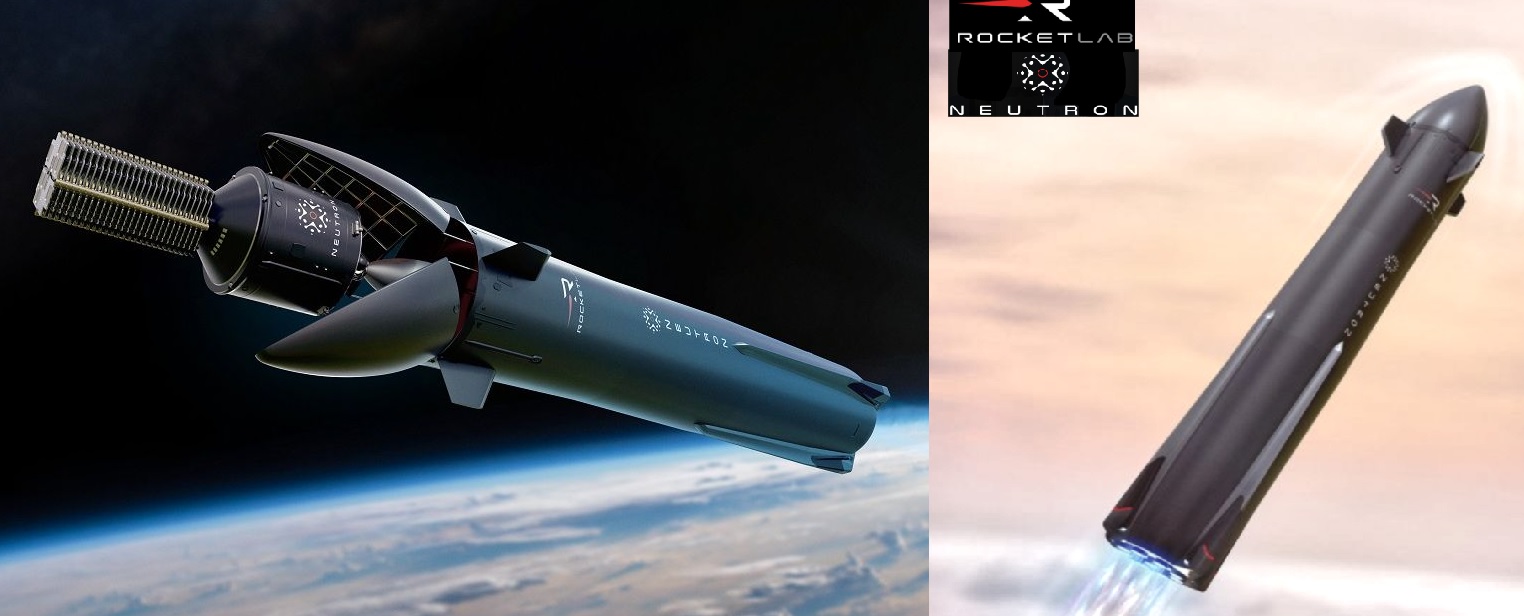
Rocket Lab has been officially selected by the United States Space Force (USSF) to compete for national security launch contracts under the National Security Space Launch (NSSL) Phase 3 program. This decision marks a major milestone for the company, as its upcoming Neutron rocket will play a crucial role in delivering sensitive defense payloads to space in the coming years. The NSSL Phase 3, Lane 1, is a five-year contract running through June 2029, with a total funding ceiling of $5.6 billion. It aims to integrate lower-cost launch providers into the U.S. defense ecosystem, enhancing America’s ability to deploy critical national security assets in space. The contract includes a minimum of 30 missions, which will be distributed among the selected providers. Rocket Lab is one of only five companies chosen, highlighting its growing influence in the aerospace industry. What is the Neutron Rocket? Neutron is Rocket Lab’s next-generation reusable launch vehicle, specifically designed for medium-lift missions. Unlike the company’s smaller Electron rocket, which primarily launches small satellites, Neutron is built to carry payloads of up to 13,000 kg to low Earth orbit (LEO). It is made of carbon composite materials, ensuring a lightweight yet robust structure. One of Neutron’s standout features is its reusability, which reduces launch costs and improves efficiency. The rocket's first stage is designed for rapid refurbishment and reuse, making it a cost-effective option for both commercial and government missions. Key Specifications of Neutron Rocket Payload Capacity: Up to 13,000 kg to LEO Material: Carbon composite for high strength and low weight Launch Site: Launch Complex 3, Wallops Island, Virginia, USA Reusability: First stage designed for multiple reuses Fairing System: Advanced design for payload protection and flexibility First Launch: Expected in the second half of 2025 Rocket Lab’s Role in the U.S. Space Force Program As part of its selection for the NSSL Phase 3 program, Rocket Lab has received an initial $5 million task order to conduct a Capability Assessment. This assessment will demonstrate how Neutron meets strict U.S. Space Force requirements such as precise launch timing, accurate orbital placement, and secure payload handling—all essential for national security missions. Rocket Lab’s founder and CEO, Sir Peter Beck, emphasized the importance of Neutron’s role in the program, stating: “Supporting assured access to space for the nation’s most important missions has always been the goal with our Neutron rocket.” He further highlighted that Neutron will offer a balance of performance, affordability, and reliability, setting a new benchmark for medium-lift launch services. Expanding Rocket Lab’s Presence in U.S. Defense Operations Rocket Lab has gained recognition with its Electron rocket, which has completed over 40 successful launches. However, Neutron represents a major leap in payload capacity, bringing the company closer to competing with larger, well-established launch providers. With significant investments in infrastructure, including new launch and production facilities in Virginia, Rocket Lab is positioning itself as a key partner for both commercial and government space missions. The U.S. Space Force’s selection of Neutron further validates the company’s technological advancements and long-term commitment to aerospace innovation. As Rocket Lab prepares for Neutron’s debut launch in 2025, its role in the U.S. national security space program is set to grow, cementing its position as a major player in the future of space exploration and defense.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:26:58Space & Technology
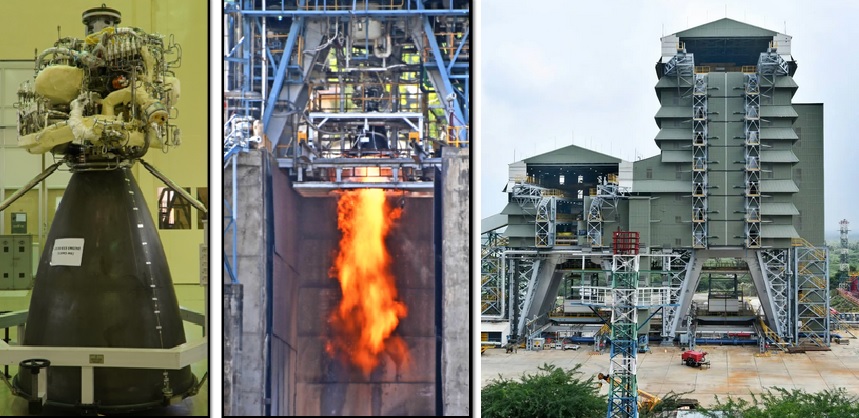
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a significant milestone with the successful hot test of its semi-cryogenic engine. This breakthrough marks a major step toward enhancing India’s space capabilities, particularly for future heavy-lift missions. The semi-cryogenic engine is a crucial component of ISRO's Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV), designed to replace the existing GSLV and PSLV rockets. Why is the Semi-Cryogenic Engine Important? A semi-cryogenic engine runs on refined kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen (LOX), offering higher efficiency and thrust compared to conventional cryogenic engines that use liquid hydrogen. This technology is vital for increasing payload capacity while reducing operational costs. Key Specifications of the Semi-Cryogenic Engine: Fuel: Refined Kerosene (RP-1) Oxidizer: Liquid Oxygen (LOX) Thrust: Approximately 2,000 kN (kilonewtons) Efficiency: Higher than conventional cryogenic engines due to better fuel density Application: Future heavy-lift missions, including crewed spaceflight and interplanetary missions With this success, ISRO is now a step closer to deploying the engine in upcoming launch vehicles, strengthening India's space exploration capabilities and reducing dependency on foreign propulsion systems. The next phases will include integrated testing and final implementation in India's new generation of launch vehicles. Russia Unveils Advanced Mobile Laser Weapon to Counter Drone Threats In response to the growing threat of drones in modern warfare, Russia has unveiled a cutting-edge mobile laser weapon designed to neutralize unmanned aerial threats with precision and speed. The new system represents a leap in directed-energy weapon technology, offering an effective way to disable enemy drones without relying on traditional missile-based air defense systems. How Does the Russian Mobile Laser Weapon Work? The laser system operates by emitting a high-energy beam that can heat and destroy the target’s electronics, rendering drones inoperative in seconds. Unlike conventional anti-air defenses, lasers provide a nearly unlimited number of shots as long as they have sufficient power, making them highly cost-effective. Key Features of the Mobile Laser Weapon: High-Power Laser: Capable of destroying drones at medium and short ranges Rapid Response: Instant target engagement without reload time Silent and Stealthy: Operates without noise or detectable missile launch signature Mobile Deployment: Mounted on a vehicle for flexible battlefield use Cost-Effective: No need for expensive missiles or traditional ammunition This new laser system is expected to be deployed in key military zones, providing Russia with a strategic advantage in electronic warfare. As drone warfare continues to evolve, laser-based defense systems could become a crucial element in modern military operations.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:23:00World
Russia Develops Advanced Mobile Laser System to Neutralize Drones Russia has unveiled a new mobile laser weapon designed to counter the growing threat of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The system, showcased at the Pan-Russian Conference on the Protection of Civilian Facilities Against Unmanned Aerial Systems, has sparked significant interest among defense experts and military strategists. Demonstration and Capabilities During a recent demonstration attended by Dmitry Medvedev, deputy chairman of Russia’s Security Council, the laser weapon successfully neutralized a small, fixed-wing drone using a directed-energy beam. The footage from the event highlighted its ability to disable drones quickly, making it a promising addition to Russia’s counter-drone arsenal. The mobile complex consists of two specialized vehicles: one equipped with a radar detection system and another carrying the laser weapon with an optical tracking system. This setup allows for early detection and precise targeting of UAVs, ensuring an effective defense against aerial threats. Technical Specifications and Features While official details remain scarce, defense analysts suggest the laser system is optimized for engaging small, commercial-grade drones within a limited range. According to reports, the weapon operates at a maximum range of 500 meters and utilizes a focused ytterbium laser beam to disable drones by targeting their bodies, propellers, engines, or batteries. This system represents a significant step in Russia’s development of directed-energy weapons (DEWs), offering key advantages such as: Unlimited ammunition: As long as there is a sufficient power supply, the laser can engage multiple targets without the need for reloading. Low operational cost: Unlike traditional missile-based defense systems, lasers reduce per-shot expenses, making them cost-effective for sustained operations. Silent and precise attack: The system operates without noise and minimizes collateral damage, crucial in both military and civilian settings. Strategic Importance in Modern Warfare The rise of First-Person View (FPV) drones in military conflicts, particularly in the Russia-Ukraine war, has intensified the demand for innovative counter-drone solutions. FPV drones, controlled in real-time via a live video feed, have proven highly effective for reconnaissance and targeted strikes. This has prompted nations to develop advanced anti-drone measures, with laser weapons emerging as a promising alternative to traditional jamming and kinetic methods. Unlike signal jamming—which can be ineffective against autonomous drones—and kinetic weapons that require physical ammunition, laser-based systems offer a reusable and energy-efficient countermeasure. However, the weapon’s effectiveness in adverse weather conditions and against multiple drone swarms remains untested in real-world combat scenarios. Comparison with Global Laser Defense Systems Russia’s new mobile laser gun aligns with global efforts to integrate directed-energy weapons into modern military strategies. Similar developments include: The U.S. Navy’s Laser Weapon System (LaWS): Capable of disabling drones and small boats from naval platforms. Israel’s Iron Beam: Designed to complement missile defense systems by neutralizing aerial threats at close range. China’s Silent Hunter: A high-energy laser system built for counter-drone operations and vehicle defense. However, Russia’s approach stands out for its compact, mobile design, potentially allowing individual soldiers or small teams to deploy it in the field. This mobility enhances its flexibility in protecting military units, key infrastructure, and civilian areas from UAV incursions. Challenges and Future Prospects Despite its promising capabilities, several challenges remain: Power and energy requirements: Portable laser systems require significant energy to operate, posing logistical hurdles in sustained battlefield use. Countermeasures from adversaries: Drones equipped with reflective coatings, maneuvering capabilities, or autonomous AI-driven responses could reduce the laser’s effectiveness. Combat durability: The system’s performance in harsh environmental conditions and prolonged engagements is yet to be publicly tested. While Russian officials have not disclosed whether the laser rifle is a prototype or ready for mass deployment, its unveiling suggests confidence in its potential. Analysts predict that if proven effective, the system could become a standard component of Russia’s ground-based air defense units, reinforcing its ability to tackle evolving aerial threats. Russia’s new mobile laser weapon signals a shift towards directed-energy solutions in the ongoing race to counter drone warfare. While questions remain about its battlefield effectiveness, the system represents a major step forward in laser-based air defense. Whether it will reshape military tactics or remain a limited-use technology depends on real-world performance and further developments in the field of energy-based weaponry.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:16:24World
A Swedish defense technology startup, Nordic Air Defence (NAD), is set to revolutionize the counter-drone sector with its new low-cost, high-speed interceptor, the Kreuger100. Designed to combat the growing threat of small unmanned aerial systems (UAS), this interceptor aims to provide an affordable and efficient solution for military forces, law enforcement agencies, and critical infrastructure operators. A Smart Approach to Drone Defense Unlike conventional systems that rely on costly onboard sensors and guidance technologies, the Kreuger100 leverages software-driven flight control and pulsed propulsion. This design allows it to maneuver with precision using controlled aerodynamics, making it both agile and cost-effective. For civil applications, the interceptor can reach speeds of 270 km/h (168 mph), while military variants are expected to achieve even higher speeds. NAD envisions a broad range of use cases, from intercepting high-altitude reconnaissance drones like the Russian Orlan-10 to neutralizing Iranian-designed Shahed drones before they can reach their targets. Field Testing and Future Deployment Currently, the Kreuger100 is undergoing daily tests, including indoor trials and secret outdoor flight tests to maintain operational security. NAD is also exploring portable configurations, which could allow troops to carry the interceptor in backpacks, providing on-the-move protection against enemy drones. Targeting the Real Threats According to Karl Rosander, CEO of NAD, the most dangerous drones on the battlefield are not just the ones dropping bombs but also those transmitting GPS coordinates for artillery strikes. Fast and affordable interceptors like the Kreuger100 are essential in neutralizing these threats before they can cause damage. As modern battlefields continue to face evolving drone threats, the Kreuger100’s modular and scalable design positions it as a flexible, low-cost, and effective countermeasure for defense forces worldwide.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:11:42World
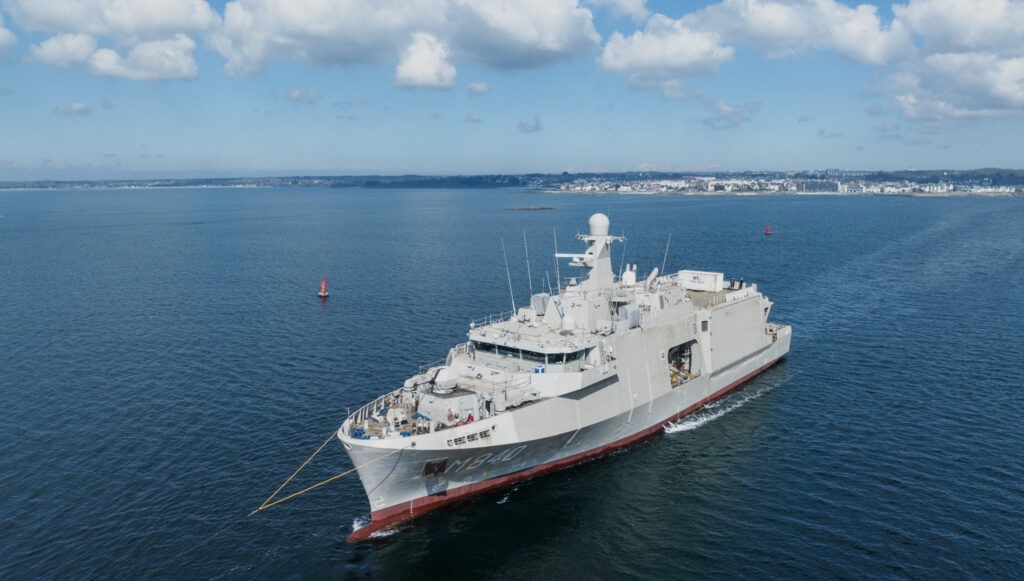
The Royal Netherlands Navy has taken a significant step forward in enhancing its mine warfare capabilities as Vlissingen, the first mine warfare mothership built for the Netherlands under the Belgian-Dutch rMCM programme, began its maiden sea trials on March 27, 2025. Departing from Concarneau, France, the vessel is undergoing rigorous testing to assess its propulsion system, maneuverability, and overall performance before delivery at the end of 2025. A Technological Leap in Mine Warfare Designed under the leadership of Belgium Naval & Robotics—a consortium of Naval Group and Exail—the rMCM (Replacement Mine Countermeasures) programme represents a major advancement in European defense collaboration. These next-generation mine warfare motherships are engineered to conduct mine countermeasure operations with minimal human intervention, utilizing a sophisticated network of unmanned systems. What sets these vessels apart is their ability to deploy and coordinate a variety of unmanned surface and underwater vehicles, aerial drones, and mine neutralization systems. With a length of 82.6 meters, displacement of 2,800 tons, and a range exceeding 3,500 nautical miles, the Vlissingen and her sister ships are designed to operate in hazardous environments while keeping their crew safe from direct exposure to underwater threats. Strategic Deployment and Fleet Expansion The rMCM programme includes twelve vessels, six each for the Belgian and Dutch navies, all scheduled for delivery by 2030. The first vessel, Oostende, intended for Belgium, is currently undergoing combat system trials, with delivery expected by mid-2025. Following this, Tournai, another Belgian ship, will begin its sea trials by the end of summer 2025. Meanwhile, Scheveningen, the second Dutch mothership, was launched in November 2024 and is on track for further trials. Each of these vessels serves as a central hub for unmanned mine-hunting operations, replacing traditional manned minesweepers and significantly improving the efficiency and safety of naval mine clearance. By leveraging Exail’s UMISOFT software suite and an array of autonomous systems—including unmanned surface vehicles, autonomous underwater drones, and mine identification and disposal systems—the new MCM motherships can clear minefields up to ten times faster than conventional methods. A European Defense Collaboration with Global Impact Naval Group and Exail have brought together multiple European industrial players to execute this ambitious project. The ships are constructed by Kership and Chantier Piriou, under the industrial oversight of Kership—a joint venture between Naval Group and Piriou. Exail, headquartered in Ostend, Belgium, is responsible for the production and maintenance of the unmanned mine warfare systems, ensuring the vessels remain at the cutting edge of maritime security technology. Beyond their autonomous mine clearance capability, these vessels are built to withstand underwater explosions and feature low acoustic, electrical, and magnetic signatures, making them stealthy and resilient in high-threat environments. Their modular design allows for rapid integration of future technological advancements, ensuring they remain relevant in evolving naval warfare scenarios. With the Vlissingen now undergoing sea trials, the Netherlands is set to revolutionize its naval mine countermeasures fleet, replacing outdated minesweepers with a highly automated, cyber-secure, and mission-flexible platform. This milestone not only strengthens Dutch and Belgian naval cooperation but also underscores Europe’s commitment to maintaining a robust and technologically advanced maritime defense network. As the rMCM programme progresses, these state-of-the-art vessels will play a critical role in securing international waters, ensuring safe maritime navigation, and countering modern mine threats more efficiently than ever before.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:09:12World
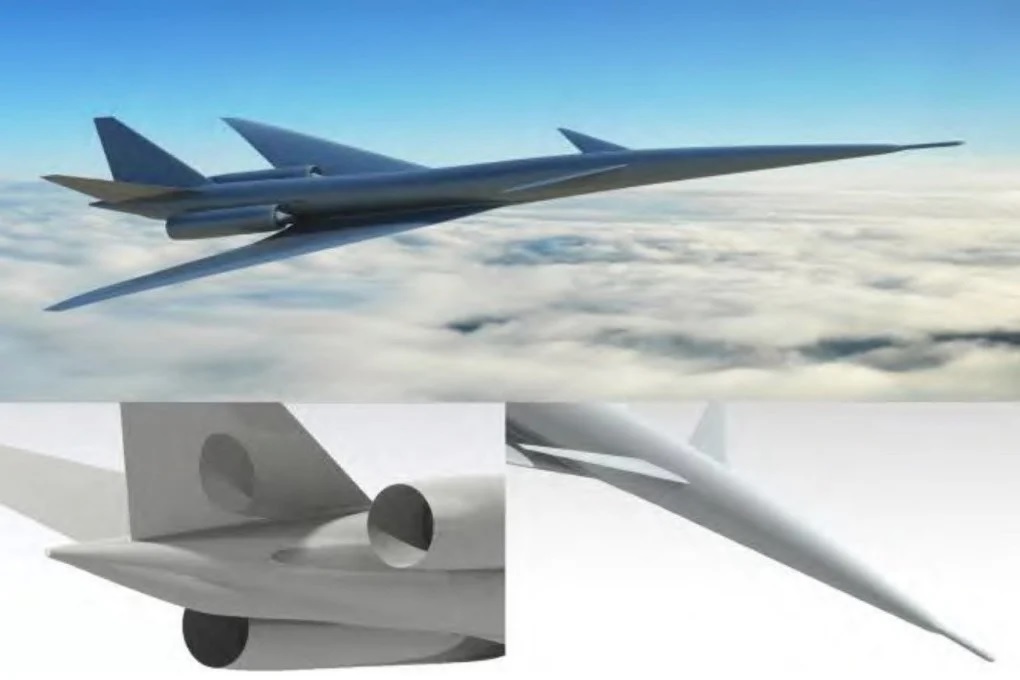
China’s state-owned aerospace giant, Comac, has quietly unveiled its ambitious supersonic airliner project—the C949. Designed to fly faster, farther, and quieter than any supersonic passenger jet before it, this revolutionary aircraft could reshape global aviation and establish China as a leader in high-speed air travel. A Supersonic Leap Beyond Concorde The C949 is engineered to achieve a maximum speed of Mach 1.6 (1,976 km/h or 1,227 mph), making it nearly twice as fast as conventional airliners. Unlike the retired Concorde, which had a range of 7,200 km (4,500 miles), the C949 is projected to cover 11,000 km (6,800 miles)—a 50% increase in range. This means direct, ultra-fast flights between cities like Shanghai and Los Angeles in just five hours. One of the most remarkable advancements of the C949 is its reduced noise pollution. Traditionally, supersonic flights have been restricted over land due to loud sonic booms. However, Comac has integrated advanced low-boom technology, cutting sonic boom levels to 83.9 perceived level decibels (PLdB)—comparable to a household hairdryer. Innovative Aerodynamic Design The C949’s sleek and futuristic shape-shifting fuselage is engineered to minimize shockwaves that create sonic booms. Key features include: A long, needle-like nose to split the shock wave into smaller, gentler pulses. Aerodynamic bulges near engines to scatter turbulence and reduce noise. Reverse-camber fuselage midsection to delay shockwave transition. To maintain stability at high speeds, the aircraft will rely on an AI-powered fly-by-wire system capable of managing extreme aerodynamic forces. Powerful and Efficient Engines The jet will be powered by twin adaptive-cycle turbofans, optimized for both Mach 1.6 cruising and Mach 1.7 eco-mode at an altitude of 16,000 meters (52,000 feet). These engines are designed to balance speed, fuel efficiency, and environmental impact, making supersonic travel commercially viable. Additionally, Comac has developed a dynamic fuel-shifting system, allowing 42,000 kg (93,000 lbs) of fuel to be redistributed between seven tanks mid-flight, optimizing the aircraft’s center of gravity for better efficiency and safety. Luxury Over Speed: Passenger Experience Unlike the Concorde, which had a 100-seat capacity, the C949 is designed to be a premium, business-class-focused aircraft. It will accommodate 28 to 48 passengers, offering more spacious and luxurious seating. The primary focus of the aircraft’s early operations will be on trans-Pacific routes, taking advantage of over-ocean corridors to minimize noise concerns. Challenges on the Horizon Despite its promising advancements, the C949 still faces hurdles: Fuel efficiency: While Comac aims to surpass the fuel performance of Concorde’s Olympus 593 engines, achieving long-term affordability remains a challenge. Public trust: The 2000 Concorde crash remains a significant psychological barrier for supersonic travel’s revival. Convincing airlines and passengers of the safety and reliability of the C949 will be crucial. Regulatory approval: Although the aircraft meets International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Chapter 14 noise regulations, gaining global certification for overland supersonic flights will require further breakthroughs. Comac has set an ambitious timeline, planning for the C949 to enter commercial service by 2049, coinciding with the 100th anniversary of the People’s Republic of China. As part of its broader strategy, Comac is also working on the C929 (a Boeing 787 competitor) and the C939 (targeting the Boeing 777X market), aiming to challenge Western aerospace dominance. While the United States pursues NASA’s X-59 QueSST and private firms like Boom Supersonic target niche markets, China’s C949 represents the boldest and most mainstream attempt yet at reviving supersonic travel. If successful, it could mark the beginning of a new era—one where long-haul flights take mere hours, and China leads the charge in next-generation aviation.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:07:58Space & Technology
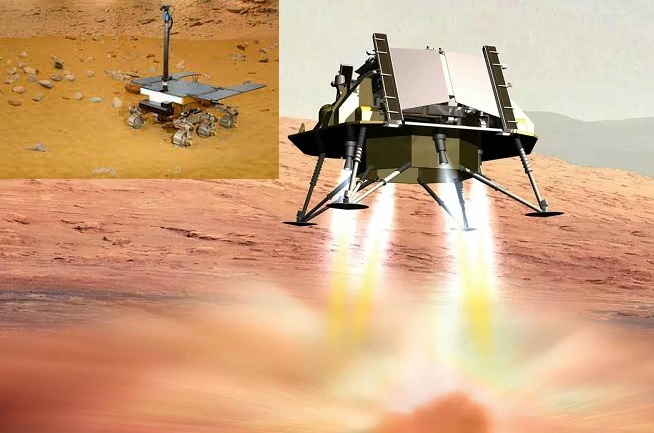
The European Space Agency (ESA) and Thales Alenia Space (TAS) have selected Airbus to develop critical systems for the ExoMars lander, a key component of the mission set to deliver the Rosalind Franklin rover to Mars. As the industrial lead, TAS—formed by Thales and Leonardo—will oversee the mission, while Airbus will provide essential mechanical, thermal, and propulsion systems to ensure a successful landing. A Precision Landing for a Historic Mission Landing on Mars is one of the greatest challenges in space exploration. The ExoMars lander will guide the UK-built Rosalind Franklin rover through the Martian atmosphere and facilitate its deployment on the surface. Airbus, leveraging its expertise in planetary exploration, is designing critical components at its Stevenage facility in the UK. The company will develop the braking system, landing structure, and gear, along with two ramps that will allow the rover to descend safely to the surface. Kata Escott, Managing Director at Airbus Defence and Space UK, emphasized the significance of this mission, saying: “Getting the Rosalind Franklin rover onto the surface of Mars is a huge international challenge and the culmination of more than 20 years’ work. Rosalind Franklin will be the first Martian rover able to analyse samples from two metres below the surface in its search for past or present life.” A Long Journey with New Challenges The Rosalind Franklin rover was initially planned for launch in 2022, but the Ukraine conflict led to delays, as ESA severed ties with Russian space agencies that were initially involved in the project. This setback forced a major restructuring of the mission, with ESA now partnering with NASA for the 2028 launch. The rover will be carried aboard a NASA rocket, and to withstand the extreme Martian conditions, it will receive new software updates and NASA-supplied Radioisotope Heater Units to maintain operational temperatures. Boost for the UK’s Space Industry The ExoMars project is a landmark moment for British science and engineering. UK Technology Secretary Peter Kyle praised Airbus' role, highlighting the mission’s significance for Britain’s global standing in space exploration: “This inspiring example of world-class British science will bring us one step closer to answering long-asked questions on potential life on Mars. Airbus will not only help Britain make history and lead the European space race but also bring hundreds of highly skilled jobs and investment.” Mars Landing in 2030 The new launch schedule aims for a Mars landing in 2030, carefully timed to avoid the planet’s global dust storm season, which can jeopardize operations. Once on the Martian surface, the Rosalind Franklin rover will begin its historic scientific mission—drilling two metres beneath the surface to search for signs of past or present life, a task no previous Mars rover has accomplished. With Airbus playing a leading role in the landing system, the ExoMars mission is a testament to international cooperation and cutting-edge technology, advancing both planetary exploration and the UK’s growing space industry.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 15:04:53World
In a significant move that could shape the future of India's indigenous fifth-generation fighter jet program, Russia has offered to co-develop an advanced flat engine nozzle for the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA). However, this offer comes with a major condition—India must choose Russia's newly developed Izdeliye 177S engine to power the AMCA. This proposal, which emerged during the Aero India 2025 exposition and subsequent bilateral discussions, underscores Russia’s desire to deepen its long-standing defence collaboration with India. With the AMCA aiming to be a true fifth-generation stealth fighter, incorporating cutting-edge avionics, supercruise capability, and low observability, the choice of engine will be a defining factor in its operational success. The Engine Dilemma: Izdeliye 177S vs Western Alternatives India's AMCA Mark 1 is currently planned to use the American General Electric F414 engine, which generates around 98 kN of thrust. However, for the AMCA Mark 2, the Indian Air Force (IAF) requires a significantly more powerful engine—ideally in the 110-130 kN range—to enable supercruise and enhance overall combat capabilities. The Russian Izdeliye 177S engine presents an enticing option. Developed by United Engine Corporation (UEC), a subsidiary of Rostec, the 177S reportedly offers 142 kN of thrust with an afterburner. It incorporates advanced stealth features, inspired by the AL-51 (Izdeliye 30) engine designed for Russia’s Su-57 "Felon" fighter, and promises improved fuel efficiency, better thrust-to-weight ratio, and an operational lifespan of up to 6,000 hours—three times that of the AL-31FP engines currently powering India’s Su-30 MKI fleet. However, India has other options. France’s Safran has expressed interest in co-developing a 110 kN-class engine based on the Rafale’s M88 core, while the United States has been exploring potential avenues for technology transfer in jet engine development. The Stealth Nozzle Advantage: Why Russia’s Offer Matters The most intriguing part of Russia's proposal is its offer to co-develop a flat, two-dimensional (2D) stealth nozzle for the AMCA. Unlike conventional round exhaust nozzles, flat nozzles—like those used on the American F-22 Raptor—help reduce an aircraft’s radar cross-section and infrared signature, enhancing its stealth characteristics. The benefits of a flat nozzle include: Reduced Radar Signature: Traditional circular nozzles reflect radar waves more predictably, making an aircraft easier to detect. A flat nozzle scatters these waves in a less uniform manner, reducing visibility. Lower Infrared Signature: By shaping and cooling the exhaust plume, the nozzle makes it harder for heat-seeking missiles to lock onto the aircraft. Thrust Vector Control (TVC): Russia has experience integrating TVC nozzles, allowing for superior maneuverability—an advantage in aerial combat. If India chooses to pursue this collaboration, the DRDO and HAL would work alongside UEC engineers to customize the nozzle for the AMCA airframe, possibly incorporating indigenous materials and control systems. This could provide India with valuable knowledge in engine design and stealth optimization—critical for its long-term goal of self-reliance in military aviation. Challenges and Strategic Considerations While the Russian proposal is technologically attractive, several risks and challenges must be considered: Development Status of Izdeliye 177S: The engine has yet to undergo extensive flight testing, and its reliability is not fully proven. Russia has indicated that it will only proceed with full-scale testing once confirmed orders are received. Integration Complexities: The AMCA's airframe has been designed around the lighter GE F414 engine. Adapting it for the heavier and more powerful Izdeliye 177S would likely require structural modifications, adding to development costs and timelines. Sanctions and Supply Chain Risks: Russia’s defence industry faces Western sanctions, which could impact the availability of critical components, affecting production schedules and long-term maintenance. Geopolitical Considerations: India has been diversifying its defence procurement strategy, reducing dependency on Russian systems. Committing to a Russian engine could limit future options for Western collaboration, especially as India strengthens defence ties with the US and France. India’s Decision: A Balancing Act If stealth superiority is the top priority, the flat nozzle co-development could be a game-changer for the AMCA. It would provide India with a technological edge over potential adversaries like China’s J-20 and upcoming J-36 fighters. Additionally, collaboration with UEC could accelerate India's expertise in advanced aero-engine technology, benefiting long-term indigenous projects. However, India must weigh the risks. Alternative engine development offers from France or the US could provide a more stable and geopolitically secure path forward. The Izdeliye 177S may be powerful, but its unproven status, along with the complexities of airframe adaptation, makes it a high-risk, high-reward proposition. Ultimately, India’s decision on the AMCA’s engine and stealth enhancements will shape the future of its air combat capabilities for decades. Whether it aligns with Russia for an F-22-style flat nozzle or pursues Western partnerships, the choice will be a defining moment for India’s quest for an advanced, indigenous fighter jet.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 13:52:06World
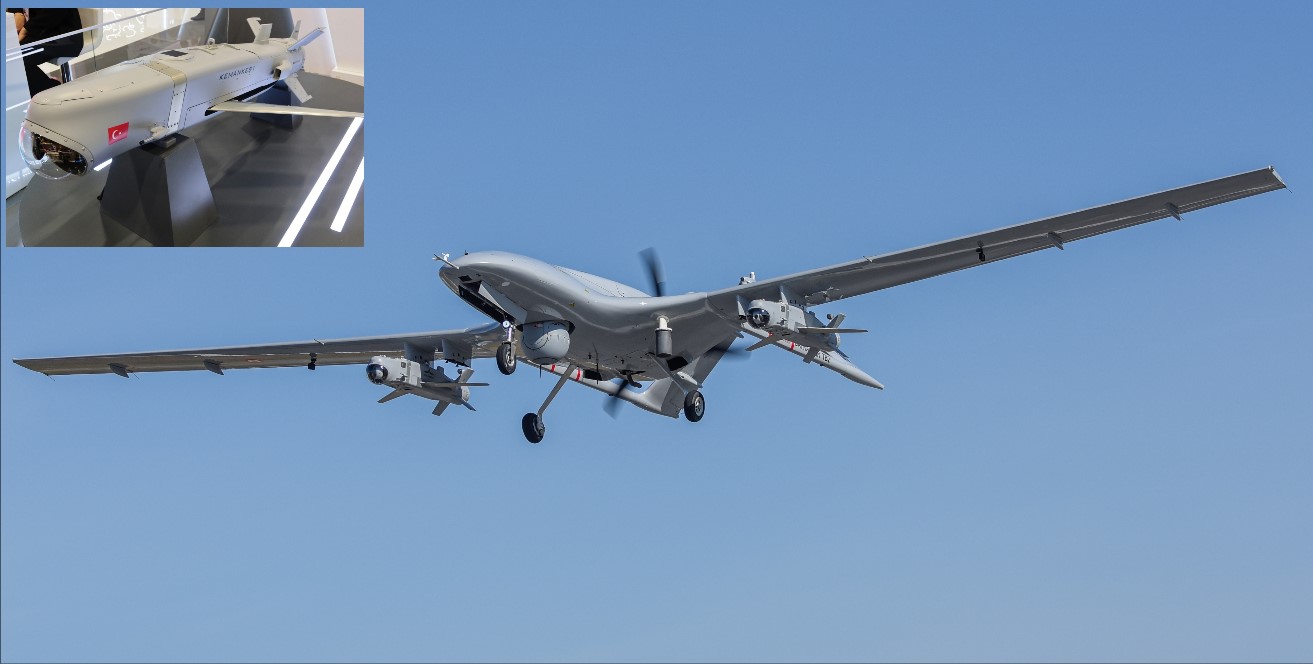
Baykar Technologies has announced the successful completion of a crucial flight test for its AI-powered mini cruise missile, KEMANKEŞ 1. The missile underwent its Maximum Flight and Dive Test at Baykar’s Flight Training and Test Center in Keşan, Edirne, marking a significant step in its development. Successful Test Flight As part of the test, two KEMANKEŞ 1 missiles were launched from a Bayraktar TB2 Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle (UCAV) and flew over 100 kilometers before landing safely using parachutes. The primary objective was to evaluate the missile’s performance in long-range flight and controlled descent, ensuring its reliability in real-world scenarios. A New Era of Mini Cruise Missiles KEMANKEŞ 1 represents a new class of intelligent mini cruise missiles designed for strategic precision strikes. The system was first introduced at TEKNOFEST 2023 in Istanbul and is named after the elite Ottoman archers, known for their remarkable accuracy in hitting distant targets. Baykar emphasized that KEMANKEŞ 1 is built to perform with precision under extreme battlefield conditions. It is fully autonomous and can engage high-risk targets deep within enemy territory, making it a game-changer in modern warfare. Key Specifications of KEMANKEŞ 1 Platform Integration: Compatible with Bayraktar AKINCI, TB2, and TB3 UCAVs. Propulsion: Powered by a jet engine for sustained flight. Endurance: Can remain airborne for up to an hour. Range: Operational range exceeds 200 kilometers. Guidance System: Features an AI-supported electro-optical guidance system for pinpoint accuracy. Jamming Resistance: Equipped with anti-jamming technology for electronic warfare resilience. Autonomy: AI-assisted autopilot allows autonomous target tracking and engagement. All-Weather Capability: Effective in day and night operations under challenging conditions. Strategic Impact on the Battlefield KEMANKEŞ 1’s autonomous flight capabilities and real-time data transmission provide enhanced battlefield situational awareness. It maintains line-of-sight communication with its host platform, ensuring accurate mission execution. Baykar stated that KEMANKEŞ 1 will play a crucial role in neutralizing high-value targets with precision, shifting the dynamics of modern warfare by offering an advanced AI-powered strike capability to UCAV platforms. With successful tests like this, Turkey’s defense industry continues to strengthen its technological edge, solidifying Baykar’s position as a leading innovator in next-generation UAV and missile technology.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 13:48:41World
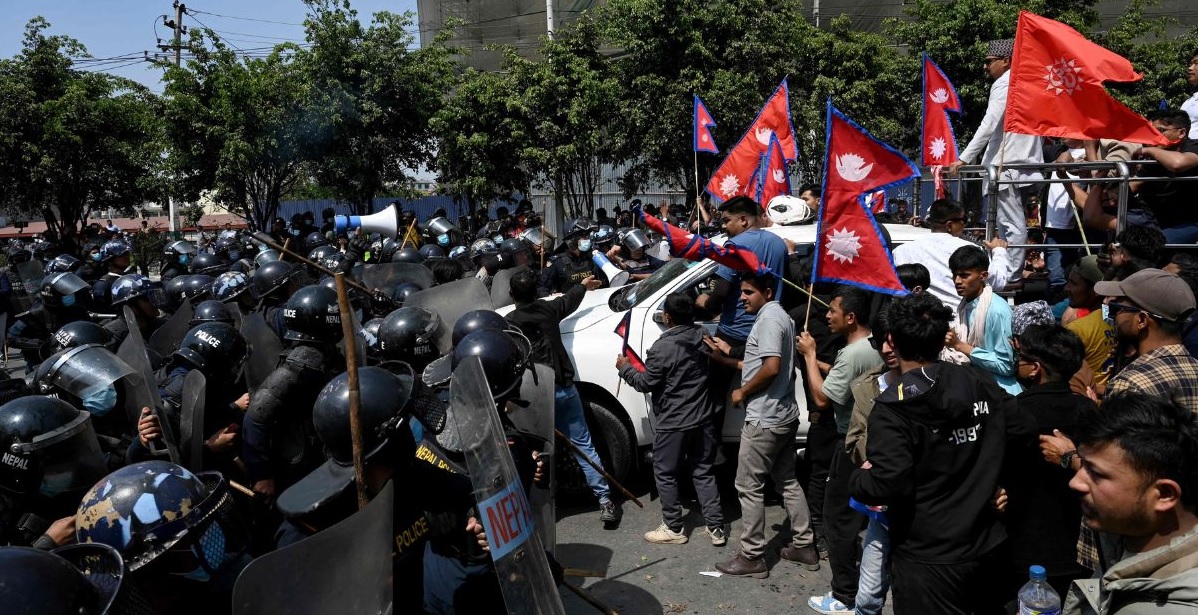
Violent clashes shook Kathmandu on March 28, 2025, as thousands of pro-monarchy demonstrators took to the streets, demanding the restoration of Nepal’s monarchy. The protests, spearheaded by businessman Durga Prasai and the Nawaraj Subedi-led joint movement committee, quickly escalated into chaos, with rioters vandalizing buildings, smashing windows, and even setting one structure on fire near Tinkune, close to Tribhuvan International Airport. The government had anticipated trouble and stationed more than 3,500 police officers across Kathmandu. As demonstrators tried to breach police barricades, law enforcement responded with tear gas, water cannons, and rubber bullets. The situation became so volatile that authorities imposed a curfew in Tinkune, Sinamangal, and Koteshwor to prevent further escalation. Adding to the tensions, a counter-demonstration by pro-republican groups, led by the Socialist Front, took place at Bhrikutimandap in support of Nepal’s federal democratic system. While both factions had obtained official permission for their protests, the simultaneous rallies intensified security concerns, with authorities struggling to prevent direct confrontations. The resurgence of pro-monarchy sentiment underscores deep-rooted frustrations with Nepal’s current political landscape. Since the monarchy was abolished in 2008, Nepal has faced chronic political instability, corruption scandals, and sluggish economic growth. Many citizens, particularly the younger generation, feel disillusioned by the promises of democracy that have yet to translate into real progress. The pro-monarchy movement, largely fueled by nostalgia for the stability of the past, has gained momentum in recent years, with figures like Prasai emerging as vocal critics of the government. In response to the unrest, the Ministry of Home Affairs held an emergency meeting, authorizing police to take decisive action if necessary. The government faces a critical challenge—balancing the right to protest with maintaining order in a politically divided nation. While Nepal's republican system remains intact, the growing calls for a return to monarchy suggest that the debate over the country’s governance is far from settled.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 13:43:40India
GE Aerospace has reinforced its commitment to India's indigenous Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) program by commencing the delivery of F404-IN20 engines, ensuring a steady production cycle for the Indian Air Force (IAF). The first of these engines was formally handed over to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) on March 25, 2025, with 11 more slated for delivery by the end of the year. This move is a critical step in stabilizing the production of the Tejas Mk1A, addressing past delays caused by supply chain disruptions and engine shortages. The F404-IN20, an advanced variant of GE's widely deployed F404 engine family, features a high-flow fan and single-crystal turbine blades to optimize performance for the single-engine Tejas fighter. With GE now ensuring a delivery rate of 20 engines per year starting from 2026, HAL can maintain its production target of 16 to 24 Tejas Mk1A jets annually. This sustained supply is crucial for the IAF as it phases out aging aircraft like the MiG-21 and strengthens its squadron numbers. The first engine shipment, dispatched from GE’s Lynn, Massachusetts facility, is expected to arrive in India by mid-April. HAL, which is contractually bound to deliver 83 LCA Mk1A aircraft under a ₹48,000-crore agreement signed in 2021, has already completed airframes for three jets and has 11 more in various stages of production. The arrival of the new engines will allow HAL to replace temporary test engines with full-fledged production powerplants, expediting aircraft induction into the IAF. This structured delivery plan not only secures the current LCA Mk1A program but also sets the stage for potential future orders. The IAF is evaluating a follow-on purchase of 97 additional Tejas Mk1A jets, which would require further engine contracts with GE, strengthening India’s long-term fighter jet production capabilities. With a four-decade partnership between GE and HAL, this latest development marks a significant step in ensuring India’s self-reliance in military aviation while reinforcing GE’s role as a key defense partner.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-29 13:38:25Space & Technology
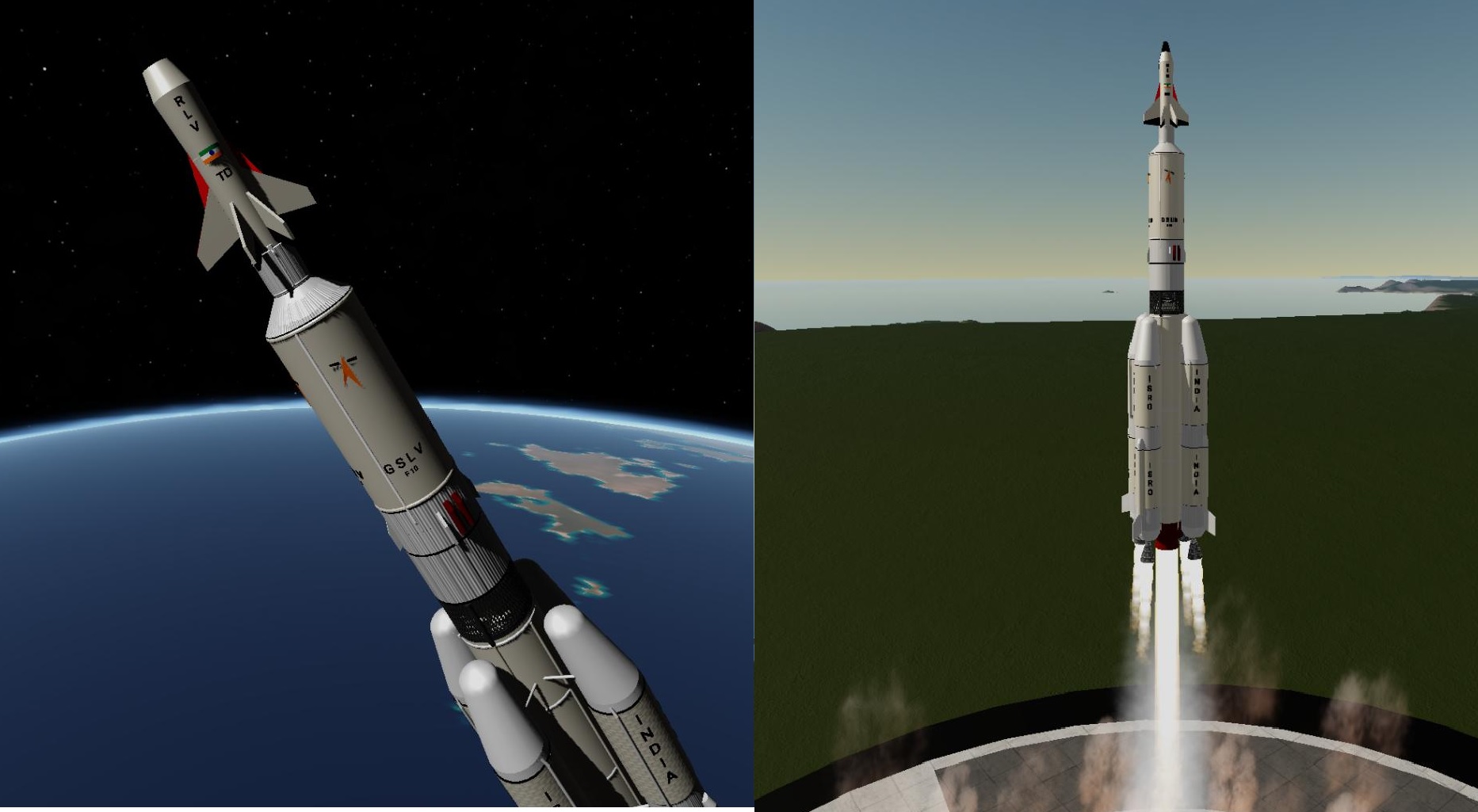
In a significant step towards developing reusable launch vehicles, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is working on a winged body Orbital Re-entry Vehicle (ORV). This advanced spacecraft will be launched into orbit using an ascent vehicle and later re-enter Earth's atmosphere, executing an autonomous runway landing. The ORV is a crucial component of India's long-term strategy for cost-effective and sustainable space exploration. Successful Trials of Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV-TD) To validate the feasibility of this technology, ISRO has successfully conducted three Autonomous Runway Landing Experiments (RLV-LEX) using the Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD). These experiments have proven the robustness of onboard autonomous navigation, guidance, and control systems, laying the foundation for a fully operational ORV. Advancements in Booster Stage Recovery Apart from the ORV, ISRO is also focusing on developing Vertical Take-off and Vertical Landing (VTVL) technology for recovering and reusing booster stages. This innovation will significantly reduce launch costs by allowing multiple reuses of the spent boosters, similar to SpaceX's Falcon rockets. Next-Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV): A Step Towards Partial Reusability The Indian government has approved the development of a Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV), which will be a three-stage launch system. The first stage of this vehicle will be recoverable and reusable, making it India's first partially reusable space launch system. This development aligns with global efforts to create cost-efficient and sustainable space access. Private Sector Involvement and Space Reforms With the introduction of space sector reforms in June 2020, private companies are now allowed to provide end-to-end space services. The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) has been set up to facilitate and regulate private sector participation. This move is expected to boost India's space economy and enable collaborations in areas such as lunar mining and deep-space exploration. Artificial Intelligence in Space Missions Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly critical role in space missions. ISRO is integrating AI-based solutions in autonomous mission management, onboard data processing, and advanced space exploration. A recent AI-driven achievement includes an autonomous sensor-based actuator system that enables precise docking sequences using pattern recognition techniques. Ensuring Responsible Use of Space As a responsible space-faring nation, India actively contributes to space debris mitigation. The country follows internationally accepted guidelines set by agencies like the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UN-COPUOS) and the Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC). The Indian Space Policy mandates strict adherence to these regulations, ensuring sustainable and safe space operations. Looking Ahead: India’s Future in Space Exploration India is setting ambitious goals, including achieving a successful lunar landing by 2040. This vision will involve extensive collaboration with private industries, academia, and international partners, driving India’s leadership in the global space domain. With continuous advancements in reusable technology, artificial intelligence, and sustainable space practices, ISRO is paving the way for a more efficient and economically viable future in space exploration. The development of the Orbital Re-entry Vehicle (ORV) and Next-Gen Launch Vehicle (NGLV) marks a new era in India’s journey toward becoming a major player in the global space industry.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-28 16:05:36World
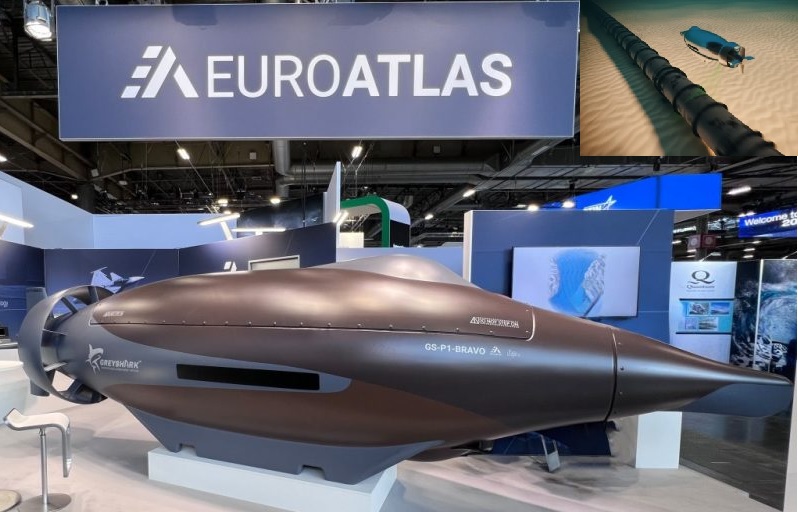
Unveiled at Euronaval 2024 in Paris and later showcased at the UDT 2025 conference in Oslo, the Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot by Euroatlas (Germany) is set to redefine the landscape of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). Designed for reconnaissance, surveillance, and infrastructure protection, this cutting-edge AUV boasts extended endurance, advanced AI-driven autonomy, and swarm operation capabilities. Next-Gen Design and Specifications The Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot features a 7.99-metre-long hydrodynamic body with a 1.8-metre maximum diameter and a 4.5-tonne mass. Constructed with composite materials, it maintains a low electromagnetic signature and ensures minimal water disturbance, making it extremely difficult to detect. At its core, the AUV is powered by a non-permanent magnetic electric ring motor, which drives a segmented ring rotor propeller. A cruciform rudder assembly at the rear enhances maneuverability, allowing extreme dive angles and tight turns. This unique propulsion system ensures: Operational speed: 10 knots Maximum speed: Classified, but "over 10 knots" Endurance: 1,100 nautical miles (NM) or 5 days at 10 knots 2,180 NM or 1.5 weeks at 8 knots 5,350 NM or 5 weeks at 6 knots 10,700 NM or 16 weeks at 4 knots (low-speed creeping mode) The fuel-cell-powered electric motor significantly extends operational time, making Greyshark ideal for long-range autonomous missions. Advanced Sensor Suite and Communication Systems Equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, the Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot delivers high-precision underwater intelligence. Key onboard systems include: USBL acoustic antennas (front) for encrypted swarm communications Telescopic antenna system (rear) for LTE and L-band communications GNSS receiving antenna for positioning Side-scan Synthetic Aperture Sonar (SAS) for ultra-high-resolution imaging Dual-element multibeam sonar (bow and hull) for obstacle detection Wideband multibeam sonar for sea-bottom mapping Doppler velocity sensor with Exail's Phins Subsea navigation system LIDAR and imaging cameras for 3D mapping Electromagnetic field detectors for anomaly detection The fusion of these sensors enables the Greyshark to operate autonomously for weeks without human intervention. It only communicates with the base when a critical event is detected, such as an intrusion or sabotage attempt on underwater infrastructure. AI-Driven Autonomy and Swarm Operations The Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot is engineered for highly autonomous missions, thanks to Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based decision-making. Its capabilities include: Automatic target recognition (ATR) Dynamic mission adaptation in case of system failure or unexpected events Swarm operations with up to six AUVs, enabling: Area surveillance with multiple units covering large zones Coordinated search and mapping Mission reconfiguration based on real-time threats Each Greyshark unit can assume leadership within the swarm, ensuring mission success even if one AUV is compromised. Mission Capabilities and Deployment Designed for stealth and endurance, the Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot supports various naval and security operations, including: Seabed surveillance and covert reconnaissance Underwater infrastructure protection (monitoring data cables, pipelines, and energy platforms) Mine warfare (autonomous detection and neutralization of sea mines) Anti-submarine operations, using active sonar decoys to deceive enemy submarines Persistent intelligence gathering in high-risk maritime zones The AUV’s logistical flexibility allows for rapid global deployment. It fits into a standard 40-foot container, transportable by truck, train, ship, or aircraft. A second container houses a charging and refueling system, ensuring quick redeployment with minimal infrastructure. Future Developments and Strategic Importance Currently undergoing testing and optimization, the Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot is expected to expand its capabilities by 2026, focusing on: Enhanced AI for greater autonomy Longer dive durations Standardized communication protocols under European initiatives like SWARMS (Smart Underwater Robotics) and SALSA (Acoustic Network for Subsea Operations) With its stealth, autonomy, and advanced AI, the Greyshark Series 2 Foxtrot is poised to become a game-changing asset for modern navies, reinforcing maritime security in an era of rising underwater threats.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-28 16:00:33Search
Top Trending
-
 Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
-
 India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
-
 Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
-
 Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
-
 What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
-
 China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
-
 China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
-
 India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
Top Trending in 4 Days
-
 Elon Musk’s SpaceX Leads Bid for Trump’s Ambitious “Golden Dome” Missile Shield
Elon Musk’s SpaceX Leads Bid for Trump’s Ambitious “Golden Dome” Missile Shield
-
 JCBL Group Seals Historic Defence Deal with Slovakia, Boosting India's Military Manufacturing Might
JCBL Group Seals Historic Defence Deal with Slovakia, Boosting India's Military Manufacturing Might
-
 India’s Affordable Artillery Offer Disrupts Global Defense Market
India’s Affordable Artillery Offer Disrupts Global Defense Market
-
 US Accuses Chinese Satellite Firm of Supporting Huthi Attacks on Red Sea Shipping
US Accuses Chinese Satellite Firm of Supporting Huthi Attacks on Red Sea Shipping
-
 Ukraine Deploys New Indigenous B-1 Combat Drone to Strengthen Frontline Strikes
Ukraine Deploys New Indigenous B-1 Combat Drone to Strengthen Frontline Strikes
-
 Explosion Destroys Key Building at Northrop Grumman’s Rocket Facility in Utah, No Major Injuries Reported
Explosion Destroys Key Building at Northrop Grumman’s Rocket Facility in Utah, No Major Injuries Reported
-
 Washington Approves $180 Million Engine Sale to Boost Israel’s Eitan Armored Vehicle Fleet
Washington Approves $180 Million Engine Sale to Boost Israel’s Eitan Armored Vehicle Fleet
-
 U.S. Marines Deploy NMESIS Missile System to Philippines for Balikatan 25, Boosting Coastal Defense and Allied Cooperation
U.S. Marines Deploy NMESIS Missile System to Philippines for Balikatan 25, Boosting Coastal Defense and Allied Cooperation