India
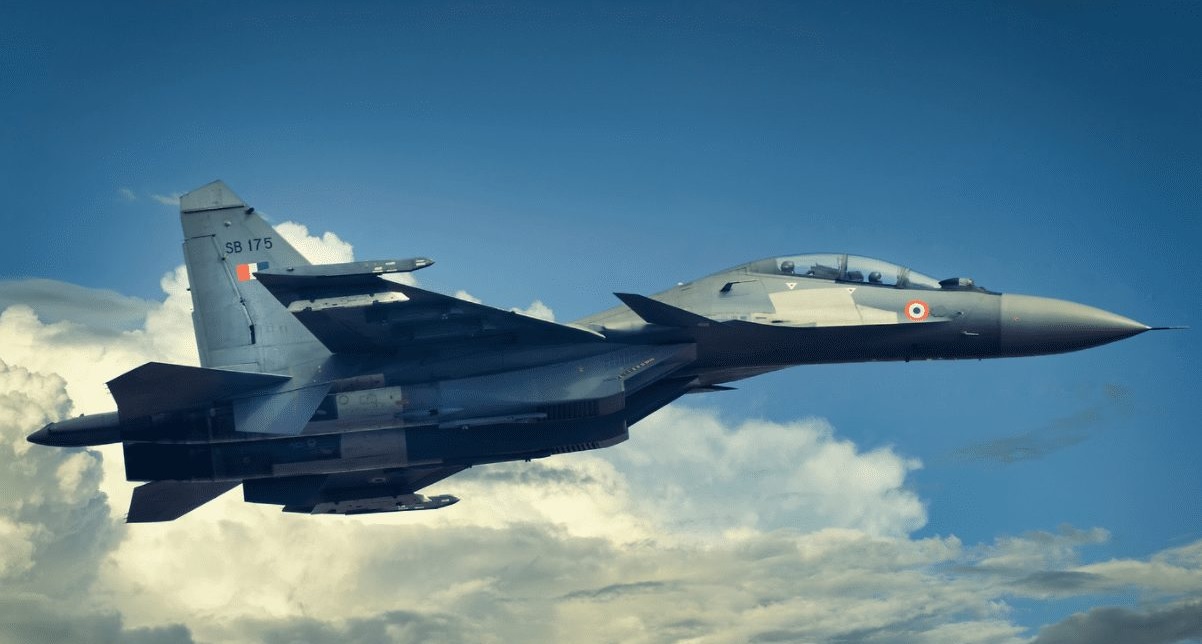
The Zhuhai Airshow 2024 marked a turning point in China's aerial combat strategy with the debut of the J-15D electronic warfare (EW) fighter jet. This new platform underscores China's focus on dominating the electronic battlefield, a key factor in modern warfare where electromagnetic supremacy can decide the outcome of conflicts. For India, this development reignites questions about its delayed plans to upgrade the Su-30MKI into a robust EW platform.A Closer Look at the J-15D The J-15D, derived from China's J-15 carrier-based fighter jet, represents a significant step forward for the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN). Built by Shenyang Aircraft Corporation, the J-15D is tailored for electronic attack missions. It features advanced jamming pods mounted under its wings, capable of disrupting enemy radars, communications, and missile guidance systems. Notably, the J-15D’s avionics suite and internal wiring have been optimized for EW tasks, and the aircraft reportedly integrates an active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar. While it draws visual and structural similarities to the J-15, the J-15D eliminates the internal 30mm cannon to make room for its EW equipment. With this, the J-15D inches closer to the U.S. Navy’s EA-18G Growler, widely regarded as the gold standard for EW fighter jets. India's Stalled "Desi Growler" While China flexes its EW capabilities, India continues to lag in this critical domain. The Indian Air Force (IAF) has long envisioned an EW variant of the Su-30MKI—one of its most versatile and capable fighter jets. However, bureaucratic inertia, funding limitations, and delayed decision-making have stalled progress on this vital project. India's proposed EW Su-30MKI, colloquially referred to as the "Desi Growler," could carry an array of indigenous systems, including DRDO-developed jamming pods and radar warning receivers. Equipped with an AESA radar and systems like the DARE-developed "Tarang" radar warning suite, such a platform could neutralize advanced enemy air defense systems while supporting strike missions deep into contested territories. The Su-30MKI has the payload capacity and endurance to accommodate the additional equipment required for an EW role. However, the absence of a clear roadmap has hindered its evolution into a multi-role electronic attack platform. Strategic Implications The J-15D’s unveiling is a wake-up call for India. As China narrows the gap with Western powers like the United States in EW technology, India's failure to prioritize similar advancements risks leaving its air force at a disadvantage in a region dominated by dense air defense networks. The Su-30MKI’s potential as an EW fighter is vast, but unlocking it requires urgent action. A dedicated EW platform would not only enhance the IAF's ability to operate in contested airspaces but also align with India's broader objectives of indigenization and strategic autonomy. By fast-tracking the "Desi Growler," India could reduce its dependence on foreign systems and reinforce its regional military posture. Conclusion The debut of the J-15D demonstrates China's rapid strides in naval and electronic warfare. For India, the writing is on the wall. To remain competitive in the evolving landscape of aerial combat, it must bridge its EW capability gap by transforming the Su-30MKI into a cutting-edge EW platform. The longer India delays, the wider the gap grows—a reality it cannot afford in an era defined by electronic dominance.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-20 15:33:52India
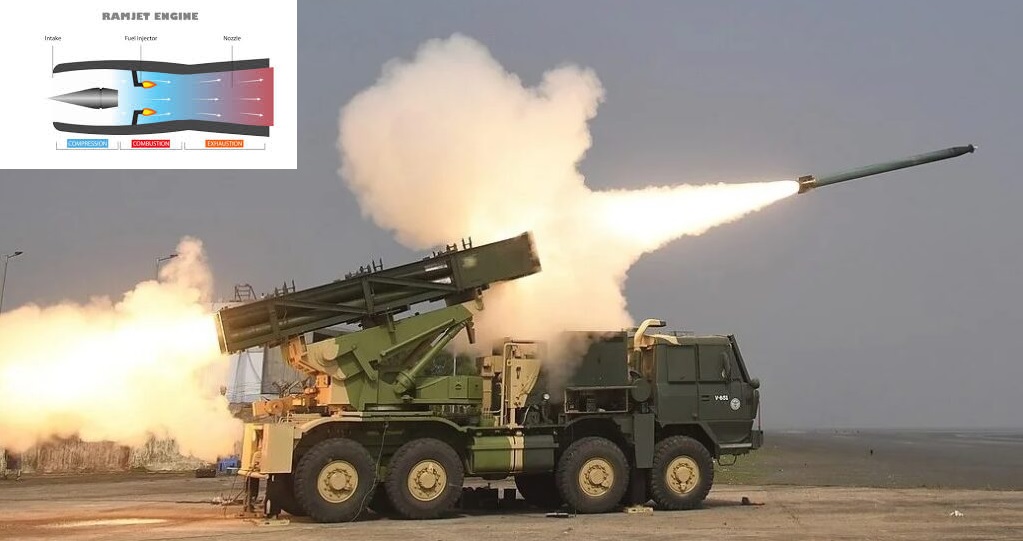
The Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT Madras) is spearheading groundbreaking research that could revolutionize India’s artillery capabilities. A team led by Lt. Gen. P.R. Shankar (Retd.), a former Director General of Artillery in the Indian Army, is developing ramjet propulsion technology to enhance the range of the Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) system. This technological leap aims to extend the rocket's range from its current 75 kilometers to an estimated 225 kilometers, marking a pivotal advancement in the nation’s defense arsenal.The Current Pinaka System The Pinaka Mk II, an integral part of India's artillery framework, operates with a high-energy composite solid-fuel rocket motor. This system allows for precise strikes up to 75 kilometers, making it an effective medium-range weapon for the Indian Army. However, as the need for longer-range and precision-strike capabilities grows, the current technology is reaching its limits. How Ramjet Technology Transforms the Pinaka Ramjet propulsion technology offers a novel solution to overcome range limitations. Unlike traditional rocket motors that carry both fuel and oxidizers, a ramjet engine is air-breathing. It uses the rocket's forward motion to compress incoming air for combustion, resulting in a lighter design and sustained thrust throughout the projectile's flight. This reduction in onboard oxidizer weight not only boosts fuel efficiency but also enables the rocket to maintain high speeds over extended distances. This means the enhanced Pinaka would achieve a significantly reduced drag profile, allowing for a range that is three times greater than its current capacity. Challenges in Adopting Ramjet Propulsion While promising, adapting the Pinaka MBRL for ramjet propulsion involves several engineering challenges. Modifications to the rocket's aerodynamics, propulsion mechanisms, and guidance systems are critical. Additionally, ramjet engines require advanced materials capable of withstanding extreme thermal and mechanical stresses during high-speed flight. Cost considerations also factor into the equation, as the integration of ramjet technology demands sophisticated manufacturing techniques and precision engineering. However, the strategic advantages far outweigh these hurdles, making it a worthwhile investment. Strategic Implications Once operational, a ramjet-powered Pinaka with a range of 225 kilometers would offer unprecedented tactical flexibility. Indian forces could engage targets deep within adversary territory while remaining at a safe distance from counterfire. This enhanced reach would also reduce the need for frequent repositioning of artillery units, improving operational efficiency during prolonged engagements. Moreover, the development aligns with India's push for self-reliance in defense technology. By advancing indigenous capabilities in propulsion and long-range strike systems, IIT Madras is contributing to the nation’s strategic preparedness and global standing in military innovation. The Road Ahead As the project progresses, the IIT Madras team is navigating the complexities of integrating ramjet propulsion into the Pinaka system. Their work is a testament to India's growing emphasis on harnessing cutting-edge technology to bolster its defense infrastructure. If successful, this breakthrough could not only redefine the Pinaka’s capabilities but also set a new benchmark for artillery systems worldwide. This innovation underscores the critical role of academia-industry collaboration in shaping the future of defense technologies and securing India’s strategic interests.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-20 15:16:47India
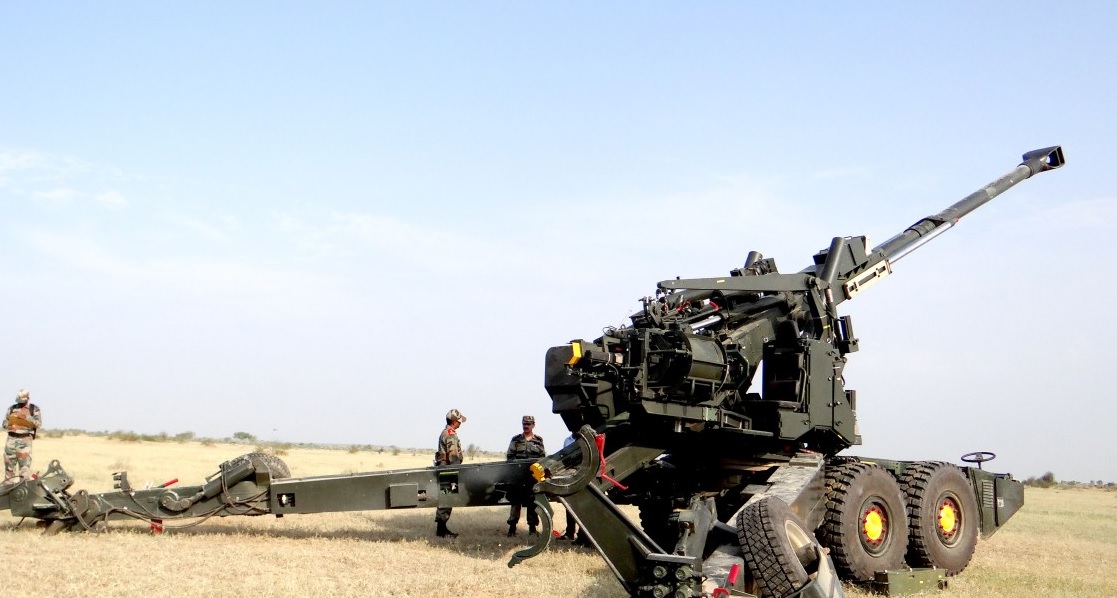
After successfully deploying and testing an initial batch of six Advanced Towed Artillery Gun Systems (ATAGS), Armenia is entering advanced discussions to acquire 78 additional units from India’s Kalyani Strategic Systems Limited (KSSL). This move underscores the growing strategic ties between Armenia and India, as well as the increasing global demand for India's cutting-edge defense technology.Proven Performance in Armenia's Unique TerrainThe six ATAGS units delivered to Armenia in 2023 were rigorously evaluated in diverse and challenging conditions, including high-altitude mountainous regions and open plains. The trials demonstrated the gun system's exceptional performance, particularly its long-range precision, adaptability, and robust reliability. To better suit Armenian operational needs, the systems were modified with features like an Armenian-language user interface, ensuring seamless integration with local forces.The Armenian Army's positive experience with these initial units has paved the way for the country’s Ministry of Defence to pursue a larger procurement of this advanced 155mm/52-calibre artillery gun. These additional units are expected to include refinements based on the feedback from the initial deployment, ensuring they are tailored to Armenia's specific tactical requirements.ATAGS: A Technological PowerhouseDeveloped by India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with private sector giants like Kalyani Strategic Systems, ATAGS boasts a range of features that set it apart on the global stage. The gun system offers:Exceptional Range: Capable of firing beyond 48 kilometers with extended-range ammunition.High Burst Rate of Fire: ATAGS can fire five rounds in short bursts, maintaining high operational efficiency.Advanced Automation: A fully automated loading system ensures speed and safety during operations.Robust Design: Designed for diverse terrains, including deserts, plains, and high-altitude areas.Strategic Mobility: Despite its heavy build, ATAGS can be efficiently deployed in varied conditions.These features make ATAGS a formidable asset, not only for Armenia but also for other countries seeking advanced yet cost-effective artillery solutions.Strengthening Indo-Armenian Defense TiesThis prospective deal builds on Armenia’s earlier purchases of Indian defense systems, such as the Pinaka multi-barrel rocket launchers. The growing partnership reflects India’s expanding footprint in global arms markets, particularly in regions like Eastern Europe. For Armenia, this collaboration aligns with its strategic need for reliable and versatile defense solutions amidst its complex regional security dynamics.A Growing Global Presence for Indian DefenseIndia's ATAGS has already gained international attention for its cutting-edge capabilities. While Armenia is advancing its partnership with KSSL, the Indian Army is simultaneously negotiating a contract to procure 307 ATAGS units. However, reports suggest that India is exploring options for a lighter, more agile artillery system with enhanced automation for future requirements.The Road AheadIf finalized, this expanded deal with Armenia would not only bolster the country’s military capabilities but also mark another milestone for India’s defense export ambitions. It would reaffirm ATAGS as a globally competitive artillery solution and further strengthen India’s position as a reliable partner in the international defense market.As Armenia and India deepen their defense ties, this partnership serves as a testament to the shared vision of innovation, security, and self-reliance in the evolving global defense landscape.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-20 14:40:05India
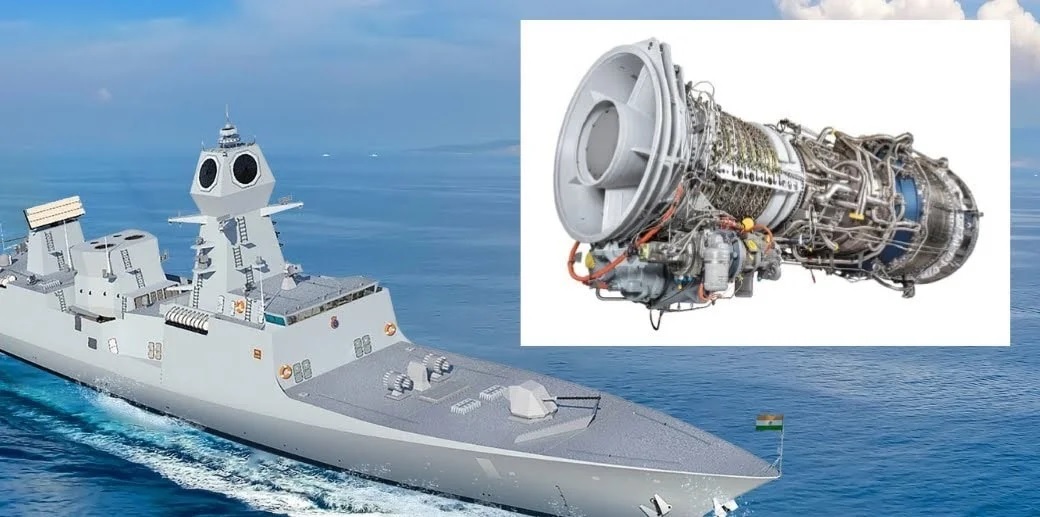
The Indian Navy is embarking on a transformative journey to achieve full self-reliance in marine and diesel propulsion systems by 2047, a target closely tied to the national vision of *Aatmanirbhar Bharat* (Self-Reliant India). This ambitious initiative not only seeks to end dependence on foreign suppliers but also aims to solidify India's position as a global leader in defense manufacturing.Current Dependency and Challenges India's reliance on imported propulsion systems for its naval fleet has long been a strategic vulnerability. Key suppliers include Ukraine, which has provided engines for frontline warships, and global aerospace giants like GE Aerospace and Rolls-Royce, known for their advanced gas turbine engines. However, geopolitical uncertainties, such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict, have highlighted the risks of relying on external sources for critical defense equipment. These challenges have galvanized efforts to develop indigenous alternatives. The Path to Self-Reliance The Indian Navy, alongside the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and its Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), has initiated a series of projects to build indigenous propulsion systems. A pivotal endeavor in this direction is the development of the Kaveri Marine Gas Turbine (KMGT). Derived from the GTX-35VS Kaveri engine originally designed for fighter jets, the KMGT represents a significant leap in adapting aerospace propulsion technologies for marine applications. Looking further ahead, the Navy plans to develop a marine gas turbine based on the advanced engine under development for the AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft), India’s fifth-generation stealth fighter. This effort underscores India's commitment to leveraging synergies across its defense platforms to create versatile, cutting-edge technologies. Indigenous Diesel Engine Development In parallel, the Navy is fostering partnerships with Indian private-sector companies specializing in heavy engineering and engine manufacturing. These collaborations aim to create diesel engines for smaller ships and auxiliary vessels. Meeting stringent naval standards, these engines are expected to ensure consistent performance while reducing operational costs. Local manufacturing offers a dual advantage: a dependable supply chain for spares and reduced maintenance downtime. The long-term cost-effectiveness of indigenous propulsion systems will also contribute to enhanced fleet readiness. Broader Implications The shift towards self-reliance in propulsion systems is more than just a technological milestone—it represents a strategic pivot for India’s naval capabilities. Indigenous propulsion systems will not only enhance the operational autonomy of the Indian Navy but also stimulate the domestic defense manufacturing ecosystem, creating jobs and fostering innovation. Moreover, achieving this goal by 2047, the centenary of India’s independence, will serve as a powerful symbol of the country’s defense and technological prowess. As these engines power India’s naval fleet across the high seas, they will embody the spirit of Aatmanirbhar Bharat in every mission. This initiative also aligns with global trends emphasizing the localization of defense manufacturing, ensuring that India stays ahead in a rapidly evolving geopolitical landscape. With focused R&D efforts, robust collaborations, and strategic investments, the Indian Navy is steadily charting a course towards a future powered by fully indigenous marine and diesel engines.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-20 14:32:16India
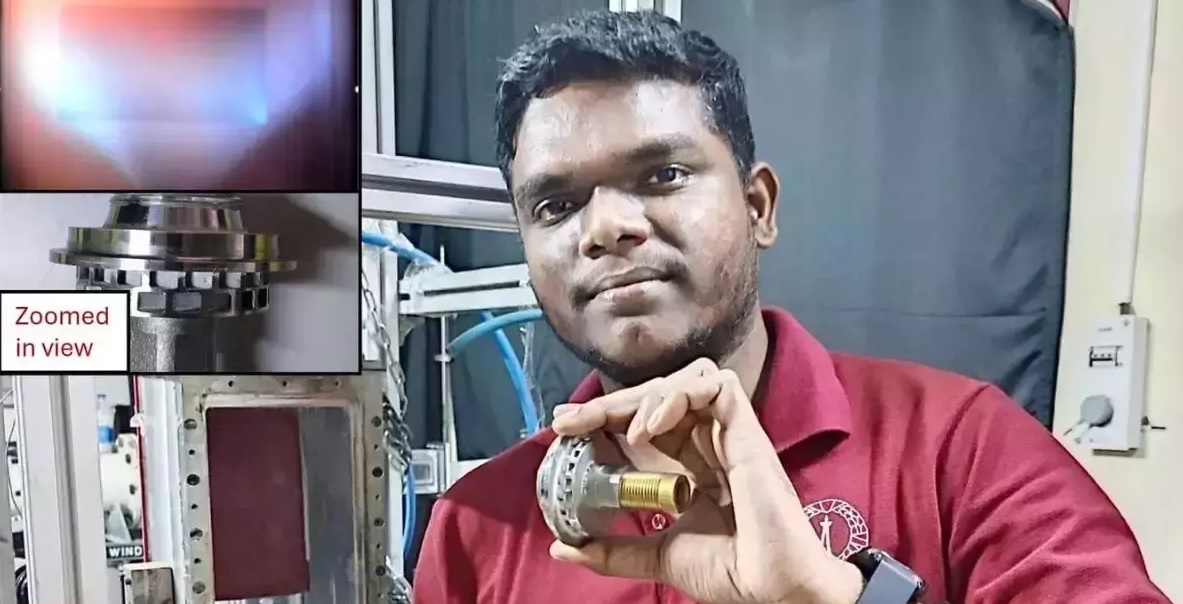
The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore has achieved a significant milestone in advancing India's self-reliance in defense technology by developing a cutting-edge indigenous fuel injection system tailored for fighter jet engines. This innovation enhances the performance and efficiency of high-speed aircraft engines, marking a critical step in India’s defense and aerospace sector.The fuel injection system designed by IISc focuses on producing finer atomized fuel droplets, ensuring more efficient combustion and reduced emissions. This system is particularly pivotal for afterburner-equipped engines, like those used in advanced fighter jets. Afterburners rely on the precise injection of additional fuel into the exhaust stream to dramatically boost thrust during combat or high-speed maneuvers. The IISc solution integrates advanced atomization techniques, improving both fuel delivery and the stability of combustion under varying operational conditions.Supported by agencies such as the Aeronautical Research and Development Board (ARDB), the research incorporated high-speed diagnostics to optimize the interplay of fuel sprays, airflow, and combustion dynamics. This innovation will significantly contribute to the performance of engines for projects like India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), a critical next-generation fighter jet under development.This development not only aligns with the "Make in India" initiative but also strengthens India's strategic capabilities in aerospace technologies, reducing dependency on foreign systems. The system has the potential for further adaptation in various high-performance engines, ensuring broader applications in both military and civilian domains.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-20 14:14:47India
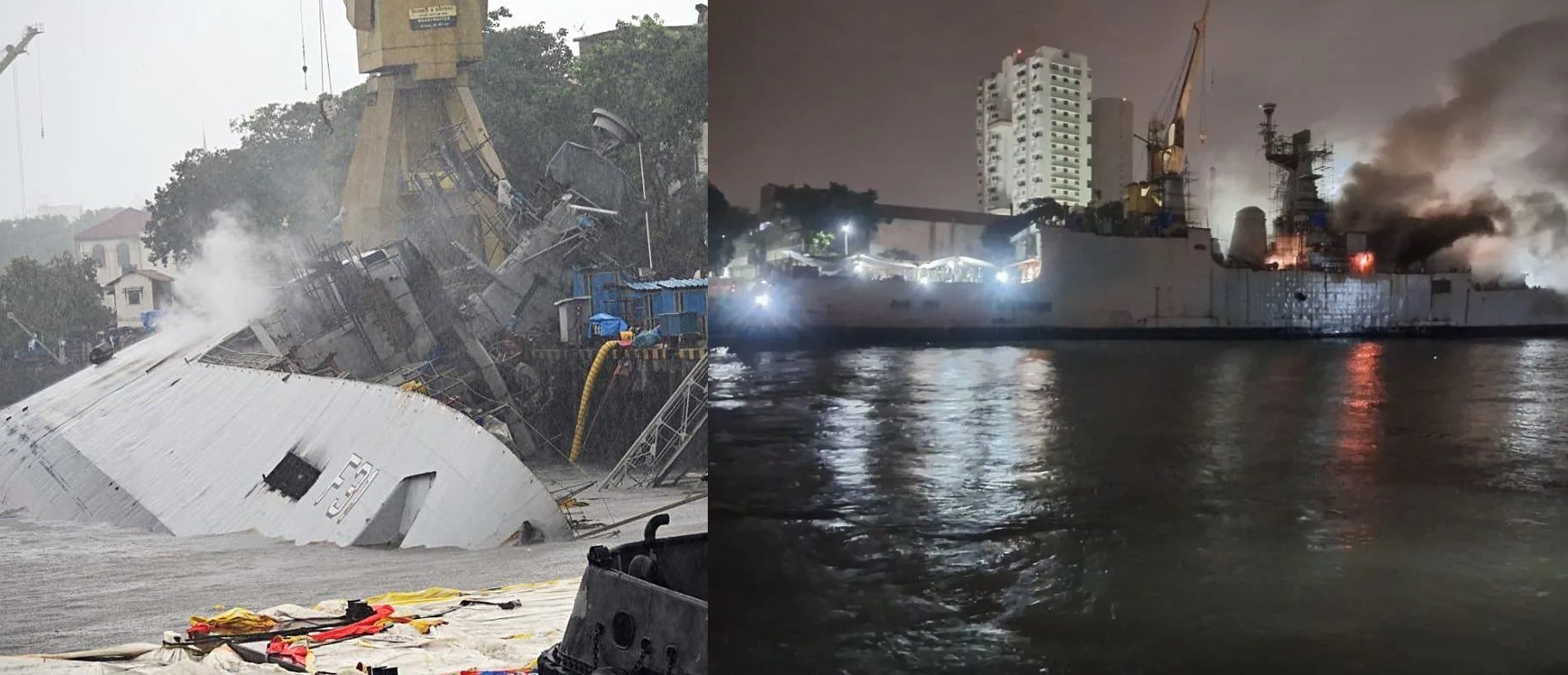
In a dramatic salvage operation, the INS Brahmaputra, an integral asset of India's naval power, has been righted after a severe fire nearly capsized it. The guided-missile frigate was undergoing a major refit at the Mumbai Naval Dockyard when a blaze broke out in July 2024, tragically killing one sailor and causing the ship to list precariously. The incident led to extensive flooding from firefighting efforts, which added substantial weight to the vessel, further complicating recovery attempts.The 24-year-old frigate, part of the Brahmaputra-class series, faced extensive structural damage that required unprecedented salvage techniques. A team of foreign experts, including specialists from Singapore, collaborated with the Indian Navy to de-ballast and stabilize the ship using large, balloon-like structures. These innovative devices were essential in gradually lifting the vessel from its 40-45 degree tilt, a process that demanded precision engineering and extensive planning.INS Brahmaputra's specifications underline its importance to India's maritime security. Commissioned in the early 2000s, the ship features a 5,300-ton displacement, is 125 meters long, and boasts a beam of 14.4 meters. Its armaments include advanced surface-to-air and surface-to-surface missile systems, torpedo launchers, and medium-range and close-range guns. It also supports helicopter operations with Seaking and Chetak aircraft, making it a formidable multi-role frigate. Despite its age, it remains vital to the Western Naval Fleet, which underscores the urgency of its restoration.Though the ship is now upright, Indian Navy officials warn that full repairs will be a slow and methodical endeavor, possibly stretching over several months. Specialists must assess the full extent of the damage before commencing comprehensive repairs to ensure the ship's structural integrity and seaworthiness. The complexity of the task is reminiscent of past naval incidents, such as the INS Betwa’s salvage, but Brahmaputra’s unique challenges have necessitated collaboration with global experts.Navy leadership, including Chief of Naval Staff Admiral Dinesh K Tripathi, has prioritized this operation, underscoring the frigate's strategic value. Vice Chief of Naval Staff Vice Admiral Krishna Swaminathan acknowledged the intricate challenges but expressed confidence in India's and the international team’s capabilities. Meanwhile, safety audits have been intensified across naval facilities to prevent future mishaps.As the salvage progresses, India's naval command continues to balance restoration efforts with operational readiness, aiming to reintegrate this key asset into the fleet as soon as possible, although the timeline remains uncertain.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-19 15:50:01India
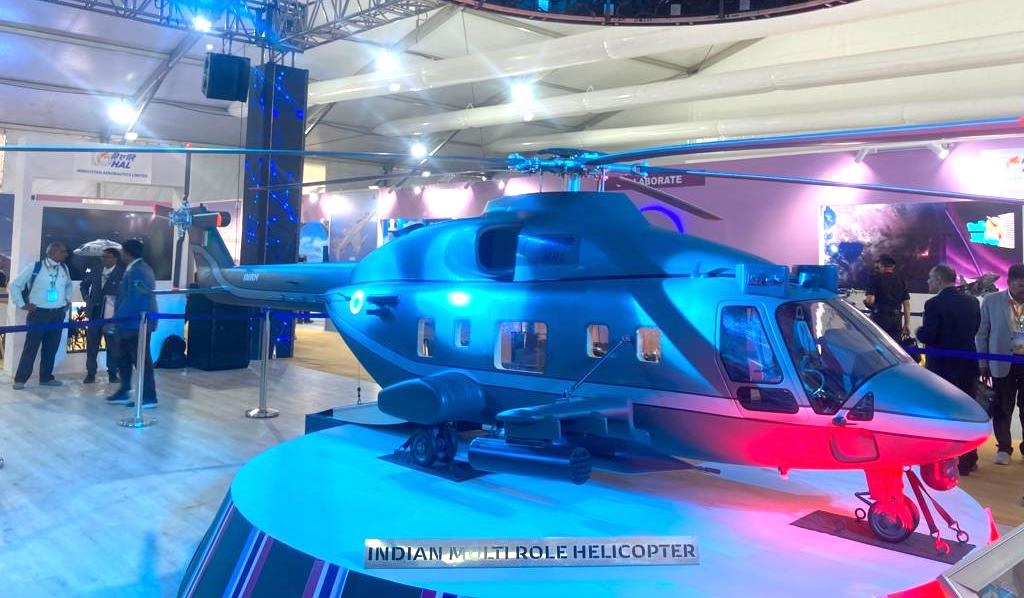
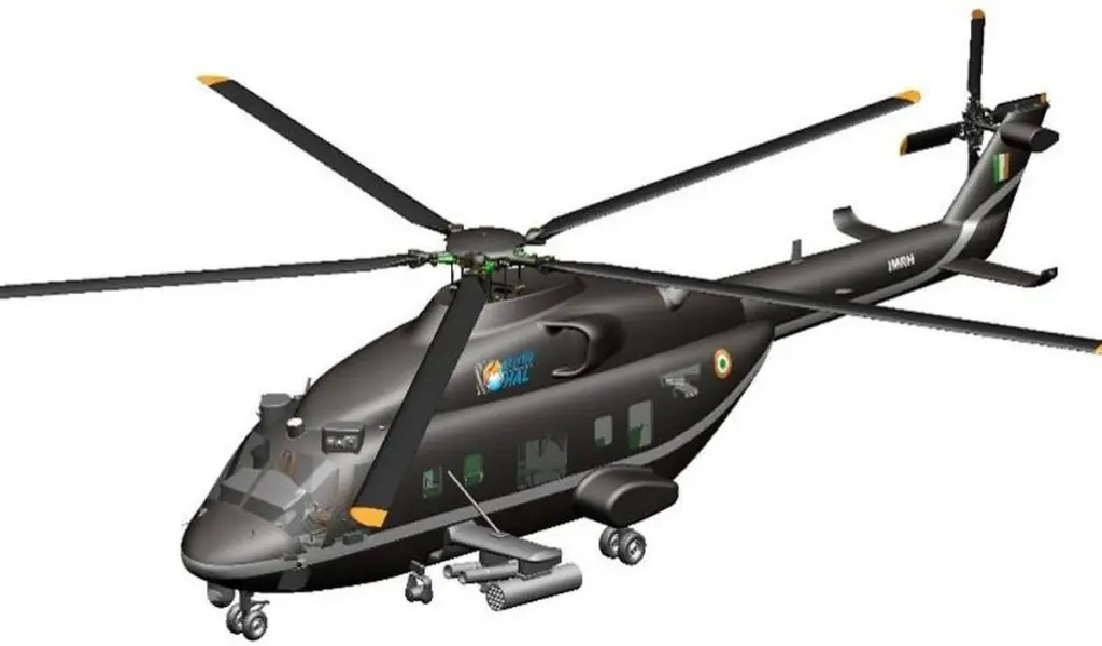
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is advancing in the development of its Indian Multi-Role Helicopter (IMRH), a bold step forward for India's aerospace industry. As part of this ambitious project, HAL has announced that the IMRH will feature the high-power Aravalli engine, developed in collaboration with SAFHAL Helicopter Engines, a joint venture with Safran Helicopter Engines. The IMRH, designed as a 13-ton medium-lift helicopter, promises to cater to the diverse needs of India’s defense forces while holding potential for civilian applications as well.First introduced during Aero India 2023, the IMRH symbolizes India’s growing prowess in aerospace technology and its commitment to self-reliance under the "Atmanirbhar Bharat" initiative. The helicopter is expected to replace a range of aging rotorcraft currently used by the Indian Armed Forces, offering a domestically produced alternative with global-level capabilities.The Aravalli Engine: A Leap Toward Self-RelianceA standout feature of the IMRH will be the integration of the indigenous Aravalli engine. This engine represents a major milestone for India's aerospace engine technology, emphasizing fuel efficiency, performance, and reliability. Developed by SAFHAL Helicopter Engines Pvt. Ltd., the engine aims to eliminate dependence on foreign powerplants and marks a transformative step for Indian aerospace engineering. The Aravalli engine will initially be rolled out in later batches of the IMRH, with early prototypes expected to use existing Safran engines.Multi-Mission Versatility and Advanced FeaturesThe IMRH’s mission profile covers a broad range of operations, such as troop transport, logistics, medical evacuation, and search and rescue. Designed to perform in extreme environments, including high-altitude regions like the Himalayas, the helicopter will be equipped with advanced avionics and safety features. The IMRH will be able to transport up to 24 fully equipped soldiers or a significant cargo load, thanks to its 13-ton lift capability.Beyond structural and aerodynamic enhancements, HAL has ensured that the IMRH's design is modular to allow for quick role changes. This versatility could extend the helicopter's utility to naval operations, where it could serve aboard warships as the Deck-Based Multi-Role Helicopter (DBMRH) variant, with design adjustments tailored to maritime conditions.Domestic and International Market PotentialHAL envisions the IMRH as a contender in the international medium-lift helicopter market, competing with established players such as the Sikorsky S-92 and Airbus H225M. Drawing on the export success of its Dhruv Advanced Light Helicopter, HAL is optimistic about the IMRH's prospects, particularly in regions where affordability and performance make Indian platforms attractive.Roadmap to 2027 and BeyondHAL has set an ambitious timeline, with the first Ground Test Vehicle and prototype expected to be ready by 2027. Following extensive testing and fine-tuning, mass production will commence, aiming to meet both domestic demand and international interest. The integration of the Aravalli engine will be a game changer, as it gradually replaces the foreign engines in the initial production runs, making the IMRH a fully indigenous product.The collaboration with SAFHAL not only aligns with India's defense self-reliance goals but also ensures that critical technologies remain within the country. With continued advancements and rigorous testing, HAL hopes that the IMRH will redefine India’s presence in the global aerospace market and enhance its strategic airlift capabilities.This development sets the stage for an exciting new chapter in Indian aviation, where cutting-edge technology and strategic foresight are driving aerospace innovation.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-19 15:34:38India
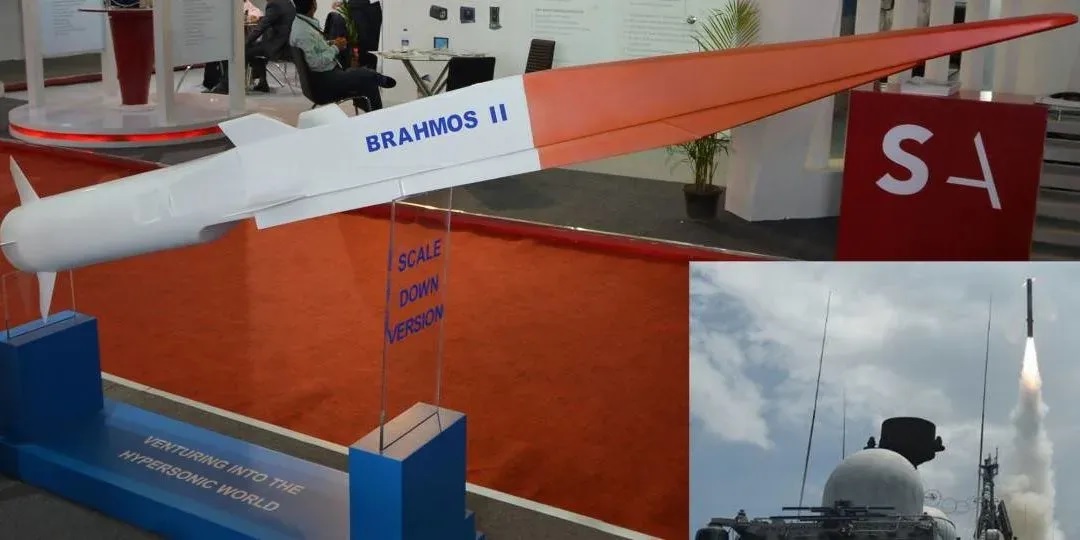
India's BrahMos-2 hypersonic missile project has hit the pause button, but this decision is rooted in strategic and financial calculations rather than technological incapacity. The BrahMos-2, envisioned as a high-speed missile based on Russia’s 3M22 Zircon, aimed to reach Mach 6-7. However, as hypersonic missile development remains an expensive frontier, Indian defense forces have expressed reservations about the program's feasibility, particularly the prohibitive per-unit cost, which could limit large-scale acquisition.Instead of pushing forward with the BrahMos-2, India has turned its attention to enhancing the capabilities of the already formidable BrahMos missile. Co-developed by India and Russia, the current BrahMos is a supersonic cruise missile capable of flying at Mach 3. The renewed focus is on upgrading its engine technology, aiming to nudge speeds closer to Mach 5. This enhancement could provide a "near-hypersonic" edge, significantly boosting the missile's ability to penetrate modern air defense systems.The BrahMos-1 missile family is a strategic asset for India, already versatile in its deployment from land, sea, and air platforms. The future upgrades are not just about speed. Plans include improving range capabilities—boosting the missile from its current reach of 450-500 km to potentially over 800 km—and exploring a lighter version, making it more adaptable for diverse launch platforms like submarines and smaller aircraft. This approach allows India to modernize its defense posture without the financial strain of investing in full-fledged hypersonic technology.Moreover, concerns about Russia's burgeoning ties with China have also complicated India's calculus. Although Moscow remains a critical defense partner, fears persist that Russia’s technology-sharing arrangements with China could potentially undercut Indian security interests. Additionally, global sanctions on Russia and the threat of Western repercussions on joint projects are significant risks that India cannot overlook. Despite the hold on the BrahMos-2, India continues to explore indigenous hypersonic capabilities through parallel projects like the Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV) and the Shaurya missile. These initiatives reflect India's broader aim of achieving self-reliance in advanced missile technology, ensuring that the country remains ahead in the rapidly evolving field of defense systems.In short, India’s decision to focus on enhancing the BrahMos missile rather than developing BrahMos-2 at this juncture is a calculated move. It ensures operational relevance while allowing time to address the challenges associated with hypersonic technologies and the complexities of global defense partnerships.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-19 15:30:57India
In an ambitious move towards reshaping its armored warfare capabilities, India's Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is developing its Future Main Battle Tank (FMBT) with the option to equip either a 120mm or 125mm smoothbore gun. This approach underlines India's effort to adapt and enhance the operational flexibility of the next-generation platform, officially called the Next Generation Main Battle Tank (NGMBT).The decision to integrate both gun systems isn’t just a minor upgrade—it signifies a profound strategic investment. Smoothbore guns, as opposed to rifled barrels, are valued for their higher projectile velocities, which translate into greater penetrative power. The Indian Army's transition to these guns for NGMBT is designed to meet emerging threats, taking a step forward from legacy technologies still present in older platforms.One of the most intriguing aspects of this development is the dual-caliber system. By creating options for both 120mm and 125mm smoothbore guns, DRDO is ensuring the tank can be tailored to various combat scenarios and ammunition advancements. The 125mm variant leverages experience with Russian-origin T-90 tanks that the Indian Army has relied upon for decades. This choice offers compatibility with existing ammunition stocks and maintains high firepower, making it ideal for situations where heavy munitions might be necessary.On the flip side, the 120mm option draws from Western tank designs and could provide advantages in terms of tank weight and mobility, crucial for high-speed maneuver warfare and for operating in terrains where agility is critical. The smoothbore design on both variants will accommodate advanced munitions like armor-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot (APFSDS) rounds and high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shells. These weapons will enable the NGMBT to engage various targets, from heavily armored vehicles to fortified positions.The NGMBT project also incorporates an array of futuristic systems that place it on par with top-tier global tanks. It is expected to feature advanced active protection systems (APS) designed to intercept incoming threats like anti-tank guided missiles, offering an additional layer of survivability. The armor itself will likely employ advanced composite materials to withstand modern kinetic energy threats while maintaining weight efficiency. Enhanced situational awareness technologies, such as 360-degree cameras and sophisticated command-and-control interfaces, will ensure crew effectiveness in both offensive and defensive roles.While these plans are impressive, the development journey will be challenging. The timelines for selecting and validating the gun systems remain flexible, but DRDO's dual-caliber strategy showcases foresight, allowing for adaptability in a rapidly evolving defense landscape. This capability enhancement is also a testament to India's growing emphasis on indigenous defense manufacturing, a goal central to the “Make in India” initiative, reinforcing the country’s position as a key player in military self-sufficiency.Overall, the NGMBT’s dual-gun flexibility and other cutting-edge features reflect India's commitment to staying ahead in regional and global armored warfare dynamics, ensuring that its forces remain versatile and formidable across diverse battle environments.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-19 15:13:09India
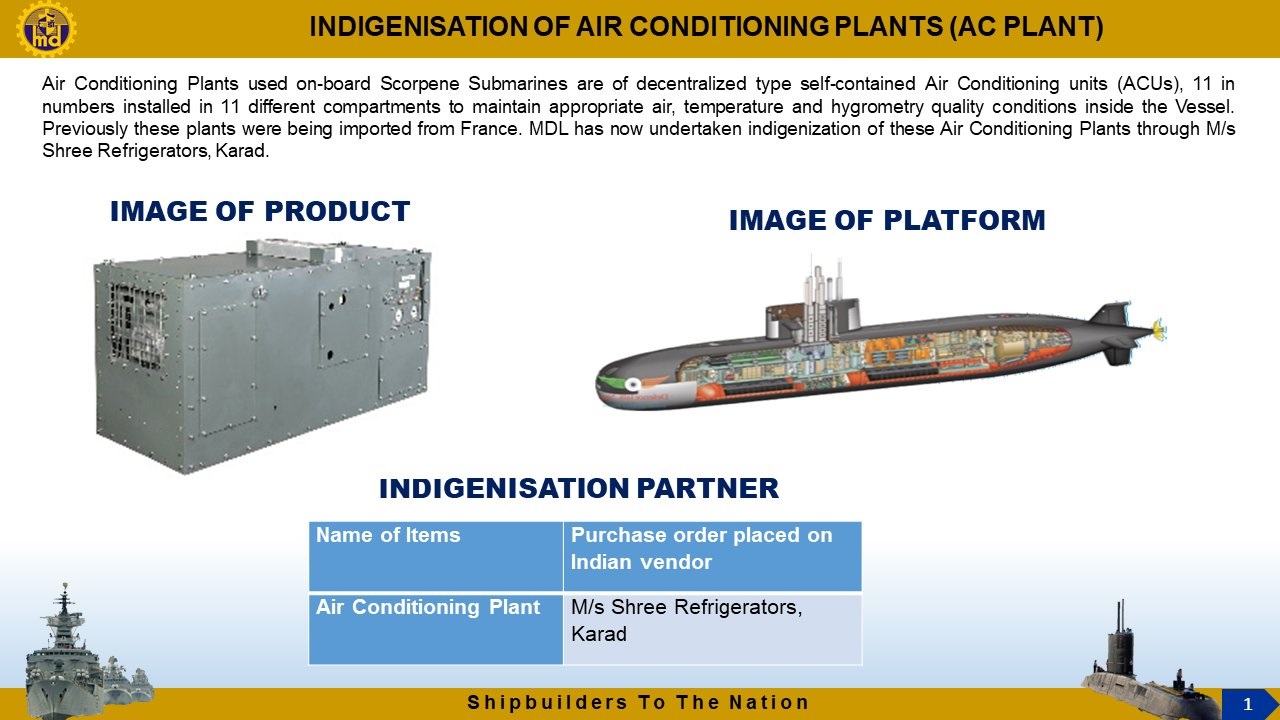
In a landmark achievement for India's defense manufacturing sector, Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd. (MDL) has indigenized the Air Conditioning Plants (ACP) used in Scorpène-class submarines. Previously sourced from France, these vital systems are now being produced domestically through a collaboration with Shree Refrigerators, Karad. This breakthrough not only enhances self-reliance in critical defense technologies but also underscores India’s growing capabilities in advanced naval engineering.The Role of Air Conditioning in Submarine OperationsThe confined, high-stress environments of submarines demand advanced climate control systems to ensure operational efficiency and crew welfare. Onboard Scorpène-class submarines, 11 decentralized, self-contained Air Conditioning Units (ACUs) are strategically placed across compartments. Each unit is tailored to maintain precise air quality, temperature, and humidity levels, catering to the unique requirements of its designated space.These systems are essential for:Crew Comfort and Health: Regulating air conditions mitigates fatigue, heat stress, and other physiological impacts of long-term underwater missions.Operational Effectiveness: A controlled environment ensures the seamless operation of sensitive equipment and electronics.Equipment Longevity: Stable temperatures and humidity levels help prevent corrosion and malfunction in critical onboard systems.A Leap Towards Self-RelianceBefore this milestone, ACPs for the Scorpène submarines were imported from France, which posed challenges in procurement, cost, and maintenance. By shifting production to India, MDL and Shree Refrigerators have not only streamlined supply chains but also established a foundation for sustained technological innovation.The indigenized ACPs meet stringent standards for submarine operations, ensuring performance reliability under demanding conditions. Their development aligns with India’s Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision, reducing dependency on foreign suppliers and increasing the Navy’s autonomy in managing its fleet.Technical Highlights of Indigenized ACPsCompact and Modular Design: The units are optimized for the cramped interiors of submarines while offering high operational flexibility.Energy Efficiency: Advanced technology ensures minimal power consumption, a critical factor in the resource-constrained environment of a submarine.Robust Durability: The systems are engineered to withstand the harsh conditions of prolonged underwater deployment, including high salinity and pressure variations.Customization: Each unit is fine-tuned to the specific climate control needs of its assigned compartment, ensuring localized environmental optimization.Strategic ImplicationsThe successful indigenization of ACPs marks a pivotal step in strengthening India’s defense industrial base. For the Navy, it translates into:Enhanced Maintenance Capability: Domestic production ensures ready availability of spares and simplified repair processes.Cost Efficiency: Local sourcing reduces costs associated with imports, benefitting the overall defense budget.Operational Independence: With a domestic supply chain, the Navy gains greater control over the lifecycle management of its submarines.This achievement also sets a precedent for future indigenization efforts, encouraging collaborations between public sector shipbuilders and private enterprises to address critical defense needs.Broader ImpactIndia’s success in producing these advanced ACPs signals its readiness to tackle complex engineering challenges and develop technologies previously dominated by global suppliers. As India continues to modernize its naval fleet, such initiatives will play a crucial role in achieving strategic self-sufficiency and bolstering national security.The indigenization of submarine ACPs isn’t just a technical feat—it’s a testament to India’s evolving defense ecosystem, where innovation and collaboration are driving the nation closer to complete self-reliance in critical military technologies.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-18 16:53:09India
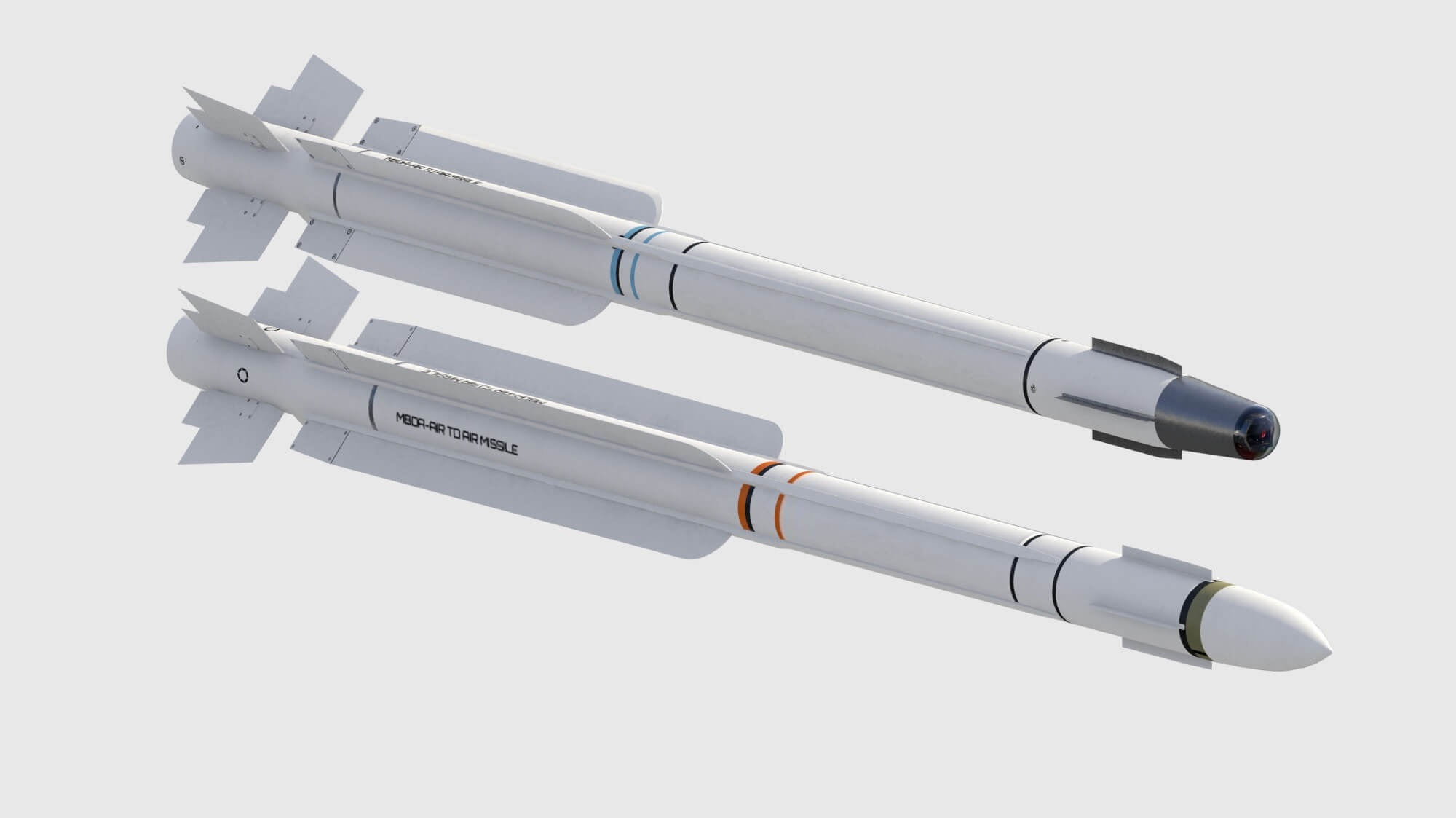
European defense giant MBDA is significantly expanding its collaboration with Indian companies, leveraging India's robust and evolving defense manufacturing capabilities for the development of its next-generation MICA NG (Nouvelle Génération) air-to-air missile. This strategic partnership reflects India's growing influence in the global defense supply chain and highlights the nation’s potential to contribute meaningfully to advanced international military projects.The collaboration isn't a sudden initiative but rather an evolution of an existing relationship. Indian firms are already involved in producing 15 major subassemblies for the current MICA missile, including intricate mechanical, electrical, and pyrotechnic components. Building on this foundation, Indian manufacturers are poised to deliver even more complex parts for the MICA NG, which is slated to be fielded from 2026. This missile system, currently used by France and 14 other countries, is known for its versatile dual seeker configuration: infrared and radio frequency, which are cleverly integrated into a single missile casing. The MICA NG aims to revolutionize air combat through a suite of upgrades while maintaining this unique adaptability. Engineers at MBDA have completely redesigned the missile’s internal electronics to free up space for additional propellant, allowing for a significantly extended operational range. This innovation is paired with a new double-pulse rocket motor, which delivers a crucial thrust boost in the terminal phase, enhancing the missile’s agility against high-speed, evasive targets. These advances ensure the MICA NG can engage threats over greater distances and with improved precision, a critical requirement in modern air warfare.In addition to these performance enhancements, the MICA NG will also feature a state-of-the-art health monitoring system. This built-in feature provides real-time diagnostics of the missile’s status throughout its life cycle, significantly reducing maintenance needs and ensuring a higher state of readiness. This advancement not only increases operational efficiency but also aligns with the modern military's need for low-maintenance and highly reliable systems.MBDA's decision to engage deeper with Indian industry underlines the strategic advantages of this collaboration. By integrating Indian expertise into its production ecosystem, MBDA aims to streamline manufacturing processes and potentially reduce costs. For India, this partnership reinforces the country’s defense manufacturing capabilities, a crucial component of the "Make in India" initiative. It also paves the way for Indian companies to work on cutting-edge technologies, further strengthening their global standing.This collaboration benefits both MBDA and Indian defense firms, creating a win-win situation where technological know-how and manufacturing excellence are seamlessly integrated into a product that is set to redefine air combat capabilities for years to come.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-18 15:58:39India
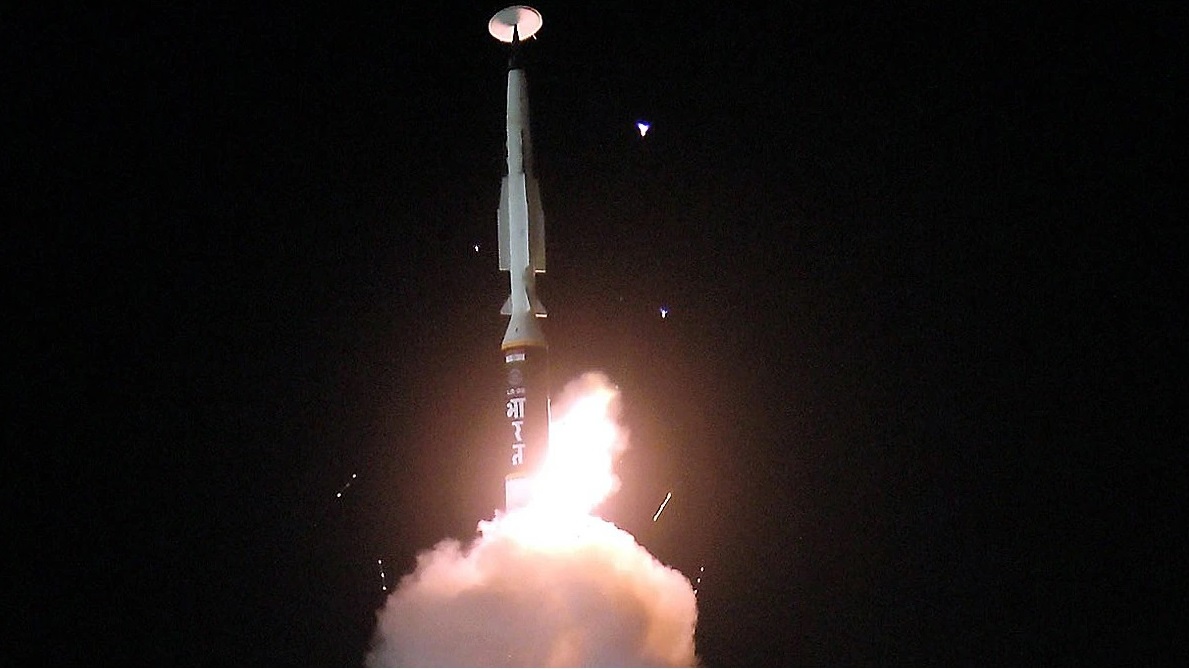
In a world where military supremacy is heavily driven by technological advancements, India has made a significant stride by successfully testing a long-range hypersonic missile, developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). This achievement, conducted from Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha, has catapulted India into an exclusive club of nations capable of wielding such advanced military technology. With a range exceeding 1,500 kilometers and the ability to carry multiple payloads, this hypersonic missile is poised to redefine India’s defence landscape.The missile’s capabilities are more than just numbers on a report. Travelling at speeds greater than Mach 5—over five times the speed of sound, or roughly a mile per second—hypersonic missiles bring unparalleled advantages to modern warfare. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh proudly hailed the achievement, emphasizing its historic significance and the nation’s newfound status in possessing one of the most advanced technologies in the world. In a world increasingly focused on rapid and unpredictable military threats, having a hypersonic arsenal not only bolsters national security but serves as a critical deterrent.What Makes Hypersonic Missiles a Game-Changer?The true strategic advantage of hypersonic missiles lies in their sheer speed and maneuverability. Unlike traditional ballistic missiles, which arc predictably through the sky and can be tracked and intercepted by existing defence systems, hypersonic missiles can change course mid-flight. This ability to maneuver, coupled with their low-altitude travel paths, makes them nearly impossible to detect and intercept. As they streak across the sky at extreme speeds, defence systems have only seconds to respond—a formidable challenge even for the most advanced nations.India’s hypersonic missile is designed as a highly adaptive and formidable weapon that can serve various military needs. It represents a response to a global arms race in hypersonic technology, where countries like Russia, China, and the United States are already well ahead. For instance, Russia claimed to have used its Kinzhal hypersonic missiles in Ukraine in 2022, and the United States continues to invest billions into projects like the Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW) to maintain its strategic edge. By joining these ranks, India is ensuring it will not be left vulnerable in the rapidly shifting dynamics of military power.The Technical Mastery Behind Hypersonic MissilesDeveloping hypersonic missiles is no small feat. The immense speeds generate tremendous heat, caused by the friction with the atmosphere, which can melt most conventional materials. To counter this, engineers at DRDO’s Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Missile Complex, along with partners from various Indian research labs, have had to rely on cutting-edge carbon composites and heat-resistant alloys. Furthermore, at such velocities, communication systems must be incredibly sophisticated to provide real-time navigation and guidance, ensuring the missile remains accurate and responsive to changing conditions.Then there’s the matter of propulsion. Two main types of hypersonic missiles dominate global development: Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs) and Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs). While the former uses a rocket launch to soar high before gliding towards its target, the latter relies on scramjet technology to sustain hypersonic speeds throughout the flight. The engineering challenges are immense, but India’s progress in mastering these technologies highlights an impressive leap forward.Why India Is Investing Heavily in HypersonicsFor India, the development of hypersonic weapons is driven by both regional and global strategic considerations. Surrounded by powerful and often hostile neighbors, such as China—which has already tested hypersonic glide vehicles—and an unpredictable Pakistan, India must ensure its defences remain impenetrable. Hypersonic missiles serve as an ideal countermeasure to advanced threats, providing a strategic deterrence that forces adversaries to think twice.Moreover, hypersonic weapons have the potential to deliver devastating strikes on critical infrastructure, even those hidden deep underground. Their speed and kinetic energy make them powerful enough to obliterate hardened bunkers, making them indispensable in neutralizing high-value targets.A Future of Advanced Deterrence and Self-RelianceIndia’s foray into hypersonic technology also signifies a broader commitment to technological self-reliance. By developing these capabilities indigenously, India is not only protecting itself from external dependencies but also strengthening its defence industry. This effort is part of a larger strategy to ensure the country can innovate and adapt to evolving warfare scenarios.While the success of this hypersonic missile test is commendable, there are challenges ahead. The cost of developing and deploying such advanced weapons is enormous, and sustaining a hypersonic weapons program will require continuous investment and innovation. Additionally, with the global arms race accelerating, the geopolitical implications are profound. India’s advancement may lead to new security dynamics in South Asia and beyond, requiring careful diplomatic management.Nonetheless, India’s entry into the hypersonic missile club is a defining moment for its military and technological prowess. By achieving this feat, India has not only secured a more robust defence posture but has also sent a clear message: it is ready to meet the demands of 21st-century warfare. The coming years will likely see further developments as India seeks to integrate these capabilities into its armed forces, positioning itself as a formidable and technologically advanced power on the global stage.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-18 15:51:19India
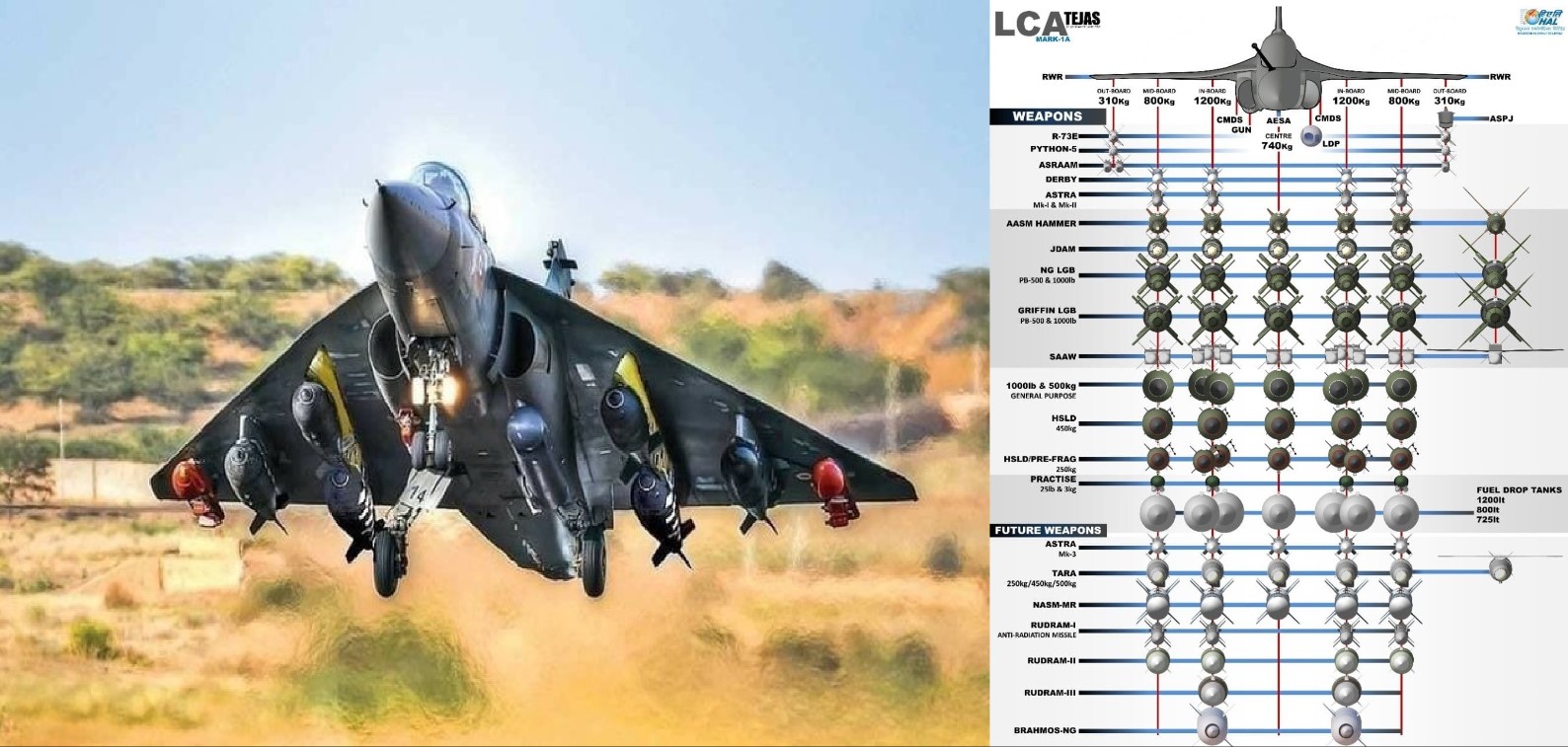
The Indian Air Force's indigenously developed fighter jet, the Tejas Mk1A, has transformed into a true powerhouse of adaptability and firepower. This advanced light combat aircraft, engineered by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), reflects India’s strategic vision of a potent yet flexible combat platform that can meet a wide variety of operational requirements. The Tejas Mk1A's integration of weapons systems from a global spectrum of manufacturers highlights not only India’s pursuit of self-reliance but also a well-thought-out approach to diversifying its defence capabilities. What truly sets the Tejas Mk1A apart is its open architecture and modular weapon systems that allow for the seamless integration of a wide range of munitions. This flexibility is a feature more commonly seen in nations with highly developed and independent defence sectors. By equipping the Tejas with weapons sourced from multiple countries—including the United States, France, Israel, the UAE, and India itself—the aircraft achieves an unprecedented level of operational versatility.Take, for instance, the JDAM-ER from the United States. This Joint Direct Attack Munition-Extended Range transforms conventional unguided bombs into precision-guided smart munitions. With an extended range and all-weather strike capability, the JDAM-ER enables the Tejas to attack enemy positions from a safe distance, minimizing exposure to hostile air defences. This precision strike system integrates seamlessly with the Tejas’s avionics, providing a robust solution for long-range engagements.The Tejas Mk1A also boasts the highly capable HAMMER missile system from France. The HAMMER (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range) is a precision-guided standoff weapon designed to strike fortified and high-value targets from a distance of up to 70 kilometers. Its modular design allows for different warheads to be tailored to specific missions, giving the Tejas a significant edge in precision and flexibility during combat scenarios.From Israel comes the SPICE family of precision-guided munitions. SPICE (Smart, Precise Impact, and Cost-Effective) bombs are renowned for their advanced electro-optical guidance systems, which allow them to function in GPS-denied environments—a crucial capability in modern warfare. This ensures that the Tejas can conduct precision strikes even when satellite navigation is compromised, offering the Indian Air Force a significant strategic advantage.The UAE’s contribution to the Tejas arsenal is the Al Tariq guided bomb system. Al Tariq bombs are known for their advanced guidance kits and versatile warhead options, including penetrative, fragmentation, and general-purpose variants. These guided munitions enhance the Tejas’s strike capabilities, making it a multi-role fighter well-suited for diverse missions. With the integration of Al Tariq weapons, the Tejas can engage a wider array of target types with exceptional precision.Furthering India's indigenous defence capabilities is the TARA Smart Bomb, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). TARA is a cost-effective, precision-guided weapon system that aligns with India’s "Make in India" ethos. It provides the Tejas with a homegrown option for high-accuracy strikes, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers and strengthening national self-sufficiency.The Tejas Mk1A's open architecture is a crucial enabler of this wide-ranging weapons integration. This flexible design allows for easy adaptation and upgrades, ensuring that the aircraft can incorporate new technologies as they become available. Such adaptability not only enhances combat effectiveness but also ensures the Tejas remains a relevant and formidable platform for decades to come.Furthermore, this diversification of munitions sources is a strategic masterstroke. By distributing its reliance across multiple nations, India reduces the risk associated with geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions. This ensures continuous access to cutting-edge military technology, even in an unpredictable global landscape. As the Indian Air Force continues to induct the Tejas Mk1A into its fleet, the aircraft’s unique combination of international and indigenous weapons systems positions it as a critical component of India's air defence strategy. The Tejas Mk1A stands ready to execute a variety of missions, from surgical strikes to extensive air-to-ground operations, solidifying its role as a multi-faceted force multiplier in South Asia’s evolving security environment.The Tejas Mk1A is, without a doubt, a game-changer for the Indian Air Force, a symbol of India’s commitment to building a modern and self-reliant defence infrastructure while leveraging the best technologies from around the world.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-18 15:35:47India
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is gearing up for a landmark moment in India’s aerospace history with the Indian Multi-Role Helicopter (IMRH), a 13-ton class medium-lift rotorcraft. This ambitious project is aimed at reducing India’s reliance on foreign helicopters and meeting the wide-ranging operational needs of the Indian Armed Forces. HAL plans to unveil the first Ground Test Vehicle and flight-ready prototype by the end of 2027, signifying a pivotal step in a development journey fueled by the government’s "Atmanirbhar Bharat" vision.The IMRH, first showcased at Aero India 2023, has evolved through rigorous design optimizations aimed at enhancing its performance, safety, and mission flexibility. Recent updates reflect HAL’s focus on aerodynamic improvements and structural safety enhancements, addressing the complexities of India’s diverse and often harsh operational environments. These refinements not only make the IMRH more robust and efficient but also elevate its competitiveness on the global stage, where it will vie with established international players.A crucial advancement in the IMRH project is the development of the indigenous Aravalli engine, an initiative spearheaded by SAFHAL Helicopter Engines Pvt. Ltd., a joint venture between HAL and French aerospace giant Safran. This collaboration is more than just a technical partnership; it represents a major push for India’s self-sufficiency in aerospace propulsion. The Aravalli engine is designed to meet the power and reliability needs of not just the IMRH but also future generations of Indian-made helicopters. Until the Aravalli engine is fully operational, the initial IMRH prototypes will rely on an existing Safran powerplant, allowing HAL to conduct essential flight tests and refine the rotorcraft’s capabilities.The IMRH’s specifications are tailored to India’s unique defense and disaster response requirements. With a medium-lift capacity of 13 tons, the helicopter can carry a variety of payloads, from troops and equipment to medical supplies for evacuation missions. It is engineered to perform effectively in demanding high-altitude terrains, such as the Himalayan region, and in extreme weather conditions. This versatility ensures the IMRH can undertake troop transport, logistics support, combat search and rescue, and disaster relief operations with equal efficiency, making it a comprehensive solution for the military.The IMRH's design is also expected to be modular, offering rapid reconfiguration based on mission needs. Its high payload capacity and extended range will make it invaluable for both tactical and strategic operations. The rotorcraft’s flight characteristics are being fine-tuned to meet stringent international standards, ensuring reliability and performance that can compete with, or even exceed, foreign models like the Russian Mi-17, which it aims to replace in Indian service.As HAL marches toward 2027, the IMRH project is not just about filling a critical capability gap for the Indian Armed Forces. It also holds promise for international markets. HAL has successfully exported its Dhruv Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) to several countries, and the IMRH could similarly capture global attention, particularly from nations that require high-performance, medium-lift helicopters at competitive pricing. The indigenous Aravalli engine will add a layer of appeal to international buyers by offering a locally supported powerplant, addressing a common concern among countries looking to avoid logistical dependency on foreign suppliers.Looking ahead, HAL’s roadmap involves extensive testing of the initial prototypes to fine-tune every aspect of the IMRH’s design. Once the Aravalli engine is ready for integration in later production models, the helicopter’s overall performance will be significantly elevated. Full-scale production is expected to follow shortly after the prototype phase, marking a new era in India’s aerospace capabilities and reinforcing the nation’s commitment to self-reliance in advanced defense technology.By aligning its efforts with national and global aviation demands, HAL’s IMRH is set to become a flagship product, bridging the gap between indigenous innovation and global competitiveness. The rollout of the IMRH is not just a leap forward for HAL but also a statement of India’s growing prowess in aerospace manufacturing.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-17 14:05:24India
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is gearing up for a significant upgrade to its long-range strike capabilities with a formidable enhancement of the BrahMos-A air-launched cruise missile (ALCM). By 2026, the IAF aims to extend the range of this weapon from 450km to a staggering 800km, a strategic leap forward that promises to redefine its air power, particularly in terms of reaching distant, high-value targets.Currently, BrahMos Aerospace—a collaborative venture between India and Russia—has armed 40 Su-30MKI fighter jets with the existing BrahMos-A missile. As part of this ambitious upgrade, an additional 20 Su-30MKIs will be modified to carry the extended-range variant, bringing the total to 60 aircraft capable of launching these supersonic, precision-guided weapons. This means that, once the enhancement is complete, a substantial part of India’s fighter fleet will be capable of striking critical enemy installations or naval assets well beyond the range of conventional air-launched weapons.The BrahMos-A missile is already celebrated for its devastating speed, which approaches Mach 3, and its unrivaled precision, guided by an advanced navigation system that combines satellite and inertial guidance. The supersonic velocity not only makes it extraordinarily difficult for enemy defenses to intercept but also allows it to deliver a heavy payload—up to 300kg of explosives—on target with surgical accuracy. This high-speed and heavy-impact capability make BrahMos-A a critical asset for preemptive and retaliatory strikes against fortified enemy bases, strategic infrastructures, and carrier groups at sea.The push to extend the missile’s range to 800km involves sophisticated advancements in propulsion technology and fuel efficiency. By optimizing the missile’s fuel composition and improving the efficiency of its ramjet engine, BrahMos Aerospace plans to achieve this increased range without sacrificing speed or payload capacity. These enhancements will allow the IAF to engage enemy targets from a safer standoff distance, giving it the ability to strike deep into hostile territory while keeping its aircraft beyond the reach of most enemy surface-to-air missile systems.However, the path to operational readiness for the 800km BrahMos-A is far from simple. BrahMos Aerospace is laying out a comprehensive series of developmental trials, which are expected to kick off in 2026. These tests will scrutinize the missile's performance under a wide array of scenarios, from assessing propulsion efficiency and aerodynamic stability at extended ranges to validating its guidance and targeting systems over vast distances. These trials are essential to ensure the missile’s reliability and to fine-tune its systems for optimal performance across diverse operational conditions.The upgraded BrahMos-A will become a linchpin in India’s strategic deterrence strategy. Its capability to deliver high-precision strikes at supersonic speeds, combined with an extended reach, will provide the IAF with a flexible and powerful response mechanism against a spectrum of threats. Moreover, in the context of the rapidly evolving security landscape in the Indo-Pacific region, the ability to launch deep-strike missions without crossing enemy airspace will be a game-changer. This upgraded missile can also serve as a credible deterrent, signaling to adversaries that India possesses a sophisticated means of neutralizing high-value targets with minimal risk to its forces.BrahMos-A's integration on the Su-30MKI platform is itself a marvel of aeronautical engineering. The robust design of the Su-30MKI, which is India's heavyweight air superiority fighter, has been modified to support the weight and aerodynamic profile of the 2.5-ton BrahMos missile. Engineers had to reinforce the aircraft’s undercarriage and refine the flight control systems to ensure stability during missile launches. The combination of the Su-30MKI's impressive range and agility with the BrahMos-A's devastating firepower makes for a fearsome weapon system capable of dominating any modern battlefield.As India continues to bolster its defense capabilities, this extended-range BrahMos-A will act as a strategic force multiplier, enhancing the IAF's ability to project power and defend against regional threats. With the Su-30MKI fleet soon to be equipped with these advanced weapons, India's air defense posture will be fortified like never before, providing a credible deterrence and a significant edge over adversaries.
Read More → Posted on 2024-11-17 13:58:10Search
Top Trending
-
 Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
Agneepath Scheme replaced with Sainik Samman Scheme 2024, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh Relaunched Agniveer Scheme
-
 China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
China's Latest DF-31AG ICBM Test: A Strategic Leap in Global Missile Capabilities
-
 India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
India's Defence Ministry Warns Against Chinese Parts in Military Drones Amid Security Concerns
-
 Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
Pakistan Announces 15% Increase in Defence Budget for 2024-25 Amid Economic Crisis
-
 China’s Super Radar Detects Mysterious Plasma Bubble Over Giza Pyramids
China’s Super Radar Detects Mysterious Plasma Bubble Over Giza Pyramids
-
 India's Indigenous Kaveri Engine Program with New Focus on Thrust and Performance
India's Indigenous Kaveri Engine Program with New Focus on Thrust and Performance
-
 Isro Draws up Ambitious Plan for 2024, says will Launch at Least 12 Missions
Isro Draws up Ambitious Plan for 2024, says will Launch at Least 12 Missions
-
 Successful Hypersonic Missile Test by U.S. Department of Defense
Successful Hypersonic Missile Test by U.S. Department of Defense
Top Trending in 4 Days
-
 South Korea’s K239 Chunmoo Rocket Artillery Spotted in Saudi Arabia
South Korea’s K239 Chunmoo Rocket Artillery Spotted in Saudi Arabia
-
 Spanish Navy Chooses Naval Strike Missile for S-80 Submarines, Phases Out Harpoon
Spanish Navy Chooses Naval Strike Missile for S-80 Submarines, Phases Out Harpoon
-
 Russia Launches Massive Missile and Drone Attacks on Ukraine's infrastructure
Russia Launches Massive Missile and Drone Attacks on Ukraine's infrastructure
-
 Elon Musk’s SpaceX Plans for 30-Minute Starship Flights from America to India Could Revolutionize Travel
Elon Musk’s SpaceX Plans for 30-Minute Starship Flights from America to India Could Revolutionize Travel
-
 DRDO Successful Test Long Range Hypersonic Anti-Ship Missile From Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island
DRDO Successful Test Long Range Hypersonic Anti-Ship Missile From Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island
-
 Peru to Acquire South Korea's K2 Black Panther Tanks
Peru to Acquire South Korea's K2 Black Panther Tanks
-
 Northrop Grumman Delivers Advanced SiAW Missile for U.S. Air Force Testing
Northrop Grumman Delivers Advanced SiAW Missile for U.S. Air Force Testing
-
 Taiwan Strengthens Communication Resilience with LEO Satellites, Make War-Proof its communications networks
Taiwan Strengthens Communication Resilience with LEO Satellites, Make War-Proof its communications networks