Can Trump’s $100 Billion ‘Golden Dome’ Protect the U.S. from Nuclear and Hypersonic Missile Threats?
World
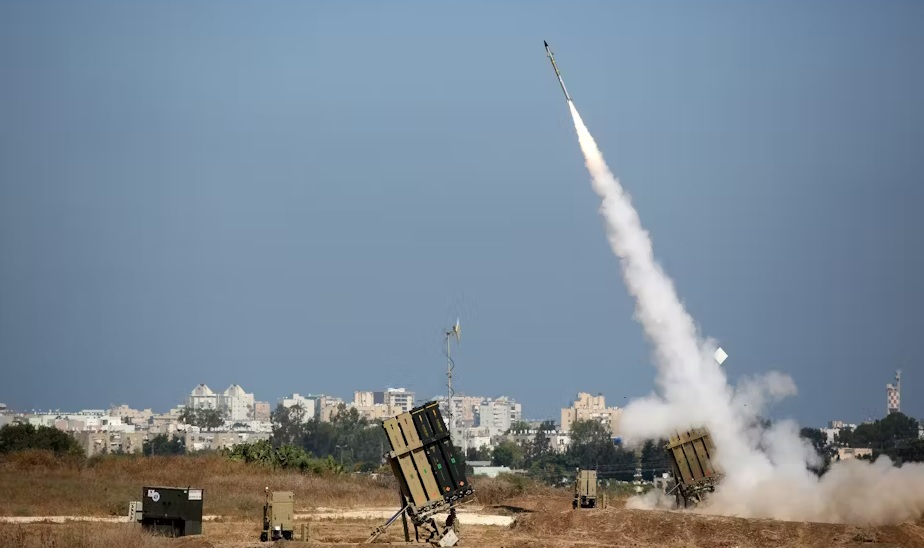
Forty years ago, President Ronald Reagan envisioned a missile defense system capable of shielding the United States from nuclear threats. Dubbed the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), it was colloquially known as "Star Wars" and ultimately shelved due to technological and strategic challenges. Today, President Donald Trump has resurrected this concept under the moniker "Golden Dome," aiming to protect the nation from modern missile threats, including intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and hypersonic weapons. Understanding the Golden Dome Initiative Announced during a congressional address, President Trump emphasized the critical importance of this defense system for national security, stating, "As a first step, I’m asking Congress to fund a state-of-the-art ‘Golden Dome’ missile defense shield to protect our homeland. All made in the USA." Unlike Israel’s Iron Dome, which is designed to intercept short-range rockets, the Golden Dome aspires to counter a broad spectrum of missile attacks over the expansive territory of the United States. Proposed Mechanisms and Technologies The Golden Dome is envisioned to integrate advanced technologies such as space-based sensors, missile interceptors, and laser weapons. General Michael Guetlein, Vice Chief of Space Operations for the U.S. Space Force, highlighted the necessity of space-based radar systems to address the unpredictability of modern missiles. He noted that long-range weapons capable of maneuvering around current land-based and sea-based radar systems necessitate a shift to space-based detection architectures. Existing systems like the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) and Patriot missile batteries offer limited protection and are primarily deployed overseas. The Golden Dome aims to establish a comprehensive, nationwide shield. Phil Jasper, CEO of Raytheon, underscored the need for a multi-layered approach, acknowledging the complexities involved in intercepting diverse threats ranging from unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to hypersonic missiles. Logistical and Financial Challenges Implementing the Golden Dome presents significant logistical and financial hurdles. Coordinating among various agencies and defense contractors is a formidable challenge. Jonathan Moneymaker, CEO of BlueHalo, emphasized that the primary obstacle lies in organizational structure rather than technology. Integrating efforts across multiple stakeholders to create a cohesive defense system is a complex endeavor. Funding is another critical concern. The Department of Defense and the Office of Management and Budget are developing a financial roadmap, with initial reports suggesting that certain components could be operational by 2026, starting with major cities like Washington, D.C., and New York. However, the overall cost is projected to be substantial. Joe Cirincione, a national security analyst, estimated that creating an Iron Dome for America could cost approximately $2.5 trillion. Edward Zoiss, President of Space and Airborne Systems at L3Harris Technologies, expressed concerns about tracking advanced missile threats. He pointed out that while ICBMs have historically followed predictable paths, hypersonic weapons possess unpredictable trajectories, necessitating an evolution in defensive systems to effectively track and intercept such threats. Industry Response and Future Outlook The defense industry has shown keen interest in the Golden Dome initiative. The Missile Defense Agency recently received over 360 proposals from companies eager to contribute to the project. Major defense contractors, including Lockheed Martin, RTX, and Northrop Grumman, are evaluating how their existing technologies can support the initiative. Frank St. John, COO of Lockheed Martin, compared the project's significance to the Manhattan Project, highlighting its critical importance to national defense. Conclusion The Golden Dome represents an ambitious endeavor to safeguard the United States from evolving missile threats. While the initiative underscores a commitment to national security, its feasibility is subject to debate. Laura Grego of the Union for Concerned Scientists expressed skepticism, noting the technical and economic challenges inherent in defending against sophisticated nuclear arsenals. As the project progresses, it will require substantial political will, industrial collaboration, and financial investment to determine whether the Golden Dome can fulfill its promise or become another costly and unworkable defense aspiration.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:50:13Secrets/Mystery
On the evening of March 24, 2025, a captivating blue spiral appeared in the night sky over Europe, leaving residents from the United Kingdom to Poland in awe and curiosity. This mesmerizing display prompted widespread speculation, with theories ranging from aircraft and satellites to galaxies and even extraterrestrial activity. The Cause: SpaceX Falcon 9 Rocket Launch The true origin of this celestial spectacle was traced back to a terrestrial source: a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. Launched earlier that day from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, the rocket was on a classified mission for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). Approximately an hour after liftoff, as the rocket's second stage passed over Europe, it released excess fuel into the upper atmosphere. This fuel, upon contact with the cold environment, froze and formed a cloud of ice particles. The subsequent interaction of sunlight with these particles resulted in the luminous blue spiral observed across the continent. Understanding the Spiral Formation Such spirals, though rare, are not unprecedented. They occur when rockets perform fuel dumps at high altitudes. The expelled fuel, freezing upon release, creates a reflective cloud that, when illuminated by sunlight, manifests as a glowing spiral. The rotation of the rocket or the dynamics of the fuel release can impart a spiral shape to the expanding cloud. Similar phenomena have been documented in the past, often linked to missile tests or space launches. Public Reaction and Expert Clarification The unexpected appearance of the spiral led to a flurry of activity on social media platforms, with users sharing images and videos, and engaging in discussions about its possible origins. While some entertained the notion of alien involvement, experts swiftly provided explanations grounded in atmospheric and aerospace science. The UK's Met Office, among other institutions, attributed the display to the SpaceX launch, elucidating the process of fuel release and the resulting optical effects. Conclusion The blue spiral that graced European skies serves as a testament to the intricate interplay between human technological endeavors and natural atmospheric phenomena. While initially enigmatic, the event underscores the importance of scientific inquiry in demystifying occurrences that, at first glance, may seem beyond earthly explanation.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:43:47World
Recent satellite and ground imagery have revealed an advanced system of Chinese amphibious bridging barges, potentially designed for a large-scale amphibious operation targeting Taiwan. The discovery of these platforms, developed by CSSC Offshore & Marine Engineering Company (COMEC), suggests a strategic push by the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) to enhance its amphibious warfare capabilities. These new designs raise questions about their intended use, operational flexibility, and strategic implications for regional security. Understanding the Amphibious Bridging Barges COMEC, a well-established supplier for the Chinese military, has diversified its shipbuilding capabilities beyond traditional vessels like replenishment oilers and hospital ships. The emergence of these amphibious bridging barges signals China’s interest in innovative systems capable of facilitating rapid force deployment across challenging maritime environments. Unlike conventional transport ships, these platforms employ a jack-up barge design. This means they can extend their legs to stand on the seabed, providing a stable platform for high-load transfers and troop movements. Notably, these are self-propelled, allowing them to travel independently across significant distances, a crucial factor for operations in the Taiwan Strait. Key Variants and Their Capabilities China appears to have developed three primary operational designs, each serving a distinct purpose: Type 2 (Shuiqiao 110): The most compact design, featuring four legs, a 140-meter ramp, and a 38-meter beam. This unit serves as a bridgehead in shallow waters, enabling a direct connection to the shore. However, it lacks the ability to berth transport ships, necessitating external support. Type 1 (Shuiqiao 135): Larger than Type 2, this variant measures 135 meters in length and has two extendable platforms, allowing Ro/Ro ferries to offload vehicles and supplies. It features six legs, longer and sturdier than those on Type 2, suggesting its capability to operate in deeper waters. Type 3 (Shuiqiao 185): The largest variant, measuring 185 meters in length with eight legs for enhanced stability. It includes an additional extendable platform at its stern, optimizing it as the terminal point in a bridging system for disembarking large military assets. These platforms were observed undergoing testing near Zhanjiang, with movements to Donghai Island, further indicating their operational significance. Strategic Implications for Taiwan The Chinese amphibious bridging system is unlikely to play a role in the initial wave of an invasion. Instead, its function would be to support the second phase of operations, where follow-on forces and heavy equipment—such as tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, and air defense systems—are rapidly transported onto secured beachheads. The initial assault would likely be conducted using PLAN’s Type 075 LHDs, Type 071 LPDs, and Type 072 LSTs, supported by hovercraft and airborne operations. Once a beachhead is established, the bridging system would accelerate logistics, ensuring the continuous flow of reinforcements and supplies. Beyond Military Applications? Some analysts have suggested that these platforms could have humanitarian applications, such as disaster relief operations. However, given their design and mobility, this seems unlikely as a primary purpose. China's existing naval logistics and amphibious capabilities are more suited for humanitarian missions, making it clear that these new barges are primarily intended for military use. Conclusion China’s amphibious bridging system represents a significant development in its military strategy, particularly regarding Taiwan. By enhancing its ability to conduct rapid force buildup after an initial assault, the PLAN is demonstrating a clear commitment to refining its invasion logistics. While these platforms may not be used in direct combat, their ability to support sustained operations poses a strategic challenge for Taiwan and its allies. As regional tensions persist, monitoring China’s advancements in amphibious warfare will remain critical for assessing potential conflict scenarios in the Indo-Pacific.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:36:50India
The Indian Navy remains steadfast in its commitment to building a second Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC-II), even as the country accelerates its nuclear-powered attack submarine (SSN) program. While recent media reports speculated that the ₹40,000 crore ($4.8 billion) SSN project approved in January 2025 might divert resources from IAC-II, Navy officials have refuted such claims, emphasizing that both initiatives are essential to India’s maritime strategy. The proposed IAC-II, a 45,000-tonne conventionally powered carrier, is envisioned as a follow-up to INS Vikrant (IAC-I), India's first domestically built aircraft carrier. This move aligns with the Navy’s long-term goal of maintaining a three-carrier fleet, ensuring that at least two are operational at all times while the third undergoes maintenance. With INS Vikramaditya, the Russian-origin carrier, expected to retire by the mid-2030s, the urgency for IAC-II has increased. Strategic Imperatives: Carrier vs. Submarine Debate The need for IAC-II is driven by the evolving security landscape in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). China’s growing naval presence, coupled with Pakistan’s ambitions, necessitates a strong power projection capability. Aircraft carriers serve as mobile airbases, enabling India to maintain sea control, conduct long-range strike missions, and support joint operations. While SSNs are crucial for undersea warfare—tracking adversary submarines, enforcing blockades, and securing sea lanes—carriers provide an unmatched ability to dominate surface and aerial domains. The Indian Navy has argued that submarines and carriers serve distinct roles and are not interchangeable. A senior naval official explained, “Submarines provide stealth and denial capability, while aircraft carriers ensure sustained presence, deterrence, and rapid response.” The Navy’s vision for a future force structure includes three aircraft carriers and 18 SSNs by 2047, ensuring a balanced maritime force. Advancing Carrier Capabilities with IAC-II Designed to improve upon Vikrant, IAC-II will incorporate advancements in aviation technology, including the integration of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) for reconnaissance and strike missions. While retaining the Short Take-Off But Arrested Recovery (STOBAR) system and ski-jump, modifications will enhance its ability to operate modern aircraft. The Navy’s ongoing Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter (TEDBF) program, intended to replace the MiG-29K fleet, could see its first operational deployment on IAC-II. The estimated cost of IAC-II stands at ₹50,000 crore ($6 billion), and the Navy is pushing for Ministry of Defence (MoD) approval to initiate construction by 2027. Unlike Vikrant, which took 13 years due to funding and technical delays, IAC-II is expected to be completed within a decade. Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), having gained expertise from Vikrant’s construction, is likely to lead the project. Budgetary Constraints and Future Outlook Despite the operational necessity of IAC-II, financial limitations pose a challenge. The Navy’s capital budget of ₹2.5 lakh crore ($30 billion) over the next decade must cover multiple priorities, including 62 warships, the SSN program, and next-generation naval aircraft. To mitigate this, a phased approach has been proposed—advancing IAC-II in the near term while spreading SSN development over two decades. This strategy ensures that India does not compromise on either capability while managing budgetary constraints. Conclusion: A Balanced Naval Expansion The Indian Navy’s unwavering pursuit of IAC-II, alongside the SSN program, underscores its commitment to becoming a formidable blue-water force. As geopolitical tensions in the IOR rise, India’s ability to maintain strategic dominance will hinge on a balanced mix of surface and subsurface assets. With both projects deemed indispensable, the Navy’s vision of a three-carrier fleet and a robust submarine force remains firmly on track.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:27:41World
Teledyne FLIR has secured a $7.8-million contract to supply Saudi Arabia with cutting-edge long-range thermal surveillance systems. The agreement, signed with the Middle East Task Company (METCO), involves delivering the company’s next-generation Lightweight Vehicle Surveillance System (LVSS) to a high-profile military entity in the Kingdom. Along with the surveillance units, the contract includes mission support equipment and specialized training to ensure seamless integration and operation. Stan Crawford, Senior Director of Business Development for the Middle East at Teledyne FLIR, highlighted the importance of the LVSS in strengthening Saudi Arabia’s national security. He emphasized that the system will enhance border protection, critical infrastructure monitoring, and shoreline defense. “We’re honored to work with METCO in supporting a key military entity in its critical mission of safeguarding the nation,” he said. While Teledyne FLIR has not disclosed the number of LVSS units to be delivered, the system’s capabilities make it a significant addition to Saudi Arabia’s security infrastructure. LVSS: A High-Tech Mobile Surveillance Solution The Lightweight Vehicle Surveillance System (LVSS) is a compact and mobile surveillance platform designed for rapid deployment in critical missions. The system is mounted in the bed of a standard commercial pickup truck, making it highly versatile for military and security operations. At its core, the LVSS integrates Teledyne FLIR’s TacFLIR 380HD thermal imaging system with the Ranger R20SS radar, enabling advanced detection capabilities. The system can track and identify up to 500 objects at distances exceeding 10 miles (16 kilometers), making it ideal for monitoring vast areas. One of its standout features is a 16-foot (5-meter) retractable mast, which provides an elevated view to overcome obstacles like trees and structures. The LVSS can be fully deployed by a single operator in under 30 seconds, offering unmatched speed and flexibility. Designed for both air- and ground-based threat detection, the LVSS is particularly well-suited for protecting military bases, vital infrastructure, and personnel. Its ability to operate efficiently in rugged environments makes it a critical tool in securing Saudi Arabia’s borders and key assets. With this latest contract, Teledyne FLIR continues to strengthen its presence in the Middle East, providing advanced surveillance technology to support regional security initiatives.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:22:02World
In a bold and highly coordinated operation, Ukrainian forces executed a rare cross-border strike, successfully destroying four Russian helicopters stationed in the Belgorod region. This strike, carried out by Ukraine’s Special Operations Forces in collaboration with the Main Directorate of Intelligence and Rocket and Artillery Forces, underscores Kyiv’s growing ability to reach deep behind enemy lines. The attack specifically targeted a concealed Russian “jump site” — a forward base used for rapid helicopter deployment and surprise assaults. Ukrainian forces eliminated two Ka-52 Alligator attack helicopters and two Mi-8 Hip transport helicopters using GMLRS M30A2 precision-guided rockets. These munitions, equipped with tungsten ball warheads, were reportedly launched from the highly effective HIMARS (High Mobility Artillery Rocket System) platforms. Footage from the operation, captured via drone surveillance, shows direct hits on the parked helicopters, reducing them to wreckage. The Ukrainian military emphasized that the location had been under careful observation before the strike, ensuring maximum impact in disrupting Russian rotary-wing operations near the border. A Ukrainian Special Operations Forces statement highlighted the significance of the attack: “In another coordinated strike, the enemy’s illusion of safety deep behind the front lines was shattered. Once again, we have shown that nothing is out of reach for our units. The work continues.” The Ka-52 Alligator is one of Russia’s most advanced attack helicopters, used for both reconnaissance and precision strikes against ground targets. Meanwhile, the Mi-8 serves as a crucial logistics and transport aircraft, ferrying troops and supplies to frontline positions. By targeting these assets, Ukraine has likely disrupted key Russian military operations in the region. The use of GMLRS munitions reflects Ukraine’s continued reliance on Western-supplied precision weaponry to strike critical enemy positions beyond traditional battlefield ranges. These rockets are designed for pinpoint accuracy, making them highly effective against high-value targets such as parked aircraft, command centers, and supply depots. As of now, Russian authorities have not officially confirmed the loss of these helicopters. However, the attack demonstrates Ukraine’s expanding strategic reach and its ability to challenge Russian airpower even beyond the frontline.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:18:25World
American defense contractor HII has been selected by the U.S. Army’s Rapid Capabilities and Critical Technologies Office (RCCTO) to develop a cutting-edge high-energy laser (HEL) weapon system. This next-generation system is designed to provide a powerful countermeasure against unmanned aircraft systems (UAS), ensuring robust force protection in modern battlefields. A Highly Adaptable and Scalable Defense System HII’s HEL weapon will leverage an open-architecture framework, allowing seamless integration with various military platforms. It is primarily aimed at neutralizing Group 1-3 drones, which range from small commercial quadcopters to larger tactical UAS. The system will be deployable in both fixed and mobile configurations, enabling military forces to adapt to rapidly changing operational needs. One of the key advantages of this system is its scalability. The modular design allows for easy enhancements, ensuring that new technologies can be incorporated as threats evolve. The laser weapon will offer a sustainable alternative to traditional kinetic air defense systems, reducing reliance on costly missiles while maintaining high precision and efficiency. Technological Edge and Strategic Importance HII’s prototype will include a high-powered directed energy weapon capable of engaging multiple aerial threats at once. This system will integrate advanced tracking, targeting, and engagement software to provide real-time threat assessment and response. The HEL’s ability to fire multiple times without reloading makes it a cost-effective and continuous-use defense asset. As part of the contract, HII will provide critical system data to support further innovation and the competitive development of subsystems. This aligns with the Army’s Modular Open Systems Approach, emphasizing cost efficiency, interoperability, and rapid upgrades. According to Grant Hagen, President of HII’s Mission Technologies Warfare Systems group, “We are proud to provide a critical enabler for the Army, delivering an effective, interoperable, sustainable, and scalable system that will meet force protection requirements and support U.S. strategic objectives.” From Prototype to Deployment The HEL project will undergo extensive field testing to assess its performance, safety, and operational viability. The goal is to transition the weapon to the Army’s Program Executive Office for Missiles and Space, which could lead to low-rate initial production in the near future. This initiative marks a significant step in the Army’s efforts to counter the increasing threat of drone warfare. As adversaries continue to develop and deploy unmanned aerial systems, high-energy laser weapons offer a critical advantage by providing an efficient, rapid-response solution for battlefield protection. HII: A Leader in Defense Innovation Based in Virginia, HII is the largest military shipbuilder in the United States, employing over 44,000 personnel. The company is known for its expertise in all-domain defense solutions, including unmanned systems, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and synthetic training. This latest project further reinforces HII’s role in advancing U.S. military capabilities and ensuring national security.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:15:34India
Morocco and India’s Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) are strengthening their defense ties with an ambitious plan to develop new battlefield variants of the Wheeled Armoured Platform (WhAP), an 8x8 armored vehicle known for its adaptability. This collaboration will introduce high-caliber gun-equipped models and a dedicated medical variant, enhancing the vehicle’s capabilities to meet Morocco’s evolving military needs. The move follows a major agreement in late 2024, under which TASL secured a contract to supply the Royal Moroccan Army with 150 WhAP units. A key aspect of the deal is the establishment of a local production hub in Casablanca, operated by Tata Advanced Systems Maroc (TASM), which aims to increase Moroccan manufacturing content from 35% to 50% over time. The facility is also positioned to serve as an export center for other African nations, marking a significant step in India's expanding defense footprint in the region. A Battlefield Workhorse with Enhanced Firepower The WhAP, originally developed in collaboration with India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is a highly versatile armored vehicle designed for various battlefield roles. Depending on its configuration, it weighs between 20 and 27 tons and features a modular design that allows for easy adaptation to different mission requirements. The baseline model, which Morocco has already ordered, comes with a 30mm cannon and is fully amphibious, giving it an operational edge in diverse terrains. Moroccan trials in 2022 demonstrated the WhAP’s superior performance over China’s Type-08 armored vehicle, solidifying its selection. Powered by a 600hp Cummins diesel engine, it offers excellent mobility and protection against small arms fire and improvised explosive devices (IEDs). Advanced active protection systems can be added to enhance its survivability further. Building on this foundation, Morocco plans to introduce a variant equipped with a 105mm cannon for enhanced direct combat capability. Additionally, a more powerful 120mm cannon version is under consideration, potentially giving the WhAP the ability to engage heavier armored targets—an important capability for modern battlefield scenarios. The specific source of these cannons has not been officially disclosed, but Morocco’s current armored fleet includes aging Soviet-era T-72B/BK tanks and VT-1A Al Khalid tanks, both equipped with 125mm guns. Given this disparity in calibers and the obsolescence of some of these platforms, Morocco is likely to turn to external suppliers for the WhAP’s new weaponry. Potential candidates include European defense firms like John Cockerill and Indian companies such as DRDO and Bharat Forge, both of which have experience in designing compatible gun systems. A Battlefield Medical Hub Alongside firepower upgrades, Morocco is also prioritizing battlefield medical support with a WhAP-based armored ambulance variant. This version will retain the 8x8 chassis for mobility but replace armament with a dedicated medical compartment designed for casualty evacuation and emergency treatment. Equipped with life-saving equipment, this model will provide critical support for frontline operations, further diversifying Morocco’s armored capabilities. The addition of this medical variant aligns with Morocco’s broader military modernization strategy, which seeks to replace aging French-supplied armored vehicles with more versatile and unified platforms. The Royal Moroccan Army is keen on improving battlefield logistics and personnel survivability, and the introduction of a dedicated medical evacuation platform is a logical step toward that goal. A Gateway to African Defense Markets For TASL, the Moroccan WhAP contract marks a strategic entry into the African defense market, with significant long-term potential. The deal, first announced at the Marrakech Air Show 2024, has already drawn interest from other nations in the region. By establishing a local production facility, India not only strengthens its defense industry’s global presence but also enables Morocco to develop its manufacturing base and create new job opportunities. The success of the WhAP program in Morocco could pave the way for future Indo-Moroccan defense cooperation, including joint development projects and further localized production. With the African continent emerging as a growing market for military equipment, TASL’s Moroccan expansion could serve as a launchpad for wider regional exports. As Morocco diversifies its defense partnerships and enhances its military capabilities, the WhAP program represents a forward-looking investment in battlefield adaptability, firepower, and operational readiness.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:06:10World
The U.S. Navy is on the verge of selecting a contractor for its next-generation carrier-based stealth fighter jet, known as the F/A-XX program. This initiative aims to replace the aging F/A-18E/F Super Hornet fleet and represents a significant long-term investment, potentially spanning several decades and amounting to hundreds of billions of dollars. Strategic Significance The F/A-XX program is a critical component of the U.S. military's strategy to address emerging challenges in the Indo-Pacific region, particularly in response to China's growing influence. The new aircraft is expected to feature advanced stealth capabilities, extended operational range, and enhanced integration with uncrewed combat aircraft and existing carrier-based air defense systems. These advancements will enable the Navy to conduct extended missions and operate effectively in networked combat environments. Contractor Competition The competition for the F/A-XX contract has been intense, with major defense contractors Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman submitting detailed proposals and prototypes. However, recent reports indicate that Lockheed Martin has been eliminated from the competition due to challenges in meeting the Navy's specific radar and carrier landing requirements. This development leaves Boeing and Northrop Grumman as the primary contenders for the contract. Boeing has recently secured the U.S. Air Force's F-47 contract, demonstrating its capability to manage large-scale defense projects. Despite facing setbacks such as labor strikes and issues with the KC-46 tanker and Starliner capsule, Boeing's success with the F-47 contract suggests potential economies of scale if it can leverage shared technology and bulk procurement strategies. Northrop Grumman is renowned for producing advanced stealth platforms, including the B-2 and B-21 bombers. The company's proven track record in delivering cutting-edge aerospace systems strengthens its position as a strong contender for the F/A-XX program. Program Timeline The U.S. Navy has not yet made a public announcement regarding the contractor selection. The newly confirmed Secretary of the Navy, John Phelan, has not issued a statement on the matter. The first F/A-XX aircraft are anticipated to enter service in the 2030s, with the current F/A-18 fleet expected to remain operational into the 2040s. Analysis The F/A-XX program represents a pivotal advancement in naval aviation, aiming to equip the U.S. Navy with superior capabilities to maintain air dominance in increasingly contested environments. The emphasis on stealth, extended range, and integration with uncrewed systems reflects a strategic shift towards more versatile and survivable platforms. The elimination of Lockheed Martin from the competition underscores the Navy's stringent requirements and the challenges inherent in developing next-generation fighter aircraft. The remaining contenders, Boeing and Northrop Grumman, each bring unique strengths to the table, and the forthcoming decision will significantly influence the future trajectory of U.S. naval air power. As the program progresses, it will be essential to monitor how the selected contractor addresses the technical and operational challenges associated with developing and deploying the F/A-XX. The success of this initiative will have far-reaching implications for the U.S. Navy's ability to project power and maintain strategic advantages in key regions around the world.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 15:02:37India
India's semiconductor industry is on a promising growth trajectory, but a recent Jefferies report highlights significant hurdles that must be addressed to realize its full potential. The country is making strides in semiconductor design and policy support, yet challenges such as an underdeveloped supply chain, a shortage of specialized manufacturing talent, and fierce global competition threaten to slow progress. Supply Chain Bottlenecks and Material Shortages One of the major roadblocks in India's semiconductor manufacturing ambitions is the limited availability of critical raw materials. High-purity silicon wafers, specialty chemicals, ultra-pure water, and semiconductor-grade gases are essential components in chip production, yet India remains dependent on imports for most of these resources. While the country has a strong base in chemical and gas manufacturing, particularly in Gujarat’s Dahej region, it lacks the infrastructure and expertise to produce semiconductor-grade materials at scale. To bridge this gap, the government has launched initiatives aimed at localizing the supply chain. However, building a self-reliant semiconductor ecosystem will take time, as it requires significant investments in refining processes and establishing partnerships with global suppliers. Talent Shortages in Semiconductor Fabrication India has a well-established presence in semiconductor design, contributing nearly 20% of the global chip design workforce. Companies such as Tata Electronics and Wipro are actively involved in chip design, but the country falls short when it comes to semiconductor fabrication (chip manufacturing) and testing expertise. Unlike established players like Taiwan, South Korea, and the U.S., India lacks a trained workforce that can handle complex fabrication processes, which require precision engineering and specialized skills. To address this issue, the government is working with educational institutions to develop relevant courses and training programs. Several semiconductor firms are also investing in workforce development to ensure a steady pipeline of skilled professionals. However, it will take years of structured training to develop an industry-ready workforce that can compete globally. Global Competition and Policy Incentives India's semiconductor industry faces stiff competition from established global hubs such as China, Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, and South Korea. These nations have spent decades perfecting their semiconductor ecosystems and offer lucrative incentives to attract top manufacturers. Recognizing this, India has rolled out an ambitious incentive program, including financial support for semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) and tax benefits for manufacturers. However, setting up advanced fabrication units in India presents inherent risks. Semiconductor manufacturing requires high precision and involves initial production hurdles, such as maintaining yield quality and addressing defects in early production runs. The long-term success of India's semiconductor strategy will depend on securing consistent demand for locally manufactured chips and establishing strong export channels. The Road Ahead: Innovation and Investment The rapid evolution of semiconductor technology means that India must not only catch up but also invest heavily in R&D to stay competitive. Global leaders in the industry are pushing the limits of chip miniaturization and efficiency, and any delay in technological advancements could hinder India’s ambitions. Despite these challenges, India's semiconductor industry has enormous potential, thanks to government backing, industry collaboration, and foreign investments. If the country can develop a robust supply chain, bridge its talent gap, and establish itself as a reliable manufacturing hub, it has the opportunity to become a key player in the global semiconductor market. The next few years will be crucial in determining whether India can turn its semiconductor aspirations into a sustainable, world-class industry.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 14:59:32India
In a significant enhancement of India's defense capabilities, the Indian Army and Air Force are set to acquire approximately 250 BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, each capable of striking targets beyond 800 kilometers. This development follows the Defence Acquisition Council's approval and awaits final clearance from the Cabinet Committee on Security. Enhanced Range and Capabilities The BrahMos missile, originally designed with a range of about 300 kilometers, has undergone substantial upgrades. The extended-range variant now boasts the ability to engage targets over 800 kilometers away, providing the Indian armed forces with a significant strategic advantage. This enhancement allows for deep-strike capabilities, enabling precise targeting of high-value assets from considerable distances. Deployment and Strategic Implications The newly acquired missiles will be integrated into units operating in diverse terrains, including both desert regions and high-altitude areas. This deployment strategy ensures operational flexibility and readiness across various potential conflict zones. The extended range of the BrahMos missiles enhances India's deterrence posture, allowing for rapid and precise responses to emerging threats. Indigenization and Export Potential BrahMos Aerospace, the Indo-Russian joint venture responsible for developing the missile, has achieved notable success in indigenizing major components of the weapon system. Collaborations with the private sector have further bolstered this effort, reducing reliance on foreign technology and fostering self-reliance in defense manufacturing. The missile's export success, exemplified by the deal with the Philippines, underscores its growing international demand and India's emergence as a key player in the global defense market. Future Developments Looking ahead, BrahMos Aerospace is focusing on the development of the BrahMos Next Generation (NG) missiles. These advanced variants promise enhanced performance and versatility, with production slated to commence in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh. The BrahMos NG aims to further solidify India's position in cutting-edge missile technology and expand its footprint in the international defense arena. The acquisition of the extended-range BrahMos missiles marks a pivotal step in augmenting India's defense capabilities, ensuring preparedness to address evolving security challenges effectively.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 14:55:03World
Israel has recently conducted a series of advanced interception tests for its renowned Iron Dome air defense system, integrating ELTA Systems' state-of-the-art Multi-Mission Radar (MMR). These tests represent a significant advancement in Israel's defensive capabilities, showcasing the system's enhanced ability to detect and neutralize a diverse array of aerial threats. Enhanced Detection and Tracking Capabilities The MMR, developed by ELTA Systems—a subsidiary of Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)—is a sophisticated mobile S-Band radar equipped with an advanced 4D Active Electronically Steered Array (AESA). This technology enables the Iron Dome to perform rapid identification and accurate tracking of incoming threats, providing critical data for the system to effectively intercept and neutralize multiple targets simultaneously. Rigorous Testing Scenarios During the recent trials, two Iron Dome batteries, each armed with 20 interceptors, were subjected to a variety of challenging scenarios. These included confronting numerous rocket and drone threats approaching from multiple directions. Notably, some interceptors demonstrated the capability to follow slower rockets before successfully intercepting them from behind. The MMR played a pivotal role in precisely detecting and tracking these simulated cruise missile trajectories, ensuring accurate and timely interceptions. Operational Lessons and Continuous Improvement The Israeli Missile Defense Organization (IMDO) emphasized that these tests incorporated new capabilities, marking a significant leap in the Iron Dome's performance and its ability to counter a diverse range of threats. The scenarios simulated both current and anticipated future challenges, all of which were reportedly handled successfully. This progression builds upon operational lessons learned from previous engagements with Hamas in the south and Hezbollah in the north. Moshe Patel, head of the IMDO, highlighted that throughout these conflicts, the Iron Dome has remained a critical asset, even when facing intense barrages. He noted that the latest tests have validated several new capabilities, reinforcing confidence in the system's ability to safeguard Israel and its citizens. Manufacturer's Perspective Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Ltd., the primary contractor for the Iron Dome's development under the IMDO, hailed these tests as the most extensive and significant ever conducted. They emphasized that the successful outcomes enhance Israel's capacity to address evolving and future threats effectively. The successful completion of these advanced interception tests underscores Israel's commitment to continually enhancing its defensive technologies. By integrating ELTA Systems' MMR, the Iron Dome has significantly improved its detection, tracking, and interception capabilities, ensuring robust protection against a wide spectrum of aerial threats.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-25 14:51:14Space & Technology
India's robotics sector has witnessed significant advancements, with several companies making notable strides in humanoid and semi-humanoid robot development. Here's an overview of some key players and their achievements: 1. Addverb Technologies Founded in 2016, Addverb Technologies specializes in industrial robotics and warehouse automation. In November 2024, the company announced its entry into humanoid robotics, aiming to launch a next-generation humanoid robot in 2025. This robot is designed to process multi-modal data from vision, audio, and touch inputs, enabling it to navigate complex environments and perform intricate tasks across industries such as warehousing, defense, and healthcare. Addverb's collaboration with Reliance, leveraging Jio's AI platform and 5G services, underscores its commitment to advancing India's robotics capabilities. 2. Svaya Robotics Hyderabad-based Svaya Robotics has emerged as a pioneer in collaborative robots that work alongside humans to enhance productivity and flexibility. The company's robots are designed for tasks ranging from assembly and machine tending to packaging and inspection. In March 2023, Svaya developed India's first indigenous quadruped robot and wearable exoskeleton for the defense sector. These innovations aim to assist soldiers in navigating challenging terrains and carrying heavy loads with reduced effort, thereby minimizing fatigue and potential health impacts. Svaya's advancements have garnered attention from defense officials and underscore the company's role in augmenting India's defense capabilities through robotics. 3. Vanar Robots Specific information about Vanar Robots is limited based on current sources. It is advisable to consult the company's official communications or industry reports for detailed insights into their projects and achievements in humanoid or semi-humanoid robotics. 4. General Autonomy Detailed information about General Autonomy's endeavors in humanoid or semi-humanoid robotics is not readily available from the provided sources. For comprehensive details, referring to the company's official channels or recent industry analyses would be beneficial. 5. Perceptyne Information regarding Perceptyne's involvement and progress in the field of humanoid or semi-humanoid robotics is currently scarce. To gain a better understanding of their work, consulting official publications or industry-specific resources is recommended. In summary, while companies like Addverb Technologies and Svaya Robotics have made significant contributions to India's humanoid and semi-humanoid robotics landscape, information on Vanar Robots, General Autonomy, and Perceptyne remains limited. As the industry evolves, it is anticipated that more detailed information about these and other emerging players will become available.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 16:01:16World
The United States Air Force's (USAF) Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program has sparked intrigue and debate with the release of concept images for Boeing’s proposed F-47 sixth-generation fighter. While the aircraft’s futuristic design hints at cutting-edge advancements, one particular detail—the inclusion of canards in some renderings—has triggered speculation among defense analysts and aviation experts. Canards vs. Stealth: A Design Dilemma The images show two strikingly different configurations of the F-47. One version features a sleek, tailless delta-wing design, aligning with expectations for stealth-focused airframes. The other, more controversial, includes forward-mounted canards—small aerodynamic surfaces that enhance maneuverability but can also increase an aircraft's radar cross-section (RCS). Traditionally, stealth aircraft such as the F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II have avoided such protrusions to maintain low observability. Canards, while beneficial for agility—as seen in the Eurofighter Typhoon and Dassault Rafale—are generally not favored in stealth designs due to their potential to reflect radar signals. This has led to questions about whether Boeing has found a way to integrate them without compromising stealth or if the canard-equipped F-47 represents a specialized variant. Misdirection or a Technological Leap? The presence of two distinct designs has fueled speculation about whether Boeing’s canard-equipped rendering is a genuine proposal or a deliberate misdirection. The defense industry has a history of using misleading concept art to obscure the true nature of classified projects. Some analysts suggest that the canards might be part of a modular or mission-adaptive design, allowing the aircraft to swap configurations depending on operational needs. Another possibility is that advances in materials and radar-absorbing coatings have enabled a design that mitigates the radar reflectivity of canards. If so, this could represent a significant leap in stealth technology. Additionally, Boeing's claim that the F-47 could reach speeds of Mach 2 suggests improvements in thermal-resistant stealth coatings, a factor that could contribute to managing radar signature. What Does This Mean for NGAD? The USAF’s NGAD program aims to replace the F-22 with a highly advanced fighter capable of dominating future battlefields. Given the secrecy surrounding NGAD, it’s unclear whether the F-47 will be a singular aircraft or part of a family of systems, including both crewed and uncrewed platforms. The two F-47 designs hint at different mission priorities. A canard-equipped version would likely excel in close-range dogfighting and high-agility engagements, possibly operating alongside uncrewed Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA). Conversely, a canard-less, pure-delta-wing configuration would prioritize stealth, making it more suited for long-range strikes and deep penetration missions. There is also speculation that NGAD could field multiple variants of the F-47 to fulfill diverse roles, similar to how the F-35 program developed the A, B, and C models for different branches of the military. If Boeing is pursuing a modular approach, allowing the aircraft to adapt to various mission profiles, this could redefine fighter jet development but would also pose significant engineering challenges. A Puzzle with Many Pieces The contrasting F-47 renderings offer a glimpse into the evolving strategy behind the USAF’s air dominance ambitions. Whether the canards are part of the final design, a testbed for new technologies, or a tactical diversion remains to be seen. However, the discussion surrounding them highlights the complex trade-offs between stealth, maneuverability, and mission versatility in next-generation air combat. As the NGAD program progresses, more details about the F-47 will likely emerge. Until then, the debate over Boeing’s controversial canard design remains an intriguing puzzle—one that may hold clues to the future of U.S. air superiority.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:54:56India
The Indian Army has issued a Request for Information (RfI) to identify potential vendors capable of manufacturing rocket ammunition for its 122mm GRAD BM-21 Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) system. This initiative aims to ensure a steady supply of compatible ammunition for the system, which plays a crucial role in the Army's artillery operations. About the 122mm GRAD BM-21 MBRL System The BM-21 "Grad" (Russian for "hailstorm") is a self-propelled 122mm multiple rocket launcher developed in the early 1960s. Renowned for its simplicity and effectiveness, the system can deliver a high volume of rockets over a wide area in a short time. It has been widely adopted and remains a staple in various military arsenals worldwide. Operational Requirements for the Ammunition The Indian Army has outlined specific operational requirements for the ammunition to be procured: Caliber: 122mm. Deployment Environments: The ammunition should be suitable for use in diverse terrains, including plains, high altitudes, semi-deserts, and desert regions, aligning with the varied geographical landscapes where the Indian Army operates. Range Compatibility: The rockets must have defined maximum and minimum ranges and be compatible with the existing 122mm GRAD BM-21 Rocket System. Each launch tube is approximately 2.8 meters in length. Fire Control System Integration: The ammunition should seamlessly integrate with the current Fire Control System to ensure accuracy and efficiency during operations. Transportation: The rockets should be transportable using existing ammunition-carrying vehicles without necessitating special arrangements, facilitating logistical convenience. Service Life: A minimum service life of 10 years is required. Additionally, the design should allow for extensions through in-house inspections, replacements, and repairs of sub-components as needed. Storage and Maintenance: The ammunition must be capable of being stored and maintained under field conditions, ensuring readiness and reliability during deployments. Standards Compliance: All components and sub-assemblies should conform to relevant military standards (MIL STD), ensuring quality and interoperability. Strategic Implications By seeking domestic manufacturers for this ammunition, the Indian Army aims to bolster its self-reliance in defense production, reduce dependence on foreign suppliers, and ensure a consistent and reliable supply chain for critical artillery resources. This move aligns with the broader national objective of promoting indigenous defense capabilities and fostering collaboration with local industries. The issuance of this RfI represents a significant step towards enhancing the operational readiness and effectiveness of the Indian Army's artillery units equipped with the 122mm GRAD BM-21 MBRL system.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:50:01World
Lockheed Martin, long considered a leader in the development of advanced combat aircraft, has found itself in an unusual position after losing out on the U.S. Air Force’s Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program. The announcement, made by former President Donald Trump, confirmed Boeing as the primary contractor for the highly classified program, which aims to replace the F-22 Raptor with a new, next-generation fighter. While Lockheed expressed disappointment, the company made it clear that it remains fully committed to pushing the boundaries of air superiority technologies. The NGAD program, officially designated as the F-47, represents a paradigm shift in air combat. Featuring cutting-edge stealth, sensors, and propulsion systems, the aircraft will integrate manned and unmanned teaming—an approach expected to define future warfare. The initial engineering and manufacturing development contract, reportedly valued at over $20 billion, is only the beginning. With production and operational deployment, the program could see total costs soaring into the hundreds of billions. Lockheed Martin had been one of the strongest contenders, given its track record with the F-22 and F-35. The company’s expertise in stealth technology, advanced avionics, and integrated combat systems made it a natural fit for NGAD. However, Boeing, which has also been involved in numerous classified programs, ultimately secured the contract. The decision reflects shifting dynamics within the defense industry, where competition is intensifying as the Pentagon seeks diversified solutions for maintaining air dominance. Despite this setback, Lockheed Martin is unlikely to fade into the background. The defense giant remains deeply invested in developing next-generation air combat solutions. The company has emphasized that it will continue to work on technologies such as sixth-generation fighter capabilities, artificial intelligence-driven combat networks, and next-level unmanned systems. Lockheed’s Skunk Works division—responsible for many of the U.S. military’s most advanced aircraft—remains a powerhouse of innovation, and its ongoing projects could still shape the future of aerial warfare. Moreover, NGAD is not the only game in town. The U.S. military’s modernization roadmap includes multiple programs aimed at sustaining its dominance in contested airspace. Lockheed’s continued involvement in classified initiatives, potential collaborations with allied nations, and possible participation in future upgrade cycles for NGAD suggest that it remains a key player in next-generation combat aviation. While losing NGAD is a blow, Lockheed Martin’s long-term strategy remains focused on developing and delivering cutting-edge air superiority solutions. In an era where air dominance is increasingly defined by adaptability and multi-domain operations, the company’s experience and innovation will likely ensure its relevance in future programs.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:40:58
EU Unveils €800 Billion Defence Plan to Strengthen Military Power by 2030 Amid Rising Russian Threat
World
The European Union has taken a decisive step toward strengthening its defence capabilities, unveiling an ambitious €800 billion plan aimed at fortifying Europe against external threats—particularly from Russia. The move signals a shift in strategy as the EU seeks to reduce its reliance on the United States for security, reinforcing the bloc’s defence infrastructure with a mix of direct investments, loans, and industrial development initiatives. A Call for European Military Autonomy For years, European security has been underpinned by the NATO alliance, with the United States playing a pivotal role in ensuring stability across the region. However, the EU's latest policy pivot reflects growing concerns about the uncertainty of long-term US commitments, particularly amid fluctuating political dynamics in Washington. EU foreign policy chief Kaja Kallas underscored the urgency of the initiative, warning, “We don’t have a cold war, but we have a hot war on European soil, and the threat is existential.” Echoing her concerns, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen stressed that Europe must achieve “readiness 2030,” ensuring it has the military strength and industrial capacity to act independently. The centrepiece of the plan is a €150 billion defence loan programme, designed to help EU nations modernize their arsenals while promoting homegrown military manufacturing. To sustain Europe's defence industry, the initiative requires that at least 65% of funds be spent within the EU, Norway, or Ukraine. This stipulation has drawn criticism from countries like Poland and the Netherlands, who argue it could hinder collaboration with key non-EU allies such as the United Kingdom and the United States. Geopolitical Tensions and NATO Concerns As tensions escalate with Russia, European leaders are grappling with the question of NATO’s durability. Danish intelligence agencies recently warned that if NATO appears weak, Moscow could launch a large-scale offensive in Europe within five years. This assessment has accelerated calls for a robust EU-led defence framework, with Danish Prime Minister Mette Frederiksen urging leaders to prepare for a fully capable European military by 2030. One of the most contentious aspects of the EU's plan is the exclusion of key allies like the UK, the US, and Turkey from receiving defence funding unless they sign formal security agreements with the bloc. While the UK remains a crucial military partner, no formal EU-UK defence pact exists, raising concerns over potential diplomatic fallout. Financial Hurdles and Political Divisions While the EU’s vision for military self-reliance is clear, its financing remains a significant challenge. The €800 billion target combines €150 billion in direct EU-backed loans with €650 billion in additional fiscal flexibility, allowing member states to borrow more for defence without violating EU spending rules. However, this plan has divided member nations. Germany and the Netherlands, both fiscally conservative, are hesitant to endorse large-scale EU-backed loans, while southern European countries remain wary of accumulating further national debt. Former Italian Prime Minister Mario Draghi has cautioned that Europe's security remains at risk due to uncertainties in US foreign policy, particularly regarding former President Donald Trump's past stance on Russia. At the same time, German officials have insisted that Europe's new strategy should not be seen as a move to “decouple” from Washington. EU as a Central Defence Buyer? Another major proposal under discussion is giving the European Commission the authority to act as a central buyer for military equipment—similar to how it procured COVID-19 vaccines. If implemented, this would allow the EU to negotiate and purchase critical defence assets such as missiles and drones on behalf of member states, potentially streamlining procurement and ensuring better cost efficiency. EU Defence Commissioner Andrius Kubilius emphasized the need for Europe to assume greater responsibility for its own security, stating, “The EU’s 450 million citizens should not have to depend on 340 million Americans to defend ourselves against 140 million Russians, who cannot defeat 38 million Ukrainians. We really can do better.” Pressure to Strengthen Defence Industry Funding The European Parliament is advocating for even greater investment in defence, arguing that the proposed European Defence Industry Programme (EDIP) falls short of what is needed. Lawmakers are pushing for an additional €15 billion from the Security Action for Europe (SAFE) fund to finance joint weapons procurement, along with another €5 billion to bolster Ukraine’s defence industry. To qualify for EU funding, defence companies must operate in at least five EU member states, Norway, or Ukraine. However, to prevent non-European firms from dominating, any involvement from Norwegian or Ukrainian companies must be balanced by at least one additional EU-based manufacturer. A Pivotal Moment for Europe’s Defence Strategy Despite broad agreement on the need for stronger military preparedness, the EU still faces major hurdles in implementing this plan. Disagreements over financing, restrictions on non-EU suppliers, and how much preference should be given to European manufacturers remain unresolved. Nevertheless, the message from Brussels is clear: Europe must take responsibility for its own security. As Russian aggression continues and NATO’s future stability remains uncertain, the EU’s push for military self-sufficiency could reshape the continent’s defence landscape for decades to come.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:36:50World
On March 21, 2025, Türkiye marked a significant achievement in its defense capabilities with the successful test-firing of the SOM-J (Stand Off Munition-J) cruise missile. Developed collaboratively by TÜBİTAK SAGE and Roketsan, the missile was launched from an F-16 of the Turkish Air Force's 401st Test Squadron, striking a naval target with pinpoint accuracy. Enhanced Capabilities and Strategic Importance The SOM-J is designed to engage both land and sea targets, offering versatility in modern combat scenarios. Key features include post-launch control via data link, allowing for retargeting, target updates, mission cancellation, and communication silencing. Its compatibility with Türkiye's indigenous air platforms, such as KAAN and KIZILELMA, underscores its integration into the national defense strategy. Equipped with an infrared seeker and an optimized warhead for surface targets, the missile also boasts low radar visibility, enhancing its stealth characteristics. Technical Specifications Length: Approximately 3.9 meters Weight: Around 540 kilograms Range: Up to 275 kilometers Warhead Weight: Approximately 140 kilograms Seeker: Imaging Infrared (IIR) Speed: High subsonic Guidance Systems: INS (Inertial Navigation System), GPS, TRN (Terrain Relative Navigation), ATA (Automatic Target Acquisition) Integration with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Plans are underway to integrate the SOM-J missile with Türkiye's advanced unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs), including the Bayraktar AKINCI and AKSUNGUR. This integration will enable these UCAVs to carry and deploy long-range cruise missiles, significantly extending their strike capabilities and adding a new dimension to unmanned warfare. Strategic Implications The development and successful testing of the SOM-J missile reflect Türkiye's commitment to enhancing its indigenous defense technologies. By equipping both manned and unmanned platforms with advanced munitions like the SOM-J, Türkiye aims to bolster its deterrence and operational effectiveness in modern warfare environments. This milestone not only demonstrates technological prowess but also signifies a strategic shift towards greater self-reliance in defense capabilities, positioning Türkiye as a formidable force in regional and global security dynamics. For a visual overview of Türkiye's advancements in air-launched cruise missile technology, you may find the following informative:
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:32:44World
China’s decade-long military transformation isn’t just about modernizing weapons or rooting out corruption—it’s about tightening control. Since taking office, President Xi Jinping has waged a relentless anti-corruption campaign that has purged nearly five million officials, including high-ranking military figures. His real objective? A battle-ready military, primed for a potential takeover of Taiwan by 2027. A newly declassified U.S. intelligence report, Wealth and Corrupt Activities of the Leadership of the Chinese Communist Party, paints a troubling picture of internal graft. Despite Xi’s sweeping crackdown, reports suggest that up to 65% of Chinese government officials still engage in bribery or corruption, and the practice of buying promotions within the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) remains common. The recent downfall of key figures like General Li Shangfu and Admiral Miao Hua—both once seen as untouchable—signals deeper concerns about loyalty within China’s military. A Blockade Before an Invasion? While an outright military invasion of Taiwan would be a high-risk operation, China has a far more effective strategy: an economic and military blockade. The PLA has rehearsed this scenario repeatedly. In October 2023, China conducted large-scale air and naval drills, involving a record 125 military aircraft alongside warships and missile units. Taiwan’s Ministry of Defense described it as a simulated blockade, one that included port closures and a full-scale encirclement of the island. China’s growing naval power makes this approach increasingly viable. The PLA Navy now has over 370 warships—more than any other country in the world. By 2030, that number is expected to reach 425, surpassing even the U.S. fleet. Though its aircraft carriers still lag behind their American counterparts in capability, China is rapidly closing the gap. But China’s most potent weapon in such a scenario may not be military at all—it could be cyberwarfare. Every time China conducts military exercises near Taiwan, it is accompanied by a surge in cyberattacks against Taiwan’s government networks and infrastructure. The island’s vulnerabilities were further exposed in 2024 when undersea internet cables connecting it to the outside world were mysteriously severed. Taiwan’s Vulnerabilities: Energy, Food, and Isolation Taiwan’s biggest weakness isn’t its military—it’s its dependence on imports. The island relies on foreign sources for 96% of its energy, importing nearly all its oil, coal, and natural gas. A prolonged blockade could deplete Taiwan’s reserves, forcing blackouts or even surrender. Food security is another major concern. Taiwan imports about 70% of its food supply. A Chinese blockade could strangle the island economically, creating shortages and pressure to negotiate. Rather than an overt military blockade, China could implement a “quarantine,” selectively restricting shipments to Taiwan. By imposing inspections on vessels heading to Taiwanese ports, China could disrupt trade without immediate military confrontation. Shipping companies unwilling to comply would face exclusion from China’s lucrative markets—an economic chokehold with far-reaching consequences. Can Taiwan Hold the Line? A direct Chinese invasion of Taiwan would be one of the most complex military operations in modern history. The Taiwan Strait is notoriously rough, limiting the window for amphibious landings. Taiwan’s rugged coastline, combined with urban defense preparations, makes it an incredibly tough target. Advanced U.S.-supplied missile systems further strengthen its defense. Taiwan’s military has been preparing for this scenario. In March 2025, it conducted a five-day war game simulating a full-scale Chinese attack. Later this year, another exercise will focus on China’s potential invasion plans for 2027—aligning with U.S. intelligence assessments. Yet Taiwan’s fate may not be decided solely by military capability. The biggest question mark is the United States. While Washington maintains a policy of “strategic ambiguity” on defending Taiwan, recent global events have cast doubt on its commitment. Former President Donald Trump’s decision to suspend U.S. support for Ukraine shook allies worldwide. A similar move regarding Taiwan would embolden Beijing. Huang Chung-ting, a defense expert at Taiwan’s Institute for National Defense and Security Research, warned that Taiwan’s biggest threat may not be China’s military but U.S. isolationism. “Our worst nightmare scenario involving a blockade actually comes from American disengagement—where the U.S. decides to completely step away from Taiwan Strait issues,” he stated. The Road to 2027: Diplomacy or Confrontation? Despite China’s military build-up, Beijing appears to be walking a fine line. While ramping up war rhetoric, China has also maintained diplomatic engagement with Washington. Economic stability remains a priority for Xi, and an abrupt escalation could hurt China as much as Taiwan. Taiwan’s newly elected President Lai Ching-te has taken a harder stance against Beijing, referring to China as a “foreign hostile force” for the first time. In response, China issued 18 separate condemnations in just four days, labeling him a “cornered dog.” Such reactions indicate that China is keeping the pressure on but stopping short of outright war—at least for now. Meanwhile, tensions between the U.S. and China continue to simmer. However, there are signs of de-escalation. Former President Trump recently hinted that Xi Jinping could visit Washington soon, potentially opening the door to renewed diplomacy. But for Taiwan, time is running out. With 2027 fast approaching, the island must prepare for the very real possibility that China’s military drills could become the real thing. The world is watching. And so is Xi.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:29:31World
India’s ambitious Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program is set to receive a major boost as the Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has proposed a budget of at least $4.5 billion (approximately ₹37,500 crore) to develop a next-generation jet engine. The new engine, capable of generating 110-120 kilonewtons (kN) of thrust, is expected to play a crucial role in enhancing the country’s indigenous fighter jet capabilities. The proposed engine aims to match the performance of powerplants used in leading fighter jets such as the Eurofighter Typhoon’s EJ200 engine and the Dassault Rafale’s Snecma M88. Its advanced design will focus on improving the thrust-to-weight ratio, increasing fuel efficiency for extended flight durations, and ensuring greater durability. Additionally, features to lower the aircraft’s radar signature may be incorporated, making the AMCA a formidable stealth fighter. Developing such a high-performance engine is an enormous challenge, requiring extensive research, testing, and validation. A significant portion of the proposed funding will be allocated to R&D, which includes designing, prototyping, and evaluating engine performance under diverse flight conditions. The manufacturing process will involve cutting-edge techniques to produce highly complex components, while specialized test facilities will be established to conduct full-scale trials. Beyond development, the budget also covers the crucial integration of the engine into the AMCA aircraft, followed by comprehensive flight tests and the certification process. These steps are essential to ensure the engine meets safety and performance standards before it can be used in combat-ready jets. Successfully developing this engine will mark a major milestone for India’s defence sector, reducing dependence on foreign technology and strengthening the country’s position in advanced military aviation. If funded and executed as planned, this project will not only power future Indian fighter jets but also open doors for indigenous engine technology in upcoming defence projects.
Read More → Posted on 2025-03-24 15:24:17Search
Top Trending
-
 Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
-
 India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
India's TEDBF Program Takes Shape First Flight by 2028: Aiming for Naval Supremacy with Advanced Stealth and Technology
-
 Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
-
 China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
China Unveils the 6th-Generation “Baidi B-Type” Aerospace Fighter Concept
-
 Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
Key Differences Between 5th vs. 6th Generation Fighter Jets
-
 China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
-
 What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
What Would Happen if the USA Left NATO? A Comprehensive Analysis
-
 India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
Top Trending in 4 Days
-
 China’s Xinghuo: The World’s First Fusion-Fission Power Plant Set to Revolutionize Energy by 2030
China’s Xinghuo: The World’s First Fusion-Fission Power Plant Set to Revolutionize Energy by 2030
-
 U.S. Navy Nears Decision on Next-Generation F/A-XX Stealth Fighter Contractor
U.S. Navy Nears Decision on Next-Generation F/A-XX Stealth Fighter Contractor
-
 China’s Tiny Deep-Sea Drone Conquers the Mariana Trench, Outpacing US Navy Technology
China’s Tiny Deep-Sea Drone Conquers the Mariana Trench, Outpacing US Navy Technology
-
 India's $500 Kamikaze Drones: The Strategic Equalizer Against $10 Million War Machines
India's $500 Kamikaze Drones: The Strategic Equalizer Against $10 Million War Machines
-
 India Advances Ghatak Stealth Drone with Full-Scale Prototype, But Funding Holds the Key
India Advances Ghatak Stealth Drone with Full-Scale Prototype, But Funding Holds the Key
-
 Morocco and Tata Expand WhAP Armored Vehicle Lineup with Battlefield Upgrades, Including Medical and High-Caliber Cannons
Morocco and Tata Expand WhAP Armored Vehicle Lineup with Battlefield Upgrades, Including Medical and High-Caliber Cannons
-
 Bayraktar TB3 UCAV Demonstrates Precision Strike with IHA-122 Supersonic Missile
Bayraktar TB3 UCAV Demonstrates Precision Strike with IHA-122 Supersonic Missile
-
 Can Trump’s $100 Billion ‘Golden Dome’ Protect the U.S. from Nuclear and Hypersonic Missile Threats?
Can Trump’s $100 Billion ‘Golden Dome’ Protect the U.S. from Nuclear and Hypersonic Missile Threats?